
说明
- 操作系统:Windows 10
- Python 版本:3.7x
- 虚拟环境管理器:virtualenv
- 代码编辑器:VS Code
实验
环境初始化
# 创建项目目录
mkdir helloworld
cd helloworld
# 创建虚拟环境
python -m virtualenv venv
# 激活虚拟环境
venvScriptsactivate
# 安装环境包
pip install flask flask-restplus
# 启动 VS Code
code .
实验示例
Hello World
from flask import Flask
from flask_restplus import Api, Resource
app = Flask(__name__)
api_app = Api(app=app,
version='1.0',
title='Main',
description='Main APIs')
name_space = api_app.namespace(name='helloworld',
description='The helloworld APIs EndPoint.')
@name_space.route('/')
class HelloWorld(Resource):
def get(self):
return {
'status': 'you get a request.'
}
def post(self):
return {
'status': 'you post a request.'
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
程序运行效果如下图所示:

此时,我们可以通过 Swagger UI 或者 curl 来请求我们上面创建的 一个 get 和 一个 post 请求接口。
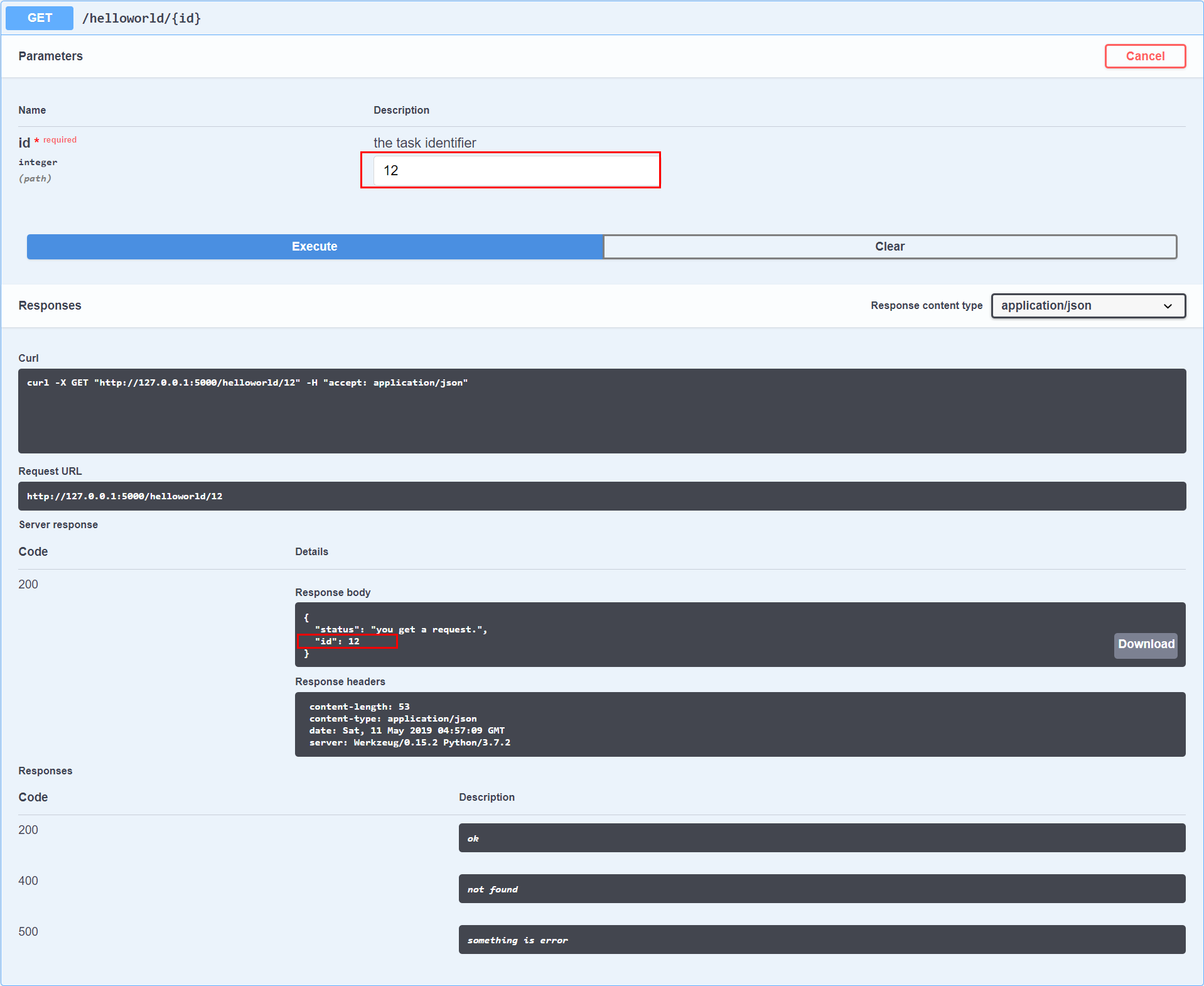
参数传递
参数传递,我们只需要将我们的接口定义添加参数配置即可,如下示例代码所示:
@name_space.route('/<int:id>')
class HelloWorld(Resource):
@api_app.doc(responses={
200: 'ok',
400: 'not found',
500: 'something is error'
}, params={
'id': 'the task identifier'
})
def get(self, id):
return {
'status': 'you get a request.',
'id': id
}
def post(self, id):
return {
'status': 'you post a request.'
