本文作者:hhh5460
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hhh5460/p/10134855.html
问题情境
一个2*2的迷宫,一个入口,一个出口,还有一个陷阱。如图
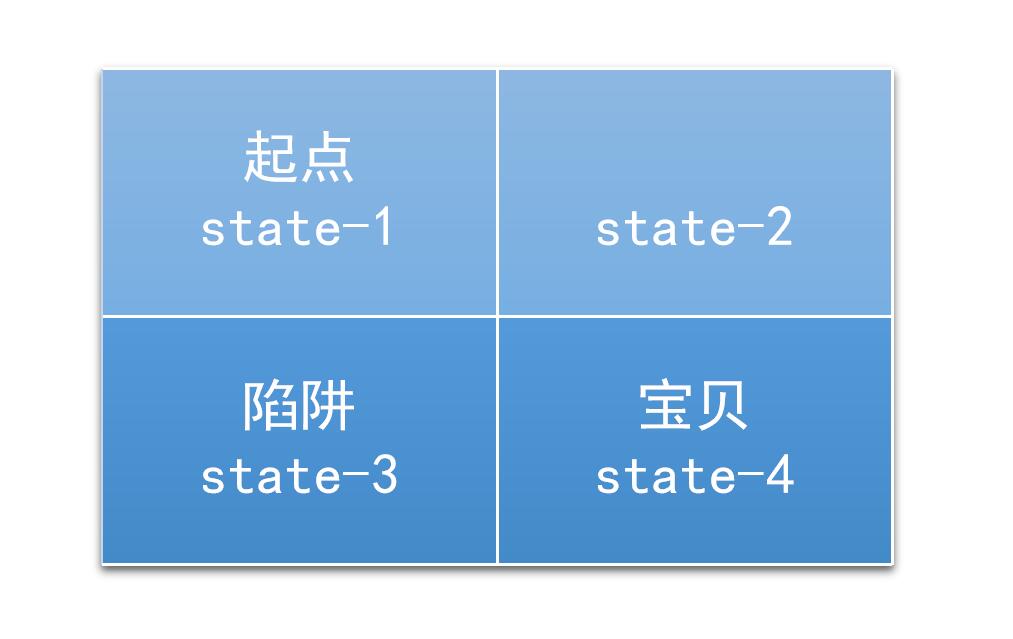 (图片来源:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning)
(图片来源:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning)
这是一个二维的问题,不过我们可以把这个降维,变为一维的问题。
感谢:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning。网上看了无数文章,无数代码,都不得要领!直到看了这篇里面的三个矩阵:reward,transition_matrix,valid_actions才真正理解q-learning算法如何操作,如何实现!
的代码先睹为快,绝对让你秒懂q-learning算法,当然我也做了部分润色:

import numpy as np import random ''' 2*2的迷宫 --------------- | 入口 | | --------------- | 陷阱 | 出口 | --------------- # 来源:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning 每个格子是一个状态,此时都有上下左右停5个动作 任务:通过学习,找到一条通径 ''' gamma = 0.7 # u, d, l, r, n reward = np.array([( 0, -10, 0, -1, -1), #0,状态0 ( 0, 10, -1, 0, -1), #1 (-1, 0, 0, 10, -1), #2 (-1, 0, -10, 0, 10)],#3 dtype=[('u',float),('d',float),('l',float),('r',float),('n',float)]) q_matrix = np.zeros((4, ), dtype=[('u',float),('d',float),('l',float),('r',float),('n',float)]) transition_matrix = np.array([(-1, 2, -1, 1, 0), # 如 state:0,action:'d' --> next_state:2 (-1, 3, 0, -1, 1), ( 0, -1, -1, 3, 2), ( 1, -1, 2, -1, 3)], dtype=[('u',int),('d',int),('l',int),('r',int),('n',int)]) valid_actions = np.array([['d', 'r', 'n'], #0,状态0 ['d', 'l', 'n'], #1 ['u', 'r', 'n'], #2 ['u', 'l', 'n']])#3 for i in range(1000): current_state = 0 while current_state != 3: current_action = random.choice(valid_actions[current_state]) # 只有探索,没有利用 next_state = transition_matrix[current_state][current_action] next_reward = reward[current_state][current_action] next_q_values = [q_matrix[next_state][next_action] for next_action in valid_actions[next_state]] #待取最大值 q_matrix[current_state][current_action] = next_reward + gamma * max(next_q_values) # 贝尔曼方程(不完整) current_state = next_state print('Final Q-table:') print(q_matrix)
0.相关参数
epsilon = 0.9 # 贪婪度 greedy alpha = 0.1 # 学习率 gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值
1.状态集
探索者的状态,即其可到达的位置,有4个。所以定义
states = range(4) # 状态集,从0到3
那么,在某个状态下执行某个动作之后,到达的下一个状态如何确定呢?
