Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4080 Accepted Submission(s): 2043
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
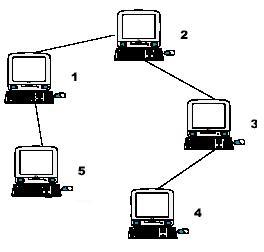
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.

Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
经典的问题,第一次Dp先处理好子树的 最远 , 次远距离( 有一边[ u , v , w ] , u 的次远可能是最远路上儿子 v 的最远( u的次远 + w ) )~~
解决的时候考虑 temp 是来自父亲路径上的最长路,然后对 儿子分成 是否是最远路上的~ 来求解答案~

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; const int N = 10010 ; int dp[N][2] , son[N][2] , ans[N] , n ; int eh[N] , et[N<<1] , nxt[N<<1] , ew[N<<1] , tot ; void init() { memset( eh , -1 , sizeof eh ); tot = 0 ; } void addedge( int u , int v , int w ) { et[tot] = v ; ew[tot] = w ; nxt[tot] = eh[u] ; eh[u] = tot++ ; et[tot] = u ; ew[tot] = w ; nxt[tot] = eh[v] ; eh[v] = tot++ ; } int Dp( int u , int fa ) { for( int i = eh[u] ; ~i ; i = nxt[i] ) { int v = et[i] , w = ew[i] ; if( v == fa ) continue ; int tmp = Dp( v , u ) + w ; if( tmp > dp[u][1] ) { dp[u][1] = tmp ; son[u][1] = v ; } if( dp[u][1] > dp[u][0] ) { swap( dp[u][1] , dp[u][0] ) ; swap( son[u][1] , son[u][0]) ; } } return dp[u][0] ; } void Solve( int u , int fa , int tmp ) { ans[u] = max( dp[u][0] , tmp ) ; for( int i = eh[u] ; ~i ; i = nxt[i] ) { int v = et[i] , w = ew[i] ; if( v == fa ) continue ; if( v == son[u][0] ) { Solve( v , u , max( dp[u][1] , tmp ) + w ) ; } else { Solve( v , u , max( dp[u][0] , tmp ) + w ) ; } } } int main () { while( ~scanf("%d",&n) ) { init(); for( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++i ) { int v , w ; scanf("%d%d",&v,&w); addedge( i , v , w ) ; } memset( dp , 0 , sizeof dp ) ; Dp( 1 , 0 ); //for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i ) cout << i << ' ' << dp[i][0] << ' ' << dp[i][1] << endl ; Solve( 1 , 0 , 0 ); for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i ) printf("%d ",ans[i]); } return 0 ; }
