示例代码:示例代码_for_Csharp稳固基础:传统遍历与迭代器 (下载)
Hello,Coders。我们除了天天的码 if…else…之外,还会不断的码出foreach。我今天要说的是:传统遍历需实现的接口及我们还有一种更简洁优雅的方式实现多种迭代器。
传统遍历
传统的遍历即通过让集合类实现IEnumerable、IEnumerator或IEnumerable<T>、IEnumerator<T>接口来支持遍历。
public interface IEnumerable // 可枚举接口
{
IEnumeratorGetEnumerator();
}
public interface IEnumerator // 枚举器接口
{
object Current { get; }
boolMoveNext();
void Reset();
}
1. 分析:
1) 从这两个接口的用词选择上,也可以看出其不同:
a) IEnumerable是一个声明式的接口,声明实现该接口的类是可枚举。
b) IEnumerator是一个实现式的接口,IEnumerator对象说明如何实现枚举器。
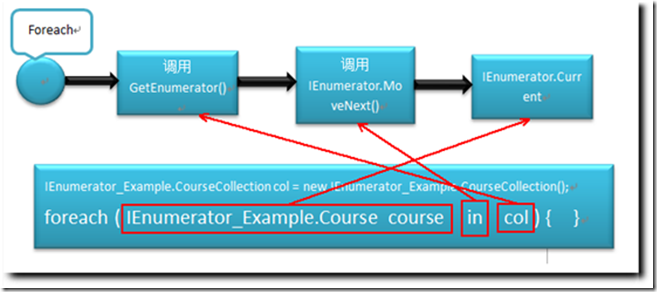
2) Foreach语句隐式调用集合的无参GetEnumerator方法(不论集合是否有实现IEnumerable接口,但只要有无参GetEnumerator方法并返回IEnumerator就可遍历)。
3) 集合类为什么不直接实现IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口?
这样是为了提高并发性。Eg:一个遍历机制只有一个Current,一旦并发就会出错。然而“将遍历机制与集合分离开来”如果要实现同时遍历同一个集合,只需由集合IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() 返回一个新的包含遍历机制(IEnumerator)的类实例即可。
1. 调用过程
插播一段:由foreach执行过程可知其迭代器是延迟计算的。
因为迭代的主体在MoveNext() 中实现,foreach中每次遍历执行到 in 的时候才会调用MoveNext() ,所以其迭代器耗时的指令是延迟计算的。
延迟计算(Lazy evaluation):来源自函数式编程,在函数式编程里,将函数作为参数来传递,传递过程中不会执行函数内部耗时的计算,直到需要这个计算结果的时候才调用,这样就可以因为避免一些不必要的计算而改进性能。 (另外还有linq、DataReader等也运用了延迟计算的思想)
1. 具体实现示例
/// <summary>
/// 课程
/// </summary>
public class Course
{
public Course(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
private String name = string.Empty;
public String Name
{
get { return name; }
}
}
public class CourseCollection : IEnumerable<Course>
{
public CourseCollection()
{
arr_Course = new Course[]
{
new Course("语文"),
new Course("数学"),
new Course("英语"),
new Course("体育")
};
}
private Course[] arr_Course;
public Course this[int index]
{
get { return arr_Course[index]; }
}
public int Count
{
get { return arr_Course.Length; }
}
public IEnumerator<Course> GetEnumerator()
{
return new CourseEnumerator(this);
}
#region 实现 IEnumerable<T>
private sealed class CourseEnumerator : IEnumerator<Course>
{
private readonly CourseCollection courseCollection;
private int index;
internal CourseEnumerator(CourseCollection courseCollection)
{
this.courseCollection = courseCollection;
index = -1;
}
public Course Current
{
get { return courseCollection[index]; }
}
bool IEnumerator.MoveNext()
{
index++;
return (index < courseCollection.Count);
}
void IEnumerator.Reset()
{
index = -1;
}
……
}
#endregion
……
}
有了对“传统遍历”实现方式的理解才能快速明白下一节“迭代器”的实现原理。要知道绝大部分最新的概念其实都可以用最简单的那些概念组合而成。而只有对基本概念理解,才能看清那些复杂概念的实质。
迭代器(iterator)
迭代器是 C# 2.0 中的新功能。它使类或结构支持foreach迭代,而不必“显示”实现IEnumerable或IEnumerator接口。只需要简单的使用 yield 关键字,由 JIT 编译器帮我们编译成实现 IEnumerable或IEnumerator 接口的对象(即:本质还是传统遍历,只是写法上非常简洁)。
对于本节提到的编译后的代码,可通过 Reflector.exe , ILSpy.exe 进行查看。
1. 分析
1) yield 语句只能出现在 iterator 块(迭代块)中,该块只能用作方法、运算符或get访问器的主体实现。这类方法、运算符或访问器的“主体”受以下约束的控制:
a) 不允许不安全块。
b) 方法、运算符或访问器的参数不能是 ref 或 out。
2) 迭代器代码使用 yield return 语句依次返回每个元素。yield break 将终止迭代。
a) yield return 的时候会保存当前位置(状态机)并把控制权从迭代器中交给调用的程序,做必要的返回值处理,下一次进入迭代器将从之前保存的位置处开始执行直到迭代结束或调用yield break。
b) yield break 就是控制权交给调用程序就不回来了从而终止迭代。
3) yield return 语句不能放在 try-catch 块中。但可放在后跟 finally 块的 try 块中。
4) yield break 语句可放在 try 块或 catch 块中,但不能放在 finally 块中。
5) yield 语句不能出现在匿名方法中。
6) 迭代器必须返回相同类型的值,因为最后输出为IEnumerator.Current是单一类型。(见下面示例)