def get_next_state(state, action): '''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态''' #u,d,l,r,n = -2,+2,-1,+1,0 if state % 2 != 1 and action == 'r': # 除最后一列,皆可向右(+1) next_state = state + 1 elif state % 2 != 0 and action == 'l': # 除最前一列,皆可向左(-1) next_state = state -1 elif state // 2 != 1 and action == 'd': # 除最后一行,皆可向下(+2) next_state = state + 2 elif state // 2 != 0 and action == 'u': # 除最前一行,皆可向上(-2) next_state = state - 2 else: next_state = state return next_state
2.动作集
探索者处于每个状态时,可行的动作,只有上下左右4个。所以定义
actions = ['u', 'd', 'l', 'r'] # 动作集。上下左右,也可添加动作'n',表示停留
那么,在某个给定的状态(位置),其所有的合法动作如何确定呢?
def get_valid_actions(state): '''取当前状态下的合法动作集合,与reward无关!''' global actions # ['u','d','l','r','n'] valid_actions = set(actions) if state % 2 == 1: # 最后一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['r']) # 去掉向右的动作 if state % 2 == 0: # 最前一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['l']) # 去掉向左 if state // 2 == 1: # 最后一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['d']) # 去掉向下 if state // 2 == 0: # 最前一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['u']) # 去掉向上 return list(valid_actions)
3.奖励集
探索者到达每个状态(位置)时,要有奖励。所以定义
rewards = [0,0,-10,10] # 奖励集。到达位置3(出口)奖励10,位置2(陷阱)奖励-10,其他皆为0
显然,取得某状态state下的奖励就很简单了:rewards[state] 。根据state,按图索骥即可,无需额外定义一个函数。
4.Q table
最重要。Q table是一种记录状态-行为值 (Q value) 的表。常见的q-table都是二维的,基本长下面这样:
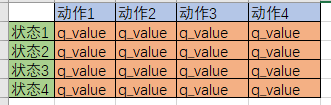 (注意,也有3维的Q table)
(注意,也有3维的Q table)
所以定义
q_table = pd.DataFrame(data=[[0 for _ in actions] for _ in states], index=states, columns=actions)
5.Q-learning算法
Q-learning算法的伪代码

Q value的更新是根据贝尔曼方程:
$$Q(s_t,a_t) leftarrow Q(s_t,a_t) + alpha[r_{t+1} + lambda max _{a} Q(s_{t+1}, a) - Q(s_t,a_t)] ag {1}$$
好吧,是时候实现它了:
# 总共探索300次 for i in range(300): # 0.从最左边的位置开始(不是必要的) current_state = 0 #current_state = random.choice(states) while current_state != states[-1]: # 1.取当前状态下的合法动作中,随机(或贪婪)地选一个作为 当前动作 if (random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon) or ((q_table.ix[current_state] == 0).all()): # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: current_action = q_table.ix[current_state].idxmax() # 利用(贪婪) # 2.执行当前动作,得到下一个状态(位置) next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) # 3.取下一个状态所有的Q value,待取其最大值 next_state_q_values = q_table.ix[next_state, get_valid_actions(next_state)] # 4.根据贝尔曼方程,更新 Q table 中当前状态-动作对应的 Q value q_table.ix[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (rewards[next_state] + gamma * next_state_q_values.max() - q_table.ix[current_state, current_action]) # 5.进入下一个状态(位置) current_state = next_state print(' q_table:') print(q_table)
可以看到,与例一的代码一模一样,不差一字!
