离散序列的标准互信息计算
来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/ziqiao/archive/2011/12/13/2286273.html
一、离散序列样本
X = [1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3];
Y= [1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 1 1 3 3 3];
二、计算离散序列X与Y的互信息(Mutual information)
MI可以按照下面的公式(1)计算:
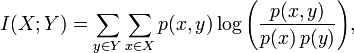
X和Y的联合分布概率p(x,y)和边缘分布律p(x)、p(y)如下:

其中,分子p(x,y)为x和y的联合分布概率:
p(1,1)=5/17, p(1,2)=1/17, p(1,3)=0;
p(2,1)=1/17, p(2,2)=4/17, p(2,3)=1/17;
p(3,1)=2/17, p(3,2)=0, p(3,3)=3/17;
分母p(x)为x的概率函数,p(y)为y的概率函数,
对p(x):
p(1)=6/17,p(2)=6/17,p(3)=5/17
对p(y):
p(1)=8/17,p(2)=5/17,P(3)=4/17
把上述概率代入公式(1),就可以算出MI。
三、计算标准化互信息NMI(Normalized Mutual information)
标准化互信息,即用熵做分母将MI值调整到0与1之间。一个比较多见的实现是下面所示:
![]()
H(X)和H(Y)分别为X和Y的熵,H(X)计算公式如下,公式中log的底b=2。
![]()
例如,H(X) = -p(1)*log2(p(1)) - -p(2)*log2(p(2)) -p(3)*log2(p(3))。
四、计算标准互信息的MATLAB程序
function MIhat = nmi( A, B ) %NMI Normalized mutual information % http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mutual_information % http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/htmledition/evaluation-of-clustering-1.html % Author: http://www.cnblogs.com/ziqiao/ [2011/12/13] if length( A ) ~= length( B) error('length( A ) must == length( B)'); end total = length(A); A_ids = unique(A); B_ids = unique(B); % Mutual information MI = 0; for idA = A_ids for idB = B_ids idAOccur = find( A == idA ); idBOccur = find( B == idB ); idABOccur = intersect(idAOccur,idBOccur); px = length(idAOccur)/total; py = length(idBOccur)/total; pxy = length(idABOccur)/total; MI = MI + pxy*log2(pxy/(px*py)+eps); % eps : the smallest positive number end end % Normalized Mutual information Hx = 0; % Entropies for idA = A_ids idAOccurCount = length( find( A == idA ) ); Hx = Hx - (idAOccurCount/total) * log2(idAOccurCount/total + eps); end Hy = 0; % Entropies for idB = B_ids idBOccurCount = length( find( B == idB ) ); Hy = Hy - (idBOccurCount/total) * log2(idBOccurCount/total + eps); end MIhat = 2 * MI / (Hx+Hy); end % Example : % (http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/htmledition/evaluation-of-clustering-1.html) % A = [1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3]; % B = [1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 1 1 3 3 3]; % nmi(A,B)% ans = 0.3646
为了节省运行时间,将for循环用矩阵运算代替,1百万的数据量运行 1.795723second,上面的方法运行3.491053 second; 但是这种方法太占内存空间, 五百万时,利用matlab2011版本的内存设置就显示Out of memory了。
版本一:
function MIhat = nmi( A, B ) %NMI Normalized mutual information % http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mutual_information % http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/htmledition/evaluation-of-clustering-1.html % Author: http://www.cnblogs.com/ziqiao/ [2011/12/15] if length( A ) ~= length( B) error('length( A ) must == length( B)'); end total = length(A); A_ids = unique(A); A_class = length(A_ids); B_ids = unique(B); B_class = length(B_ids); % Mutual information idAOccur = double (repmat( A, A_class, 1) == repmat( A_ids', 1, total )); idBOccur = double (repmat( B, B_class, 1) == repmat( B_ids', 1, total )); idABOccur = idAOccur * idBOccur'; Px = sum(idAOccur') / total; Py = sum(idBOccur') / total; Pxy = idABOccur / total; MImatrix = Pxy .* log2(Pxy ./(Px' * Py)+eps); MI = sum(MImatrix(:)) % Entropies Hx = -sum(Px .* log2(Px + eps),2); Hy = -sum(Py .* log2(Py + eps),2); %Normalized Mutual information MIhat = 2 * MI / (Hx+Hy); % MIhat = MI / sqrt(Hx*Hy); another version of NMIend % Example : % (http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/htmledition/evaluation-of-clustering-1.html) % A = [1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3]; % B = [1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 1 1 3 3 3]; % nmi(A,B) % ans = 0.3646
版本二:
A = [1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3]; B = [1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 1 1 3 3 3]; if length( A ) ~= length( B) error('length( A ) must == length( B)'); end total = length(A); %17 A_ids = unique(A); %[1,2,3] A_class = length(A_ids); % 3 B_ids = unique(B); %[1,2,3] B_class = length(B_ids); %3 % Mutual information idAOccur = double (repmat( A, A_class, 1) == repmat( A_ids', 1, total )); idBOccur = double (repmat( B, B_class, 1) == repmat( B_ids', 1, total )); idABOccur = idAOccur * idBOccur'; Px = sum(idAOccur') / total; Py = sum(idBOccur') / total; Pxy = idABOccur / total; miMatrix = Pxy .* log2(Pxy ./(Px' * Py)+eps); %加上一个很小的数,log2的真数部分不能<=0. mi = sum(miMatrix(:)); % Entropies(熵) Hx = -sum(Px .* log2(Px + eps),2); Hy = -sum(Py .* log2(Py + eps),2); %Normalized Mutual information nmi= 2 * mi / (Hx+Hy) % nmi = mi / sqrt(Hx*Hy); another version of nmi