A. Little Artem
签到。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/8 22:36:43
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 100 + 5;
int a[N][N];
void run() {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
a[i][j] = ((i + j) & 1);
if(n * m % 2 == 0) {
if((n + m) & 1) a[n][m] = 0;
else {
a[n][m] ^= 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
a[i][j] ^= 1;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cout << (a[i][j] ? "W" : "B");
}cout << '
';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
B. Kind Anton
签到。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/8 22:50:49
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n;
int a[N], b[N];
void run() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
bool f1 = false, f2 = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(a[i] != b[i]) {
if(a[i] < b[i]) {
if(!f1) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
} else {
if(!f2) {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
}
}
if(a[i] == 1) f1 = true;
if(a[i] == -1) f2 = true;
}
cout << "YES" << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) run();
return 0;
}
C. Eugene and an array
题意:
给定一个序列,询问该序列含有多少个连续子区间,满足该子区间中不含有任意一段其和为(0)。
思路:
得到序列(a)的前缀和数组(sum),那么区间([l,r])和为(0)等价于(sum_{l-1}=sum_r)。
那么从后往前枚举区间左端点,维护最远的区间右端点计算答案即可。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/8 22:58:55
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n;
int a[N];
ll sum[N];
void run() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i], sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
map <ll, int> mp;
ll ans = 0;
int rb = n + 1;
for(int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if(mp.find(sum[i]) != mp.end()) {
int l = min(rb, mp[sum[i]]) - i - 1;
ans += l;
rb = min(rb, mp[sum[i]]);
} else ans += rb - i - 1;
mp[sum[i]] = i;
}
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
D. Challenges in school №41
题意:
(n)个人占成一列,每个人都有一个朝向,若两个人面面相对则可以在一次操作中他们两个人朝向进行翻转。
一次操作中可以选择多对满足条件的人进行翻转。
问是否能在恰好(k)次操作使得不存在两个人面面相对。
思路:
- 抽象成给出一个(01)串,若遇到(10)则交换这两个数。
- 容易发现操作过程类似于冒泡排序,因此总的交换次数不会超过(n^2)。
- 因此暴力交换即可,用一个(vector)存储操作最少的情况下每次操作最多交换的对数。
- 之后贪心来凑(k)即可。
细节见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/9 0:12:01
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 3000 + 5;
int n, k;
char s[N];
vector <vector<int>> v;
void run() {
cin >> n >> k;
cin >> (s + 1);
int Min = 0, Max = 0;
while(1) {
vector <int> t;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if(s[i] == 'R' && s[i + 1] == 'L') {
t.push_back(i);
swap(s[i], s[i + 1]);
++i;
}
}
if(sz(t) == 0) break;
++Min, Max += sz(t);
v.push_back(t);
}
if(k >= Min && k <= Max) {
int now = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < sz(v); i++) {
if(now + sz(v[i]) + sz(v) - i - 1 <= k) {
now += sz(v[i]);
for(auto it : v[i]) {
cout << 1 << ' ' << it << '
';
}
} else {
int h = k - sz(v) + i + 1 - now;
if(h > 1) for(int j = 0; j < h - 1; j++) {
cout << 1 << ' ' << v[i][j] << '
';
++now;
}
++now;
cout << sz(v[i]) - h + 1 << ' ';
for(int j = h - 1; j < sz(v[i]); j++) {