}
运行结构如下图所示:
实体传递
在上述两个示例代码中,我们知道了如何定义 WebAPI 和 参数传递,下面我们摘录一个官方首页的 Todo 示例,来完整展示如何使用:
from flask import Flask
from flask_restplus import Api, Resource, fields
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app, version='1.0', title='TodoMVC API',
description='A simple TodoMVC API',
)
# 配置 API 空间节点
ns = api.namespace('todos', description='TODO operations')
# 配置接口数据模型(此数据模型是面向对外服务的,在实际项目中应与数据库中的数据模型区分开)
todo = api.model('Todo', {
'id': fields.Integer(readOnly=True, description='The task unique identifier'),
'task': fields.String(required=True, description='The task details')
})
# 定义接口实体
class TodoDAO(object):
def __init__(self):
self.counter = 0
self.todos = []
def get(self, id):
for todo in self.todos:
if todo['id'] == id:
return todo
api.abort(404, "Todo {} doesn't exist".format(id))
def create(self, data):
todo = data
todo['id'] = self.counter = self.counter + 1
self.todos.append(todo)
return todo
def update(self, id, data):
todo = self.get(id)
todo.update(data)
return todo
def delete(self, id):
todo = self.get(id)
self.todos.remove(todo)
# 创建种子数据
DAO = TodoDAO()
DAO.create({'task': 'Build an API'})
DAO.create({'task': '?????'})
DAO.create({'task': 'profit!'})
# 定义服务接口
@ns.route('/')
class TodoList(Resource):
'''Shows a list of all todos, and lets you POST to add new tasks'''
@ns.doc('list_todos')
@ns.marshal_list_with(todo)
def get(self):
'''List all tasks'''
return DAO.todos
@ns.doc('create_todo')
@ns.expect(todo)
@ns.marshal_with(todo, code=201)
def post(self):
'''Create a new task'''
return DAO.create(api.payload), 201
# 定义服务接口
@ns.route('/<int:id>')
@ns.response(404, 'Todo not found')
@ns.param('id', 'The task identifier')
class Todo(Resource):
'''Show a single todo item and lets you delete them'''
@ns.doc('get_todo')
@ns.marshal_with(todo)
def get(self, id):
'''Fetch a given resource'''
return DAO.get(id)
@ns.doc('delete_todo')
@ns.response(204, 'Todo deleted')
def delete(self, id):
'''Delete a task given its identifier'''
DAO.delete(id)
return '', 204
@ns.expect(todo)
@ns.marshal_with(todo)
def put(self, id):
'''Update a task given its identifier'''
return DAO.update(id, api.payload)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
程序运行效果如下图所示:

总结
基于 Flask 而创建 Swagger UI 风格的 WebAPI 包有很多,如
它们都各有各的优缺点,但是就我目前使用情况来说,还是 Flask-RESTPlus 的构建方式我更喜欢一些,所以我就在这里分享一下。
最后的最后,安利一下我个人站点:hippiezhou,里面的 必应壁纸 板块收录了每天的必应壁纸,希望你能喜欢。