7) 在同一个迭代器中可以使用多个 yield 语句。(见下面示例)
8) 自定义迭代器:迭代器可以自定义名称、可以带参数,但在foreach中需要显示去调用自定义的迭代器。(见下面示例)
9) 迭代器的返回类型必须为IEnumerator、IEnumerator<T>或IEnumerable、IEnumerable<T>。(见下面示例)
2. 迭代器的具体实现
1) 返回类型为IEnumerator、IEnumerator<T>
返回此类型的迭代器方法必须满足:
a) 必须有GetEnumerator且不带参数;
b) 必须是public公共成员;
见示例代码,我们将CourseCollection集合对象的IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() 方法实现如下:
// 注意:返回什么,泛型就为什么类型
public IEnumerator<String> GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr_Course.Length; i++)
{
Course course = arr_Course[i];
yield return "选修:" + course.Name;
// 两个 yield return
yield return Environment.NewLine;
// 每个yield return 保存当前位置并返回值,下一次进入迭代器时将从之前保存的位置处开始执行
if (String.Compare(course.Name, "体育") == 0)
yield break;
List<string> strs=new List<string>{"435435","546546"};
foreach (string s in strs)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
}
}
经过 JIT 编译后,会自动生成一个实现了 IEnumerator<String> 接口的对象。具体代码可通过 Reflector 工具查看,下面展示其中的MoveNext() 代码:
private bool MoveNext()
{
switch (this.<>1__state)
{
case 0:
this.<>1__state = -1;
this.<i>5__2 = 0;
while (this.<i>5__2 < this.<>4__this.arr_Course.Length)
{
this.<course>5__3 = this.<>4__this.arr_Course[this.<i>5__2];
this.<>2__current = "选修:" + this.<course>5__3.Name;
this.<>1__state = 1;
return true;
Label_007C:
this.<>1__state = -1;
this.<>2__current = Environment.NewLine;
this.<>1__state = 2;
return true;
Label_009C:
this.<>1__state = -1;
if (string.Compare(this.<course>5__3.Name, "体育") == 0)
{
break;
}
this.<>g__initLocal0 = new List<string>();
this.<>g__initLocal0.Add("435435");
this.<>g__initLocal0.Add("546546");
this.<strs>5__4 = this.<>g__initLocal0;
foreach (string s in this.<strs>5__4)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
this.<i>5__2++;
}
break;
case 1:
goto Label_007C;
case 2:
goto Label_009C;
}
return false;
}
通过代码,我们可以知道:
a) 同一个迭代器中有多少个 yield return语句,while 循环中就有多少个 return true 。
b) yield retuen结束本次循环,yield break结束整个循环。输出数据的顺序通过生成类中的一个state状态字段做为 switch 标识来决定要输出第几个 yield return 。yield return在每个case里面改变state内部字段,使正确执行完多个return返回数据,并最后通过return true来结束本次MoveNext()。而yield break语句直接生成break并重置state状态字段为switch中没有的值而跳出switch语句,通过执行最后的return false来结束整个循环。
c) 注意:yield return 后面的 List<string>代码段也会被执行。
2) 返回类型为IEnumerable、IEnumerable<T>
返回此类型的迭代器必须满足:
a) 必须可以在foreach语句中被调用(访问权限);
返回此类型的迭代器通常用于实现自定义迭代器,即:迭代器可以自定义名称、可以带参数。Eg:(升序和降序)
public IEnumerable<String> GetEnumerable_ASC()
{
return this;
}
public IEnumerable<String> GetEnumerable_DESC()
{
for (inti = arr_Course.Length - 1; i>= 0; i--)
{
Course course = arr_Course[i];
yield return "选修:" +course.Name;
yield return Environment.NewLine;
}
}
需如下进行迭代器调用:
yield_Example.CourseCollection col2 = new yield_Example.CourseCollection();
foreach (String str in col2.GetEnumerable_ASC()){ // col2.GetEnumerable_ASC()}
foreach (String str in col2.GetEnumerable_DESC()){//col2.GetEnumerable_DESC()}
经过 JIT 编译后,会自动生成一个直接实现IEnumerator<String>和IEnumerator<String>接口的对象,其GetEnumerator() 方法返回自己this(因为本身实现了IEnumerator接口)。
这是因为在不同foreach遍历中所访问的由编译器自动生成的迭代器具有其自己独立的状态,所以迭代器之间互不影响,不存在并发的问题。
OVER,谢谢观看。(如有缺漏或错误请留言,谢谢!!!)