这里就不更新上一文中LSTM情感分类问题了,
它只是网络结构中函数,从而提高准确率。
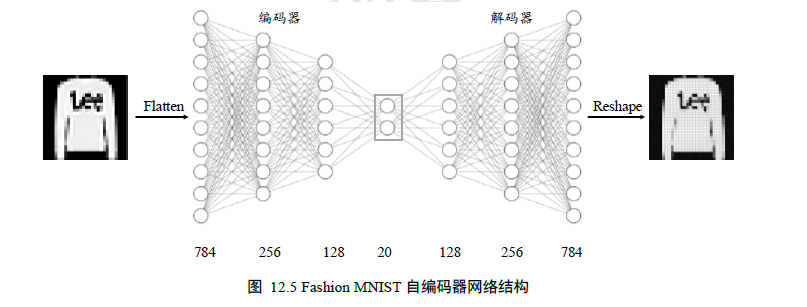
这一篇更新自编码器的图像重建处理,
网络结构如下:
代码如下:
1 import os 2 import numpy as np 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow import keras 5 from tensorflow.keras import layers, losses, optimizers, Model, Sequential 6 from PIL import Image 7 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 8 9 batchsz = 128 # 批量大小 10 h_dim = 20 # 中间隐藏层维度 11 lr = 0.001 12 13 # 加载Fashion MNIST 图片数据集 14 (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() 15 print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape, tf.reduce_max(y_train), tf.reduce_min(y_train)) 16 # x_train shape: (60000, 28, 28) tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=uint8) tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=uint8) 17 print('x_test shape:', x_test.shape) # x_test shape: (10000, 28, 28) 18 19 # 归一化 20 x_train, x_test = x_train.astype(np.float32) / 255., x_test.astype(np.float32) / 255. 21 # 只需要通过图片数据即可构建数据集对象,不需要标签 22 train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_train) 23 train_db = train_db.shuffle(10000).batch(batchsz) 24 # 构建测试集对象 25 test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_test) 26 test_db = test_db.shuffle(1000).batch(batchsz) 27 28 29 class AE(Model): 30 # 自编码器模型类,包含了Encoder 和Decoder2 个子网络 31 def __init__(self): 32 super(AE, self).__init__() 33 # 创建Encoders 网络 34 self.encoder = Sequential([ 35 layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu), 36 layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), 37 layers.Dense(h_dim)]) 38 # 创建Decoders 网络 39 self.decoder = Sequential([ 40 layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), 41 layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu), 42 layers.Dense(784)]) 43 44 def call(self, inputs, training=None): 45 # 前向传播函数 46 # 编码获得隐藏向量h,[b, 784] => [b, 20] 47 h = self.encoder(inputs) 48 # 解码获得重建图片,[b, 20] => [b, 784] 49 x_hat = self.decoder(h) 50 return x_hat 51 52 53 def save_images(imgs, name): 54 # 创建280x280 大小图片阵列 55 new_im = Image.new('L', (280, 280)) 56 index = 0 57 for i in range(0, 280, 28): # 10 行图片阵列 58 for j in range(0, 280, 28): # 10 列图片阵列 59 im = imgs[index] 60 im = Image.fromarray(im, mode='L') 61 new_im.paste(im, (i, j)) # 写入对应位置 62 index += 1 63 # 保存图片阵列 64 new_im.save(name) 65 66 67 def draw(): 68 plt.figure() 69 plt.plot(train_tot_loss, 'b', label='train') 70 plt.plot(test_tot_loss, 'r', label='test') 71 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 72 plt.ylabel('ACC') 73 plt.legend() 74 plt.savefig('exam10.1_train_test_AE.png') 75 plt.show() 76 77 78 # 创建网络对象 79 model = AE() 80 # 指定输入大小 81 model.build(input_shape=(None, 784)) 82 # 打印网络信息 83 model.summary() 84 # 创建优化器,并设置学习率 85 optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=lr) 