等待就是当运行代码时,如果页面的渲染速度跟不上代码的运行速度,就需要人为的去限制代码执行的速度。
在做 Web 自动化时,一般要等待页面元素加载完成后,才能执行操作,否则会报找不到元素等各种错误,这样就要求在有些场景下加上等待。
最常见的有三种等待方式:
-
隐式等待
-
显式等待
-
强制等待
后面会一一介绍这三种模式的使用场景。
隐式等待
设置一个等待时间,轮询查找(默认 0.5 秒)元素是否出现,如果没出现就抛出异常。这也是最常见的等待方法。
隐式等待的作用是全局的,是作用于整个 session 的生命周期,也就是说只要设置一次隐式等待,后面就不需要设置。如果再次设置隐式等待,那么后一次的会覆盖前一次的效果。
当在 DOM 结构中查找元素,且元素处于不能立即交互的状态时,将会触发隐式等待。
- Python 版本
self.driver.implicitly_wait(30)
- Java 版本
//隐式等待调用方式,设置等待时间为5秒
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
显式等待
显式等待是在代码中定义等待条件,触发该条件后再执行后续代码,就能够根据判断条件进行等待。程序每隔一段时间进行条件判断,如果条件成立,则执行下一步,否则继续等待,直到超过设置的最长时间。核心用法如下:
- Python 版本
# 导入显示等待
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions
...
# 设置10秒的最大等待时间,等待 (By.TAG_NAME, "title") 这个元素点击
WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(
expected_conditions.element_to_be_clickable((By.TAG_NAME, "title"))
)
...
这里通过导入 expected_conditions 这个库来满足显式等待所需的使用场景,但是 expected_conditions 库并不能满足所有场景,这个时候就需要定制化开发来满足特定场景。
- Java 版本
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
...
// 设置10秒的最大等待时间,等待 (By.TAG_NAME, "title") 这个元素点击
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver,10);
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(By.tagName("title")));
...
假设:要判断某个元素超过指定的个数,就可以执行下面的操作。
实战演练
def ceshiren():
# 定义一个方法
def wait_ele_for(driver):
# 将找到的元素个数赋值给 eles
eles = driver.find_elements(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="site-text-logo"]')
# 放回结果
return len(eles) > 0
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get('https://ceshiren.com')
# 显示等待10秒,直到 wait_ele_for 返回 true
WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until(wait_ele_for)
void ceshiren(){
webDriver = new ChromeDriver();
webDriver.get("https://ceshiren.com");
//显示等待10秒,直到 wait_ele_for 返回 true
new WebDriverWait(webDriver,10).until((ExpectedCondition<Boolean>) size -> waitEleFor());
}
// 定义一个方法
boolean waitEleFor(){
// 将找到的元素个数赋值给 eles
List<WebElement> elements = webDriver.findElements(By.xpath("//*[@id='site-text-logo']"));
return elements.size() > 0;
}
强制等待
强制等待是使线程休眠一定时间。强制等待一般在隐式等待和显式等待都不起作用时使用。示例代码如下
- Python 版本
# 等待十秒
time.sleep(10)
- Java 版本
// 等待2000毫秒,相当于等待2秒
Thread.sleep(2000)
实战演示
访问测试人社区:https://ceshiren.com,点击分类,然后点击答疑区:
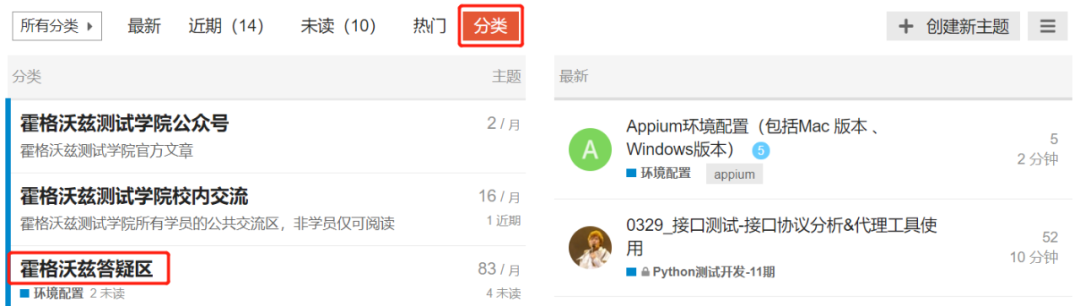
当点击分类时,元素还未加载完成,这里就需要隐式等待。在点击答疑区时,元素已加载完成,但是还处在不可点击的状态,这时要用到显式等待。
#导入依赖
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
class TestHogwarts():
def setup(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Chrome()
self.driver.get('https://ceshiren.com/')
#加入隐式等待
self.driver.implicitly_wait(5)
def teardown(self):
#强制等待
time.sleep(10)
self.driver.quit()
def test_hogwarts(self):
#元素定位,这里的category_name是一个元组。
category_name = (By.LINK_TEXT, "开源项目")
# 加入显式等待
WebDriverWait(self.driver, 10).until(
expected_conditions.element_to_be_clickable(category_name))
# 点击开源项目
self.driver.find_element(*category_name).click()
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class WebDriverWaitTest {
private static ChromeDriver driver;
@BeforeAll
public static void setUp() {
System.setProperty(
"webdriver.chrome.driver",
"/driver/chrome95/chromedriver"
);
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@AfterAll
public static void tearDown() {
driver.quit();
}
@Test
public void waitTest(){
driver.get("https://ceshiren.com/");
By locator = By.linkText("开源项目");
// 加入显式等待
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10);
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(locator));
// 点击开源项目
driver.findElement(locator).click();
}
}
在实际工作中等待机制可以保证代码的稳定性,保证代码不会受网速、电脑性能等条件的约束。
点击“下方链接”,提升测试核心竞争力! 欢迎加v~ceshiren001