1. 类的关键字
(1)struct在C语言中己经有了自己的含义,必须继续兼容
(2)在C++中提供了新的关键字class用于类定义
(3)class和struct的用法完全相同
-
用struct定义的类中所有成员默认访问级别为public
-
用class定义的类中所有成员默认访问级别为private

【编程实验】class的初探 16-1.cpp
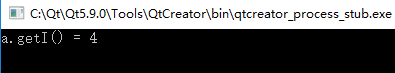
#include <stdio.h> struct A { //默认访问级别为public int i; int getI(){return i;}; }; class B { //默认访问级别为private int i; int getI(){return i;}; };
int main() { A a; B b; a.i = 4;//ok printf("a.getI() = %d ", a.getI()); //b.i = 4; //Error: private //printf("b.getI() = %d ", b.getI()); //Error: private return 0; }
运行结果:
2. 小实例:开发一个用于四则运算的类
(1)提供setOperator函数设置运算类型
(2)提供setParameter函数设置运算参数
(3)提供result函数进行运算:
-
参数为引用类型用于得到计算结果
-
返回值表示运算的合法性
【实例分析】Operator类的分析(Operator.h和Operator.cpp)
//Operator.h
#ifndef _OPERATOR_H_ #define _OPERATOR_H_ class Operator { private: char mOp; //操作符 double mP1; //操作数1 double mP2; //操作数2 public: bool setOperator(char op); void setParameter(double p1, double p2); bool result(double& r); }; #endif
//Operator.cpp
#include "Operator.h" bool Operator::setOperator(char op) { bool bRet = (op == '+') || (op == '-') || (op == '*') || (op == '/'); if(bRet) { mOp = op; } else { mOp = '�'; } return bRet; } void Operator::setParameter(double p1, double p2) { mP1 = p1; mP2 = p2; } bool Operator::result(double& r) { bool bRet = true; switch(mOp) { case '/': if((-0.000000001<mP2) && (mP2 <0.000000001)) { bRet = false; } else { r = mP1 / mP2; } break; case '+': r = mP1 + mP2; break; case '-': r = mP1 - mP2; break; case '*': r = mP1 * mP2; break; } return bRet; }
//main.cpp
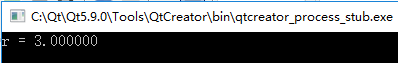
#include <stdio.h> #include "Operator.h" int main() { Operator op; double r = 0; op.setOperator('/'); op.setParameter(9, 3); if(op.result(r)) { printf("r = %lf ", r); } else { printf("Calculate error! "); } return 0; }
运行结果:
3. 类声明和实现的分离
(1).h头文件只用类的声明:成员变量和成员函数的声明
(2).cpp源文件中完成类的其它实现(如成员函数的实现)
4. 小结
(1)C++引进了新的关键字class用于定义类
(2)struct和class的区别在于默认的访问级别不同(前者public,后者private)
(3)C++中的类支持声明和实现的分离(在头文件中声明类,在源文件中实现类)