DiscardServer

1 package io.netty.example.discard; 2 3 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 4 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 7 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 8 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 9 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 10 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 11 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 12 13 /** 14 * Discards any incoming data. 15 */ 16 public class DiscardServer { 17 18 private int port; 19 20 public DiscardServer(int port) { 21 this.port = port; 22 } 23 24 public void run() throws Exception { 25 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // (1) 26 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 27 try { 28 ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); // (2) 29 b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 30 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3) 31 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // (4) 32 @Override 33 public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { 34 ch.pipeline().addLast(new DiscardServerHandler()); 35 } 36 }) 37 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5) 38 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6) 39 40 // Bind and start to accept incoming connections. 41 ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7) 42 43 // Wait until the server socket is closed. 44 // In this example, this does not happen, but you can do that to gracefully 45 // shut down your server. 46 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 47 } finally { 48 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 49 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 50 } 51 } 52 53 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 54 int port; 55 if (args.length > 0) { 56 port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); 57 } else { 58 port = 8080; 59 } 60 new DiscardServer(port).run(); 61 } 62 }
构造Bootstrap时,有一个很重要的元素就是eventLoopGroup(分为bossGroup和workerGroup,bossGroup用来accept,workerGroup用来处理socket IO),eventLoopGroup继承了eventExecutorGroup,eventExecutorGroup可以认为是eventExecutor的容器,可以通过next()获取到eventExecutor。由下面的类图可知eventExecutorGroup继承了executorService,其具有executorService的特性,比如执行提交的任务(通过next()委托给具体的eventExecutor)并获得代表任务执行进度的Future、关闭执行器(shutdown)等。
eventLoopGroup在eventExecutorGroup的基础上提供了register方法,即可以将channel注册在eventLoop上(eventLoopGroup的register内部仍然会调用next(),将channel注册到具体的eventLoop上)。所谓注册就是将eventLoop与channel绑定,对于nio来说,一个eventLoop(NioEventLoop)会绑定多个channel(还会将channel注册在与eventLoop绑定的selector上),对于oio来说,一个eventLoop(ThreadPerChannelEventLoop)只能绑定一个channel。
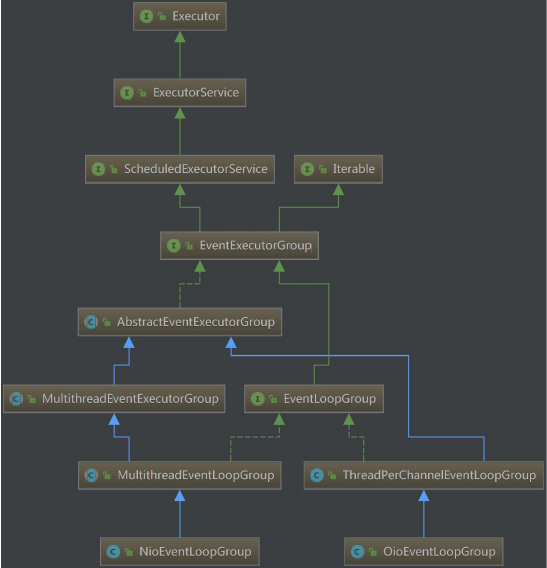
下面是EventLoop的类图,EventLoop继承了EventLoopGroup,EventLoop额外提供了inEventLoop()方法来判断当前线程是否在EventLoop中。

我们知道ExecutorService屏蔽了任务如何执行的具体机制,但通常Executor都会持有一个线程池来执行任务,并通过一个阻塞队列来缓存待执行的任务,那EventLoopGroup是怎样的呢?
这里以Nio为例,serverSocketChannel在accept后会将socketChannel注册在EventLoop上,并在EventLoop上execute完成注册操作
//childGroup即在ServerBootstrap中配置的childGroup(EventLoopGroup) childGroup.register(child)
NioEventLoop的execute方法
1 public void execute(Runnable task) { 2 if (task == null) { 3 throw new NullPointerException("task"); 4 } 5 6 boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop(); 7 if (inEventLoop) { 8 addTask(task); 9 } else { 10 //startThread()会调用executor的execute方法,这个executor就是一个java.util.concurrent.Executor 11 startThread(); 12 addTask(task); 13 if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) { 14 reject(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) { 19 wakeup(inEventLoop); 20 } 21 }
EventLoop的execute最终会调用EventLoop中executor的execute,这个executor是哪儿来的呢?
1 public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup { 2 //...... 3 4 //threadFactory会被包装为一个executor, 5 //该executor的execute方法就是threadFactory.newThread(command).start(); 6 //threadFactory的newThread一般都会新建thread,因为thread实例只能start一次。 7 public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) { 8 this(nThreads, threadFactory, SelectorProvider.provider()); 9 } 10 11 //这里传入的executor就是EventLoop中的executor, 12 //nThreads表示EventExecutor(EventLoop)的个数,这些eventExecutor会持有同一个executor, 13 //Group会持有这些eventExecutor,即children,但children还未启动。 14 //children = new EventExecutor[nThreads]; 15 //迭代children[i] = newChild(executor, args); 16 public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) { 17 this(nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider()); 18 } 19 20 //...... 21 }
由上分析可知,netty中EventLoop的核心在于executor,executor提供了真正的执行能力(即线程),下面就是NioEventLoop在executor中的执行的任务(这里的run并不是Runnable的run),可以看出,所谓EventLoop就是一个循环器,该循环器不停的在处理channel的IO事件。

1 protected void run() { 2 for (;;) { 3 try { 4 switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) { 5 case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE: 6 continue; 7 case SelectStrategy.SELECT: 8 select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); 9 if (wakenUp.get()) { 10 selector.wakeup(); 11 } 12 default: 13 // fallthrough 14 } 15 16 cancelledKeys = 0; 17 needsToSelectAgain = false; 18 final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio; 19 if (ioRatio == 100) { 20 try { 21 processSelectedKeys(); 22 } finally { 23 // Ensure we always run tasks. 24 runAllTasks(); 25 } 26 } else { 27 final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); 28 try { 29 processSelectedKeys(); 30 } finally { 31 // Ensure we always run tasks. 32 final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime; 33 runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); 34 } 35 } 36 } catch (Throwable t) { 37 handleLoopException(t); 38 } 39 // Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception. 40 try { 41 if (isShuttingDown()) { 42 closeAll(); 43 if (confirmShutdown()) { 44 return; 45 } 46 } 47 } catch (Throwable t) { 48 handleLoopException(t); 49 } 50 } 51 }