cout << v[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '
';
}
}
} else {
cout << -1 << '
';
return;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
E. Road to 1600
题意:
(n*n)棋盘上有两种棋子,每种棋子行动路径分别如下:
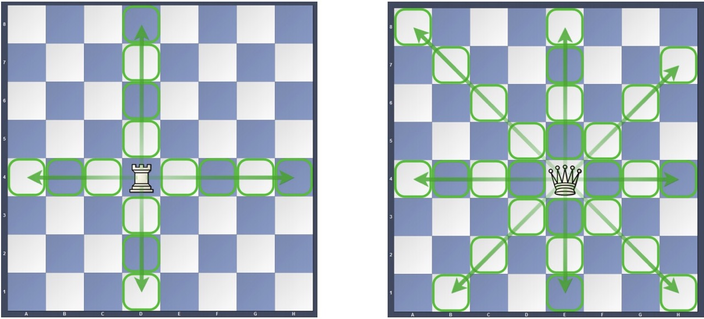
现在每个格子上有一个(1)~(n*n)大小的权值,两个棋子分别从(1)出发,按照以下规则进行行走:
- 到达当前行动路径上权值最小且没有被访问过的格子,将其标记访问;
- 若当前行动路径上格子都被访问,那么花费(1)的代价到达一个权值最小且未被访问过的格子;
- 若所有格子已被访问,那么停止操作。
现在要求构造一种权值方案,使得第一种棋子消耗的代价小于第二种棋子所消耗的代价。
思路:
这个题乍一看神仙构造题,对于(n)较大的情况,两种棋子的行走规律完全无法琢磨。但是注意到两种棋子存在重合的路径,也就是说两个棋子在横竖方向可以按照相同的路径行走。
(n)较小的情况我们可以手动进行构造,易发现(n=1,2)时不存在合法方案,(n=3)的情况可能会存在合法方案。这时我们可以暴力打表/手动构造出合法的方案。
(n>3)呢?此时依旧可以暴力打表,但这个题直接暴力计算时间复杂度不能承受。
注意到刚才提到的性质:两个棋子在水平或者垂直方向可以走相同的路径。
那么对于(n>3)的情况,我们只需要两个棋子都从外圈往里绕,那么问题即可转化为(n=3)的情况了。
总结一下:1.构造出小数据的合法解;2.利用性质将规模缩小,转化为较易求解的问题。
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/9 16:41:05
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 500 + 5;
int now, n;
int a[N][N];
void work() {
int t = n;
int x, y;
if((t & 1) == 0) {
x = t, y = 1;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(++y > t) break;
}
x = t - 1, y = t;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(--x == 0) break;
}
--t;
}
while(t > 3) {
x = 1, y = t;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(++x > t) break;
}
x = t, y = t - 1;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(--y == 0) break;
}
--t;
x = t, y = 1;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(++y > t) break;
}
x = t - 1, y = t;
while(1) {
a[x][y] = ++now;
if(--x == 0) break;
}
--t;
}
}
void run() {
cin >> n;
if(n <= 2) {
cout << -1 << '
';
return;
}
work();
a[1][3] = ++now, a[1][1] = ++now, a[1][2] = ++now;
a[2][2] = ++now, a[2][1] = ++now, a[3][2] = ++now;
a[3][3] = ++now, a[2][3] = ++now, a[3][1] = ++now;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cout << a[i][j] << "
"[j == n];
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
F. Kate and imperfection
题意:
给定一个(1...n)的集合。
现在回答对于所有(size=k,kgeq 2)的集合,(max{gcd(a_i,a_j),i
ot ={j},a_i,a_jin subset_k})为多少。
思路:
有两种思路来思考这个题,一个是正向考虑,另一个是反向考虑。
先考虑正向求解:
- 从小到达枚举答案,考虑贪心加入一些数使得答案不超过枚举值。
- 当(ans=1)时,显然我们需要加入(1)和所有的质数;
- 当(ans=x)时,我们只需要考虑加入(xcdot p_j,p_jleq p_i),其中(p_i)为(x)的最小质因子。
简要证明如下:
不妨设我们加入的(p_j>p_i),那么加入的数(s=xcdot p_j),考虑我们枚举答案到(frac{x}{p_i})时:
- 假设我们此时加入(s)能使得答案更优,那么之前我们加入(t=frac{x}{p_i}cdot p_j)也能使得答案更优,然而(gcd(s,t)>x),所以假设不成立。
以上情况有特例,即当(x=1)时,(x)不存在最小质因子,此时我们贪心选取所有素数即可。
证毕。
那么以上做法就是对的了。其实根据以上做法我们可以进一步归纳,每个数被选入集合中的答案即为(frac{x}{p_i})。所以最后按照这个排个序输出即可。
代码如下:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/9 15:53:38
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int ans[N];
bool vis[N];
int n;
void run() {
cin >> n;
ans[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) {
ans[i] = 1;
for(ll j = 1ll * i * i; j <= n; j += i) {
if(!vis[j]) ans[j] = j / i;
vis[j] = true;
}
}
}
sort(ans + 1, ans + n + 1);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) cout << ans[i] << "
"[i == n];
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
反向考虑的话即是按照答案从大到小考虑:
- 若(ans=n),易求得此时最大(gcd=x);
- 之后会依次删除一个数,那么我们每次肯定会删除(x)的倍数,直至留下一个(x)的倍数,那么答案就会减小。
这种思考起来较为简单,但是代码写起来会麻烦一些。