86 # 保存训练和测试过程中的误差情况 87 train_tot_loss = [] 88 test_tot_loss = [] 89 90 91 def main(): 92 for epoch in range(100): # 训练100 个Epoch 93 94 cor, tot = 0, 0 95 for step, x in enumerate(train_db): # 遍历训练集 96 # 打平,[b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] 97 x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784]) 98 # 构建梯度记录器 99 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: 100 # 前向计算获得重建的图片 101 x_rec_logits = model(x) 102 # 计算重建图片与输入之间的损失函数 103 rec_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=x, logits=x_rec_logits) 104 # 计算均值 105 rec_loss = tf.reduce_mean(rec_loss) 106 cor += rec_loss 107 tot += x.shape[0] 108 # 自动求导,包含了2 个子网络的梯度 109 grads = tape.gradient(rec_loss, model.trainable_variables) 110 # 自动更新,同时更新2 个子网络 111 optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables)) 112 if step % 100 == 0: 113 # 间隔性打印训练误差 114 print(epoch, step, float(rec_loss)) 115 train_tot_loss.append(cor / tot) 116 117 correct, total = 0, 0 118 for x in test_db: 119 x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784]) 120 out = model(x) 121 out_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=x, logits=out) 122 # 计算均值 123 loss = tf.reduce_mean(out_loss) 124 correct += loss 125 total += x.shape[0] 126 test_tot_loss.append(correct / total) 127 128 if (epoch == 0) or (epoch == 9) or (epoch == 99): 129 # 重建图像 130 # 重建图片,从测试集采样一批图片 131 x = next(iter(test_db)) 132 out_logits = model(tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])) # 打平并送入自编码器 133 x_hat = tf.sigmoid(out_logits) # 将输出转换为像素值,使用sigmoid 函数 134 # 恢复为28x28,[b, 784] => [b, 28, 28] 135 x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28]) 136 # 输入的前50 张+重建的前50 张图片合并,[b, 28, 28] => [2b, 28, 28] 137 x_concat = tf.concat([x[:50], x_hat[:50]], axis=0) 138 x_concat = x_concat.numpy() * 255. # 恢复为0~255 范围 139 x_concat = x_concat.astype(np.uint8) # 转换为整型 140 save_images(x_concat, 'exam10.1_rec_epoch_%d.png' % (epoch+1)) # 保存图片 141 142 143 if __name__ == '__main__': 144 main() 145 draw()
重建效果(Epoch=1, 10, 100):



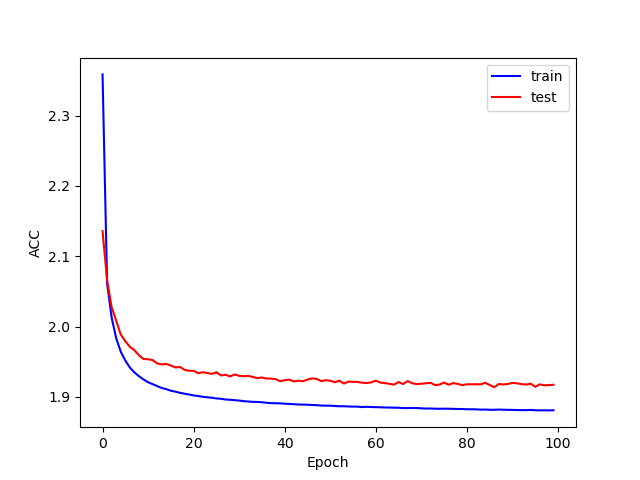
训练和测试的准确率:
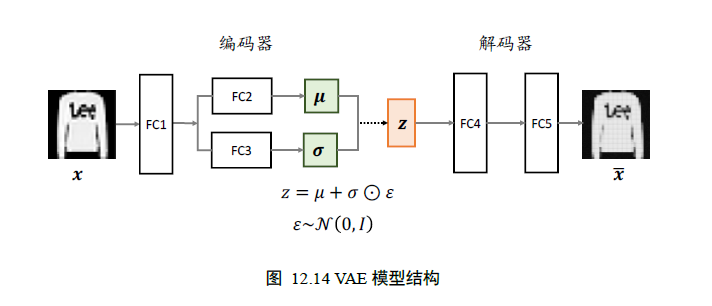
变分自编码器:
网络结构如下:
代码如下:
1 import os 2 import numpy as np 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from tensorflow import keras 5 from tensorflow.keras import layers, losses, optimizers, Model, Sequential 6 from PIL import Image 7 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 8 9 batchsz = 128 # 批量大小 10 # h_dim = 20 # 中间隐藏层维度 11 lr = 0.001 12 z_dim = 20 13 14 # 加载Fashion MNIST 图片数据集 15 (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() 16 print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape, tf.reduce_max(y_train), tf.reduce_min(y_train)) 17 # x_train shape: (60000, 28, 28) tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=uint8) tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=uint8) 18 print('x_test shape:', x_test.shape) # x_test shape: (10000, 28, 28) 19 20 # 归一化 21 x_train, x_test = x_train.astype(np.float32) / 255., x_test.astype(np.float32) / 255. 