6.环境及其更新
这里的环境貌似必须用到GUI,有点麻烦;而在命令行下,我又不知如何实现。所以暂时算了,不搞了。
7.完整代码
''' 最简单的四个格子的迷宫 --------------- | start | | --------------- | die | end | --------------- 每个格子是一个状态,此时都有上下左右4个动作
作者:hhh5460
时间:20181217 ''' import pandas as pd import random epsilon = 0.9 # 贪婪度 greedy alpha = 0.1 # 学习率 gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值 states = range(4) # 0, 1, 2, 3 四个状态 actions = list('udlr') # 上下左右 4个动作。还可添加动作'n',表示停留 rewards = [0,0,-10,10] # 奖励集。到达位置3(出口)奖励10,位置2(陷阱)奖励-10,其他皆为0 q_table = pd.DataFrame(data=[[0 for _ in actions] for _ in states], index=states, columns=actions) def get_next_state(state, action): '''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态''' #u,d,l,r,n = -2,+2,-1,+1,0 if state % 2 != 1 and action == 'r': # 除最后一列,皆可向右(+1) next_state = state + 1 elif state % 2 != 0 and action == 'l': # 除最前一列,皆可向左(-1) next_state = state -1 elif state // 2 != 1 and action == 'd': # 除最后一行,皆可向下(+2) next_state = state + 2 elif state // 2 != 0 and action == 'u': # 除最前一行,皆可向上(-2) next_state = state - 2 else: next_state = state return next_state def get_valid_actions(state): '''取当前状态下的合法动作集合 global reward valid_actions = reward.ix[state, reward.ix[state]!=0].index return valid_actions ''' # 与reward无关! global actions valid_actions = set(actions) if state % 2 == 1: # 最后一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['r']) # 无向右的动作 if state % 2 == 0: # 最前一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['l']) # 无向左 if state // 2 == 1: # 最后一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['d']) # 无向下 if state // 2 == 0: # 最前一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['u']) # 无向上 return list(valid_actions) # 总共探索300次 for i in range(300): # 0.从最左边的位置开始(不是必要的) current_state = 0 #current_state = random.choice(states) while current_state != states[-1]: # 1.取当前状态下的合法动作中,随机(或贪婪)地选一个作为 当前动作 if (random.uniform(0,1) > epsilon) or ((q_table.ix[current_state] == 0).all()): # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: current_action = q_table.ix[current_state].idxmax() # 利用(贪婪) # 2.执行当前动作,得到下一个状态(位置) next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) # 3.取下一个状态所有的Q value,待取其最大值 next_state_q_values = q_table.ix[next_state, get_valid_actions(next_state)] # 4.根据贝尔曼方程,更新 Q table 中当前状态-动作对应的 Q value q_table.ix[current_state, current_action] += alpha * (rewards[next_state] + gamma * next_state_q_values.max() - q_table.ix[current_state, current_action]) # 5.进入下一个状态(位置) current_state = next_state print(' q_table:') print(q_table)
8.效果图
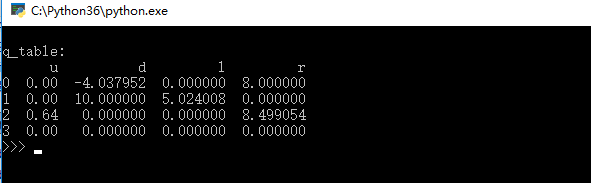
9.补充
又搞了一个numpy版本,比pandas版本的快了一个数量级!!代码如下

''' 最简单的四个格子的迷宫 --------------- | start | | --------------- | die | end | --------------- 每个格子是一个状态,此时都有上下左右停5个动作 ''' # 作者:hhh5460 # 时间:20181218 import numpy as np epsilon = 0.9 # 贪婪度 greedy alpha = 0.1 # 学习率 gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值 states = range(4) # 0, 1, 2, 3 四个状态 actions = list('udlrn') # 上下左右停 五个动作 rewards = [0,0,-10,10] # 奖励集。到达位置3(出口)奖励10,位置2(陷阱)奖励-10,其他皆为0 # 给numpy数组的列加标签,参考https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/ask/72790 q_table = np.zeros(shape=(4, ), # 坑二:这里不能是(4,5)!! dtype=list(zip(actions, ['float']*5))) #dtype=[('u',float),('d',float),('l',float),('r',float),('n',float)]) #dtype={'names':actions, 'formats':[float]*5}) def get_next_state(state, action): '''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态''' #u,d,l,r,n = -2,+2,-1,+1,0 if state % 2 != 1 and action == 'r': # 除最后一列,皆可向右(+1) next_state = state + 1 elif state % 2 != 0 and action == 'l': # 除最前一列,皆可向左(-1) next_state = state -1 elif state // 2 != 1 and action == 'd': # 除最后一行,皆可向下(+2) next_state = state + 2 elif state // 2 != 0 and action == 'u': # 除最前一行,皆可向上(-2) next_state = state - 2 else: next_state = state return next_state def get_valid_actions(state): '''取当前状态下的合法动作集合,与reward无关!''' global actions # ['u','d','l','r','n'] valid_actions = set(actions) if state % 2 == 1: # 最后一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['r']) # 去掉向右的动作 if state % 2 == 0: # 最前一列,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['l']) # 去掉向左 if state // 2 == 1: # 最后一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['d']) # 去掉向下 if state // 2 == 0: # 最前一行,则 valid_actions = valid_actions - set(['u']) # 去掉向上 return list(valid_actions) for i in range(1000): #current_state = states[0] # 固定 current_state = np.random.choice(states,1)[0] while current_state != 3: if (np.random.uniform() > epsilon) or ((np.array(list(q_table[current_state])) == 0).all()): # q_table[current_state]是numpy.void类型,只能这么操作!! current_action = np.random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state), 1)[0] else: current_action = actions[np.array(list(q_table[current_state])).argmax()] # q_table[current_state]是numpy.void类型,只能这么操作!! next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) next_state_q_values = [q_table[next_state][action] for action in get_valid_actions(next_state)] q_table[current_state][current_action] = rewards[next_state] + gamma * max(next_state_q_values) current_state = next_state print('Final Q-table:') print(q_table)
10.补充2:三维Q table实现!
经过不断的试验,终于撸出了一个三维版的Q table,代码如下!

