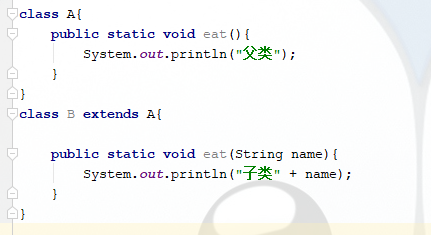
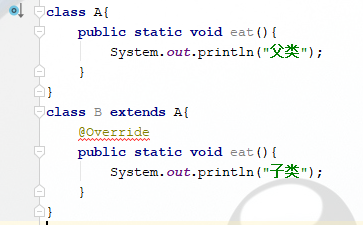
1、以下给出代码运行后的结果是? C
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] refToArray = { 10, 11 };
int var = 1;
refToArray[var - 1] = var = 2;
System.out.println(refToArray[0] + " " + refToArray[1]);
}
}
A、编译失败
B、编译通过,但运行时提示异常
C、2 11
D、10 2
连等的那一行可以换一种形式来表示:refToArray[var - 1] = (var = 2); 所以先把2赋值给var,然后再把var赋值给refToArray[var - 1],所以输出的值为2 11
16、以下代码的执行结果是: D
public class Example { x:被模数 y:模数
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte x = -64;
byte y = -6;
System.out.println(x / y + " " + x % y);
}
}
A、编译失败
B、运行时抛出异常
C、10 4
D、10 -4
//取模运算结果的符号始终和被模数的符号一致 x:被模数 y:模数
17、下列代码执行后的结果是? D
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
double x = 64.0;
double y = 0.0;
System.out.println(x % y);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
}
}
}
A、编译失败
B、输出Exception
C、输出Infinity
D、输出NaN
如果是int 0取模会抛出异常,但是对double类型的0取模则会输出NaN
18、下列代码执行后的结果是?D
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
double x = 64.0;
double y = 0.0;
System.out.println(x % y == x % y);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
}
}
}
A、编译失败
B、运行时抛出异常
C、打印输出true
D、打印输出false
所有的NaN都是不相等的, 检查是否是NaN可以用Double.isNaN(变量)来判断 返回值是boolean
19、下列代码执行后的结果是? D
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println(Float.NaN == Float.NaN);
System.out.println(Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY==Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
}
}
}
A、输出+G20:J20false false
B、输出Exception
C、输出true true
D、输出false true
// NaN任何时候都是不等的 INFINITY是相等的,可以正常的比较
21、下列代码在JDK1.5以上版本执行的结果是?
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = 10;
Integer j = 10;
System.out.println(i == j);
i = 210;
j = 210;
System.out.println(i == j);
}
}
A、抛出异常
B、输出true false
C、输出true true
D、输出false false
// 包装类中的数值如果是byte范围内的数,那么这个值会存在于常量池,所以第一个输出为true,第二个输出为false
24、有int变量i的值为16384,i>>33的结果为? C
A、运算数不符合运算符要求
B、0
C、8192
D、-1
// int类型支持的位移位数为32位,如果位移位数超过了这个位数,也不会出错,例如题中i向右位移33位,实际位移为33%32=1位,所以16384向右移一位,所得结果也就是8192
25、以下程序运行的结果是: D
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("String".replace('g', 'G') == "String".replace('g','G'));
System.out.println("String".replace('t', 't') == "String".replace('t','t'));
}
}
A、输出true true
B、输出true false
C、输出false false
D、输出false true
// g替换G返回了一个新的字符串,所以两个新字符串的地址不同, t替换t,字符串没有发生变化,还是之前的对象保持不变,所以为true
42、存在使i > j || i <= j不成立的数吗
存在 Double.NaN和Float.NaN满足
44、已知等差数列1,2,3,4…2n-1的前n项和为n^2,请根据题目中的信息编写简短程序计算一个整数的平方根整数部分
45、已知Java中常用的颜色表现形式类似0xFFA573B6,8个16进制代码平均分成四部分,从左到右分别表示透明度、红色、绿色、蓝色分量,请编写一个方法,将参数提供的颜色数据中红色和绿色部分互换
1、 指出下列程序运行的结果 B
public class Example{
String str=new String("good");
char[] ch={'a','b','c'};
public static void main(String args[]){
Example ex=new Example();
ex.change(ex.str,ex.ch);
System.out.print(ex.str+" and ");
for(int i=0;i<ex.ch.length;i++){
System.out.print(ex.ch[i]);
}
}
public void change(String str,char ch[]){
str="test ok";
ch[0]='g';
}
}
A、good and abc
B、good and gbc
C、test ok and abc
D、test ok and gbc
// ex.str在堆中指向常量池中的"good",作为参数传递,str接收的是ex.str指向常量池“good”的地址。str本身和成员变量中的str不是一个地址,但是局部变量str重新指向了一个新的常量池中的“test ok”,所以成员变量中的str没有被改变。但是ch[] 作为参数传递,传递的是数组对象地址,那么ch[0]='g';操作的是和成员变量ch同地址的对象,所以成员变量ch[]发生了改变
5、通过语句new Vector(5,10);创建一个Vector实例,向该Vector实例添加第6个元素会产生什么结果?(单项选择题) C
A、一个IndexOutOfBounds异常抛出
B、Vector实例增加容量至10
C、Vector实例容量增加至15
D、Vector实例容量未增加,因为当添加第5个元素时,容量已增加过
// new Vector(初始长度,每次溢出时增加长度)
8、以下代码的执行结果是: B
public class Example {
String s = "Outer";
public static void main(String[] args) {
S2 s2 = new S2();
s2.display();
}
}
class S1 {
String s = "S1";
void display() {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class S2 extends S1 {
String s = "S2";
}
A、S1
B、S2
C、null
D、Outer
// 由于S2中没有重写display()方法,所以在s2对象调用display()方法时,自动调用父类的display()方法,S1中的display()方法只能访问到S1中的s,所以输出的结果为S1。
15、现有基类中的一个方法:void method(){},请问以下哪些是子类中覆盖该方法的正确形式? A
A、void method(){}
B、int method(){return 0;}
C、void method(int i)
D、private void method()
// 方法重载必须方法名相同,参数列表不同 方法重写方法名,参数列表必须相同,返回值类型如果是基本数据类型,必须相同,如果是引用数据类型,则可以使该数据类型也可以是子类数据类型
15、关于重载和覆盖,以下说法错误的是 C
A、重载方法的返回值、访问修饰符以及抛出的异常都不是重载方法判断的决定因素
B、一个静态方法既可以被重载为一个静态方法,也可以被重载为一个非静态方法
C、一个静态方法既可以被覆盖为一个静态方法,也可以被覆盖为一个非静态方法
D、覆盖的方法返回值必须和源方法返回值类型保持赋值兼容,访问权限不能小于源方法,只能抛出源方法异常或源方法异常的子类
// 静态方法可以被重载成静态方法或者非静态方法,但是静态方法不能被重写,因为静态方法的重写实质是把父类的静态方法隐藏,然后子类自定义一个和父类静态方法一致的静态方法或者非静态方法,所以不算是重写。