22 # 只需要通过图片数据即可构建数据集对象,不需要标签 23 train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_train) 24 train_db = train_db.shuffle(10000).batch(batchsz) 25 # 构建测试集对象 26 test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_test) 27 test_db = test_db.shuffle(1000).batch(batchsz) 28 29 30 class VAE(keras.Model): 31 # 变分自编码器 32 def __init__(self): 33 super(VAE, self).__init__() 34 # Encoder 网络 35 self.fc1 = layers.Dense(128) 36 self.fc2 = layers.Dense(z_dim) # 均值输出 37 self.fc3 = layers.Dense(z_dim) # 方差输出 38 # Decoder 网络 39 self.fc4 = layers.Dense(128) 40 self.fc5 = layers.Dense(784) 41 42 def encoder(self, x): 43 # 获得编码器的均值和方差 44 h = tf.nn.relu(self.fc1(x)) 45 # 均值向量 46 mu = self.fc2(h) 47 # 方差的log 向量 48 log_var = self.fc3(h) 49 return mu, log_var 50 51 def decoder(self, z): 52 # 根据隐藏变量z 生成图片数据 53 out = tf.nn.relu(self.fc4(z)) 54 out = self.fc5(out) 55 # 返回数据图片 786向量 56 return out 57 58 def call(self, inputs, training=None): 59 # 前向计算 60 # 编码器[b, 784] => [b, z_dim], [b, z_dim] 61 mu, log_var = self.encoder(inputs) 62 # 采样reparameterization trick 63 z = self.reparameterize(mu, log_var) 64 # 通过解码器生成 65 x_hat = self.decoder(z) 66 # 返回生成样本,及其均值与方差 67 return x_hat, mu, log_var 68 69 def reparameterize(self, mu, log_var): 70 # reparameterize 技巧,从正态分布采样epsion 71 eps = tf.random.normal(log_var.shape) 72 # 计算标准差 73 std = tf.exp(log_var) ** 0.5 74 # reparameterize 技巧 75 z = mu + std * eps 76 return z 77 78 79 def save_images(imgs, name): 80 # 创建280x280 大小图片阵列 81 new_im = Image.new('L', (280, 280)) 82 index = 0 83 for i in range(0, 280, 28): # 10 行图片阵列 84 for j in range(0, 280, 28): # 10 列图片阵列 85 im = imgs[index] 86 im = Image.fromarray(im, mode='L') 87 new_im.paste(im, (i, j)) # 写入对应位置 88 index += 1 89 # 保存图片阵列 90 new_im.save(name) 91 92 93 def draw(): 94 plt.figure() 95 plt.plot(train_tot_loss, 'b', label='train') 96 plt.plot(test_tot_loss, 'r', label='test') 97 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 98 plt.ylabel('ACC') 99 plt.legend() 100 plt.savefig('exam10.2_train_test_VAE.png') 101 plt.show() 102 103 104 # 创建网络对象 105 model = VAE() 106 # 指定输入大小 107 model.build(input_shape=(4, 784)) 108 # 打印网络信息 109 model.summary() 110 # 创建优化器,并设置学习率 111 optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=lr) 112 # 保存训练和测试过程中的误差情况 113 train_tot_loss = [] 114 test_tot_loss = [] 115 116 117 def main(): 118 for epoch in range(100): # 训练100 个Epoch 119 120 cor, tot = 0, 0 121 for step, x in enumerate(train_db): # 遍历训练集 122 # 