''' 最简单的四个格子的迷宫 --------------- | start | | --------------- | die | end | --------------- 每个格子是一个状态,此时都有上下左右停5个动作 ''' '''三维 Q table 版!!''' # 作者:hhh5460 # 时间:20181218 import numpy as np import random # np.random.choice不能选二维元素! epsilon = 0.9 # 贪婪度 greedy alpha = 0.1 # 学习率 gamma = 0.8 # 奖励递减值 states = [(0,0),(0,1),(1,0),(1,1)] #状态集,四个位置 actions = [(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)] #动作集,上下左右 rewards = [[ 0., 0.], # 奖励集 [-10.,10.]] # q_table是三维的,注意把动作放在了第三维! # 最里面的[0.,0.,0.,0.]表示某一个状态(格子)对应的四个动作“上下左右”的Q value q_table = np.array([[[0.,0.,0.,0.],[0.,0.,0.,0.]], [[0.,0.,0.,0.],[0.,0.,0.,0.]]]) def get_next_state(state, action): '''对状态执行动作后,得到下一状态''' if ((state[1] == 1 and action == (0,1)) or # 最后一列、向右 (state[1] == 0 and action == (0,-1)) or # 最前一列、向左 (state[0] == 1 and action == (1,0)) or # 最后一行、向下 (state[0] == 0 and action == (-1,0))): # 最前一行、向上 next_state = state else: next_state = (state[0] + action[0], state[1] + action[1]) return next_state def get_valid_actions(state): '''取当前状态下的合法动作集合''' valid_actions = [] if state[1] < 1: # 除最后一列,可向右 valid_actions.append((0,1)) if state[1] > 0: # 除最前一列,可向左(-1) valid_actions.append((0,-1)) if state[0] < 1: # 除最后一行,可向下 valid_actions.append((1,0)) if state[0] > 0: # 除最前一行,可向上 valid_actions.append((-1,0)) return valid_actions # 总共探索300次 for i in range(1000): # 0.从最左边的位置开始(不是必要的) current_state = (0,0) #current_state = random.choice(states) #current_state = tuple(np.random.randint(2, size=2)) while current_state != states[-1]: # 1.取当前状态下的合法动作中,随机(或贪婪)地选一个作为 当前动作 if (np.random.uniform() > epsilon) or ((q_table[current_state[0],current_state[1]] == 0).all()): # 探索 current_action = random.choice(get_valid_actions(current_state)) else: current_action = actions[q_table[current_state[0],current_state[1]].argmax()] # 利用(贪婪) # 2.执行当前动作,得到下一个状态(位置) next_state = get_next_state(current_state, current_action) # 3.取下一个状态所有的Q value,待取其最大值 next_state_q_values = [q_table[next_state[0],next_state[1],actions.index(action)] for action in get_valid_actions(next_state)] # 4.根据贝尔曼方程,更新 Q table 中当前状态-动作对应的 Q value q_table[current_state[0],current_state[1],actions.index(current_action)] += alpha * (rewards[next_state[0]][next_state[1]] + gamma * max(next_state_q_values) - q_table[current_state[0],current_state[1],actions.index(current_action)]) # 5.进入下一个状态(位置) current_state = next_state print(' q_table:') print(q_table)
11.课后思考题
有缘看到此文的朋友,请尝试下实现更大规模的迷宫问题,评论交作业哦。迷宫如下:
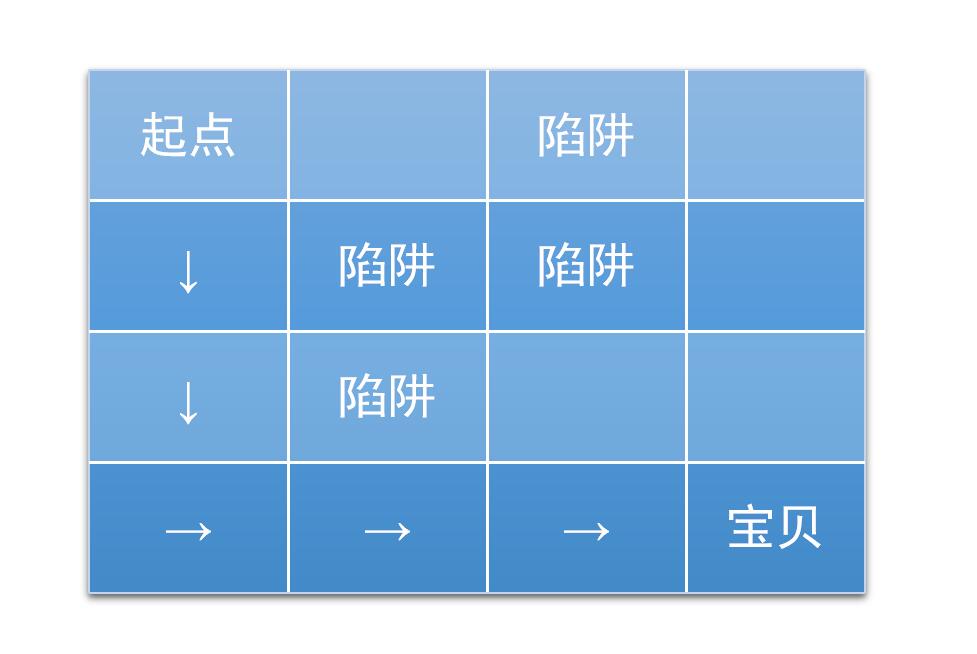 (图片来源:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning)
(图片来源:https://jizhi.im/blog/post/intro_q_learning)
