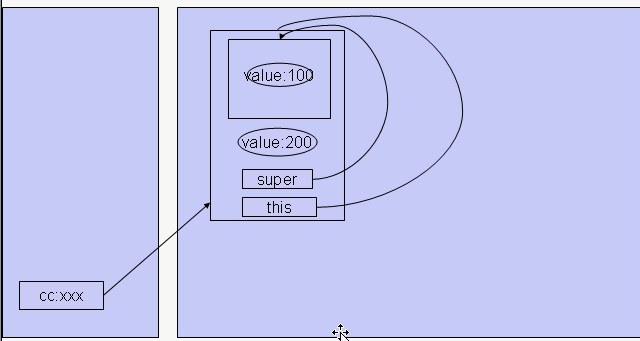
super 关键字
class FatherClass {
public int value;
public void f(){
value = 100;
System.out.println("FatherClass.value="+value);
}
}
class ChildClass extends FatherClass {
public int value;
public void f(){
super.f();
value = 200;
System.out.println("ChildClass.value="+value);
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(super.value);
}
}
public class Child {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChildClass childClass = new ChildClass();
childClass.f();
}
}
FatherClass.value=100
ChildClass.value=200
200
100
class Person {
private String name;
private String location;
Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
location = "beijing";
}
Person(String name, String location) {
this.name = name;
this.location = location;
}
public String info() {
return "name: " + name + " location: " + location;
}
}
class Student extends Person {
private String school;
Student(String name, String school) {
this(name, "beijing", school);
}
Student(String n, String l, String school) {
super(n, l);
this.school = school;
}
@Override
public String info() {
return super.info() + " school: " + school;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("A");
Person p2 = new Person("B", "shanghai");
Student s1 = new Student("C", "S1");
Student s2 = new Student("C", "shanghai", "S2");
System.out.println(p1.info());
System.out.println(p2.info());
System.out.println(s1.info());
System.out.println(s2.info());
}
}
name: A location: beijing
name: B location: shanghai
name: C location: beijing school: S1
name: C location: shanghai school: S2
1. 使用 super. 访问父类的变量
class Vehicle {
int maxSpeed = 120;
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
int maxSpeed = 180;
void display() {
System.out.println(maxSpeed);
System.out.println("Maximum Speed: " + super.maxSpeed);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car small = new Car();
small.display();
}
}
180
Maximum Speed: 120
2. 使用 super. 访问父类的方法
class Person {
void message() {
System.out.println("This is person class");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
@Override
void message() {
System.out.println("This is student class");
}
void display() {
message();
super.message();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s = new Student();
s.display();
}
}
This is student class
This is person class
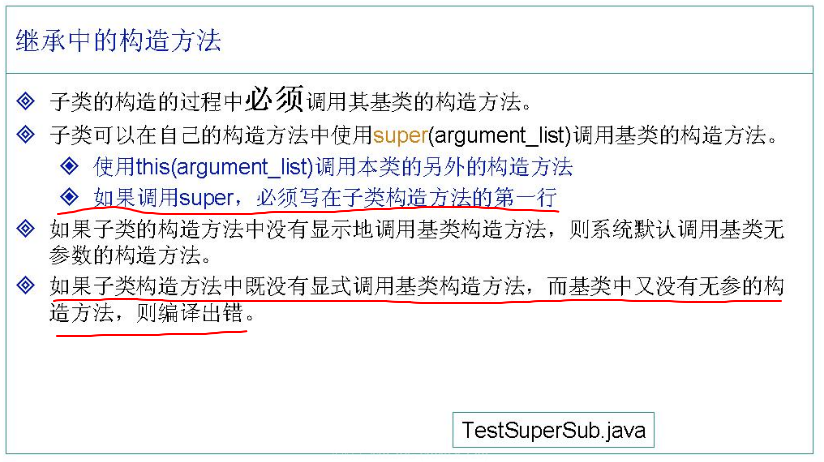
3. 使用 super 访问父类构造函数
class Person {
Person() {
System.out.println("Person class Constructor");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
Student() {
super();
System.out.println("Student class Constructor");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
}
}
Person class Constructor
Student class Constructor
注意:
在子类构造方法中通过 super() 调用父类构造方法的时候必须放在构造方法的第一行。 如果子类没有显示的调用父类的构造方法,则 Java 编译器会自动在子类构造方法中调用父类默认无参的构造方法。如果父类没有提供无参的构造方法,则会出现编译错误。 Java 程序中如何没有写构造方法,则JVM会自动生成一个无参的构造方法,如果写了构造方法的话,就不会提供了。 super()应该是任何构造函数中的第一个语句。它只能在构造函数内部使用,而不能在其他任何地方使用。super()用于仅引用父类(超类)的构造函数。* [https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/super-keyword/](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/super-keyword/)
class Grandparent {
public void Print() {
System.out.println("Grandparent's Print()");
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent {
public void Print() {
super.Print();
System.out.println("Parent's Print()");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
public void Print() {
super.Print();
System.out.println("Child's Print()");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.Print();
}
}
Grandparent's Print()
Parent's Print()
Child's Print()
不能这样使用 super.super.Print(); 会出现错误