打平,[b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] 123 x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784]) 124 # 构建梯度记录器 125 with tf.GradientTape() as tape: 126 # 前向计算 127 x_rec_logits, mu, log_var = model(x) 128 # 重建损失值计算 129 rec_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=x, logits = x_rec_logits) 130 rec_loss = tf.reduce_sum(rec_loss) / x.shape[0] 131 # 计算KL 散度 N(mu, var) VS N(0, 1) 132 # 公式参考:https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/7440/kldivergence-between - two - univariate - gaussians 133 kl_div = -0.5 * (log_var + 1 - mu ** 2 - tf.exp(log_var)) 134 kl_div = tf.reduce_sum(kl_div) / x.shape[0] 135 # 合并误差项 136 loss = rec_loss + 1. * kl_div 137 138 cor += loss 139 tot += x.shape[0] 140 # 自动求导 141 grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) 142 # 自动更新 143 optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables)) 144 if step % 100 == 0: 145 # 间隔性打印训练误差 146 print(epoch, step, 'kl div:', float(kl_div), 'rec loss:', float(rec_loss)) 147 train_tot_loss.append(cor / tot) 148 149 correct, total = 0, 0 150 for x in test_db: 151 x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784]) 152 # 前向计算 153 x_rec_logits, mu, log_var = model(x) 154 # 重建损失值计算 155 rec_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=x, logits=x_rec_logits) 156 rec_loss = tf.reduce_sum(rec_loss) / x.shape[0] 157 # 计算KL 散度 N(mu, var) VS N(0, 1) 158 kl_div = -0.5 * (log_var + 1 - mu ** 2 - tf.exp(log_var)) 159 kl_div = tf.reduce_sum(kl_div) / x.shape[0] 160 # 合并误差项 161 loss = rec_loss + 1. * kl_div 162 163 correct += loss 164 total += x.shape[0] 165 test_tot_loss.append(correct / total) 166 167 if (epoch == 0) or (epoch == 9) or (epoch == 99): 168 # 测试生成效果,从正态分布随机采样z 169 z = tf.random.normal((batchsz, z_dim)) 170 logits = model.decoder(z) # 仅通过解码器生成图片 171 x_hat = tf.sigmoid(logits) # 转换为像素范围 172 x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28]).numpy() * 255. 173 x_hat = x_hat.astype(np.uint8) 174 save_images(x_hat, 'exam10.2_epoch_%d_sampled.png' % (epoch+1)) # 保存生成图片 175 176 # 重建图片,从测试集采样图片 177 x = next(iter(test_db)) 178 logits, _, _ = model(tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])) # 打平并送入自编码器 179 x_hat = tf.sigmoid(logits) # 将输出转换为像素值 180 # 恢复为28x28,[b, 784] => [b, 28, 28] 181 x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28]) 182 # 输入的前50 张+重建的前50 张图片合并,[b, 28, 28] => [2b, 28, 28] 183 x_concat = tf.concat([x[:50], x_hat[:50]], axis=0) 184 x_concat = x_concat.numpy() * 255. # 恢复为0~255 范围 185 x_concat = x_concat.astype(np.uint8) 186 save_images(x_concat, 'exam10.2_epoch_%d_rec.png' % (epoch+1)) # 保存重建图片 187 188 189 if __name__ == '__main__': 190 main() 191 draw()
图像重建(Epoch=1, 10, 100):



图像生成(Epoch=1, 10, 100):



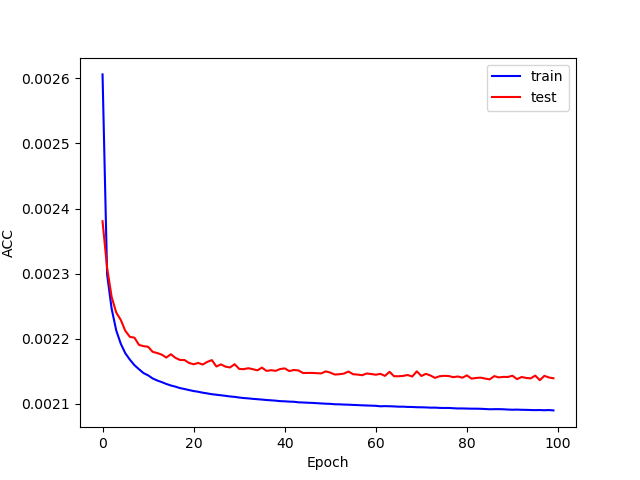
误差情况: