1、学习jdk源码,从以下几个方面入手:
类定义(继承,实现接口等)
全局变量
方法
内部类
2、hashCode
private int hash;
public int hashCode() { int h = hash; if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) { char val[] = value; for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) { h = 31 * h + val[i]; } hash = h; } return h; }
为什么是31?
(1)计算hashcode值一般选质数
(2)太小的数计算的hashcode值冲突率高,太大的数乘法计算会溢出int范围
(3)有以上两点和实验得 出:31, 33, 37, 39 ,41 作为乘子比较合适
(4)这几个数字中31的乘法运算可以被优化:31 * i == (i << 5) - i
3、构造两种:
(1)直接将otherStr引用给this
(2)数组copy
4、String对“+”的支持
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1="a" + "b";// 编译之后 String s1 = "ab"; String s = "a"; String s2= s+ "b";// 编译之后 String s = (new StringBuilder(String.valueOf(s))).append("b").toString(); }
5、jdk1.7修改subString()
// jdk1.6 String(int offset, int count, char value[]) { this.value = value; this.offset = offset; this.count = count; } // subString方法部分 return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == count)) ? this : new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex, value); // jdk1.7 public String(char value[], int offset, int count) { . . . this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count); } // subString方法部分 return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
jdk1.6的substring:
(1)直接将引用赋值,性能好,共享内部数组节约内存
(2)由于原String的value是private final,可以保证安全性
(3)可能导致内存泄漏
String aLongString = "...a very long string..."; // 很长 String aPart = data.substring(2, 4); return aPart;
假设从一个很长的字符串中提取一小段内容:
当aLongString不再使用,aPart继续使用时,
aLongString被回收,aLongString的value还被aPart的value引用,不能被回收
导致内存泄漏
6、编程技巧学习
/** * 先比较是否同一个对象 * 先比较长度 * 虽然代码写的内容比较多,但是可以很大程度上提高比较的效率 */ public boolean equals(Object anObject) { if (this == anObject) {// 先比较是否同一个对象 return true; } if (anObject instanceof String) { String anotherString = (String)anObject; int n = value.length; if (n == anotherString.value.length) {// 先比较长度 char v1[] = value; char v2[] = anotherString.value; int i = 0; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i] != v2[i]) return false; i++; } return true; } } return false; }
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount, char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount, int fromIndex) { if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) { return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1); } if (fromIndex < 0) { fromIndex = 0; } if (targetCount == 0) { return fromIndex; } char first = target[targetOffset]; int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount); for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) { /* Look for first character. 先比较第一个字符*/ if (source[i] != first) { while (++i <= max && source[i] != first); } /* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */ if (i <= max) { int j = i + 1; int end = j + targetCount - 1; for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j] == target[k]; j++, k++); if (j == end) { /* Found whole string. */ return i - sourceOffset; } } } return -1; }
/** * 三目运算符代替多个if */ public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) { return (this == anotherString) ? true : (anotherString != null) && (anotherString.value.length == value.length) && regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length); }
7、intern()
(1)String s = new String("abc");创建个几个对象
类加载时创建"abc"放入常量池 第一个
执行代码时new String() 第二个
(2)String存入常量池方式:
一,直接使用双引号声明出来的String对象,在类加载时会直接存储在常量池中。
二,如果不是用双引号声明的String对象,可以使用String提供的intern方法。
intern 方法:
如果常量池中存在当前字符串, 就会直接返回当前字符串。 如果常量池中没有此字符串, 会将此字符串放入常量池中后,再返回。
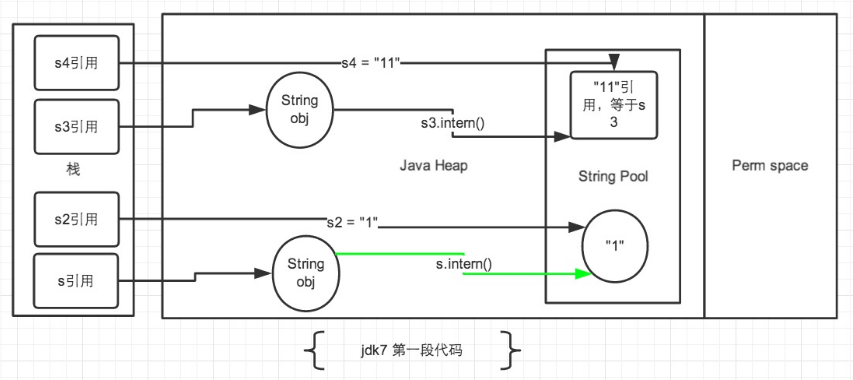
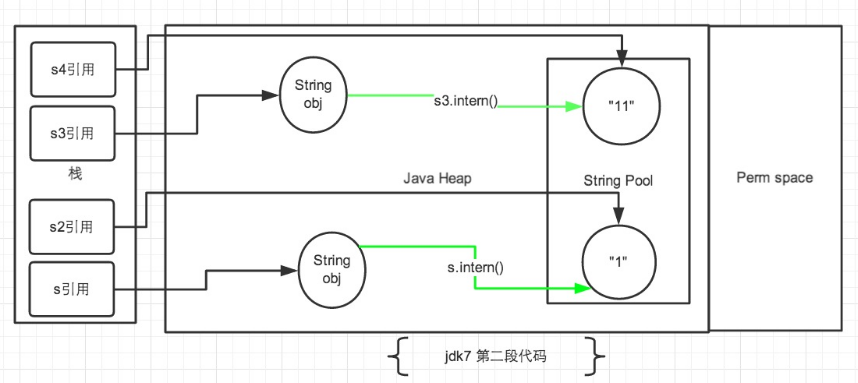
(3)jdk6 和 jdk7 下 intern 的区别
在 JDK1.2 ~ JDK6 的实现中,HotSpot 使用永久代实现方法区
JDK7+ 移除永久代 字符串常量和类引用被移动到 Java Heap中
jdk6 intern:如果常量池中存在当前字符串, 就会直接返回当前字符串。 如果常量池中没有此字符串, 会将此字符串复制一份到方法区,放入方法区中常量池,再返回。
jdk7 intern:如果常量池中存在当前字符串, 就会直接返回当前字符串。 如果常量池中没有此字符串, 会将此字符串的引用存储一份,放入堆中常量池,再返回。
String s4 = "11"; // 编译时不处理,运行到这行代码时将“11”在常量池中创建(运行时,第一次遇到字面才将其在常量池中创建)
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) { String s = new String("1"); s.intern(); String s2 = "1"; System.out.println(s == s2);// jdk1.6-false jdk1.7-false String s3 = new String("1") + new String("1"); s3.intern(); String s4 = "11"; System.out.println(s3 == s4);// jdk1.6-false jdk1.7-true } public static void main(String[] args) { String s = new String("1"); String s2 = "1"; s.intern(); System.out.println(s == s2);// jdk1.6-false jdk1.7-false String s3 = new String("1") + new String("1"); String s4 = "11"; s3.intern(); System.out.println(s3 == s4);// jdk1.6-false jdk1.7-false }
不再过多解释: (注:图中绿色线条代表 string 对象的内容指向。 黑色线条代表地址指向)

(4)应用举例:
static final int MAX = 1000 * 10000; static final String[] arr = new String[MAX]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Integer[] DB_DATA = new Integer[10]; Random random = new Random(10 * 10000); for (int i = 0; i < DB_DATA.length; i++) { DB_DATA[i] = random.nextInt(); } long t = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { arr[i] = new String(String.valueOf(DB_DATA[i % DB_DATA.length])).intern(); } System.out.println((System.currentTimeMillis() - t) + "ms"); System.gc(); }
8、private final char[] value;final--->String的长度是不能改变的
(1)常量池高效,常量池里String对象改变,引用受影响
(2)安全,不可变,只能读不能写,保证线程安全
参考资料:
1、《成神之路-基础篇》Java基础知识——String相关