


代码如下:
class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }
答:构造一个对象,先调用其构造方法来初始化其成员函数和成员变量。子类拥有父的成员变量和成员方法,必须通过调用从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法来正确的初始化。而父类不拥有子类成员,故子父类调用不可反。



代码如下:
public class ExplorationJDKSource { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(new A()); } } class A{}
使用javap -c反编译结果如下:
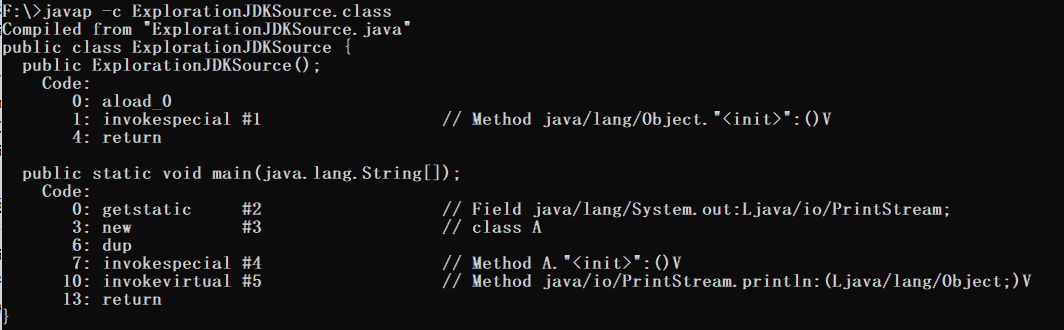
答:在编译源代码时,当遇到没有父类的类时,编译器会将其指定一个默认的父类(一般为Object),因此,main方法实际上内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。 valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() { return getClass().getName() +"@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); }
其中hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现,所以出现上述结果。

public class test extends Parent
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
test t=new test();
t.Parent();
t.Child();
}
public void Parent(){System.out.println("Child");}//parent方法的重载
public void Child(){super.Parent();}//调用父类方法parent
}
class Parent{public void Parent(){System.out.println("Parent ");}}



运行结果如下:

答:第一个调用的是父类的方法,输出为100;第二个调用的是子类的方法,输出为200;第三个中子类赋值给父类,因此调用了子类的方法,输出值为200;第四个中调用了子类的构造方法,但是value值为200,所以没有影响;第五个中调用的是子类的方法,value的值也是子类的。
当子类与父类拥有相同的方法时,方法的调用取决于对象的类型。如此代码中,子类赋值给了父类,因而此后调用都为子类。