897 递增顺序查找树
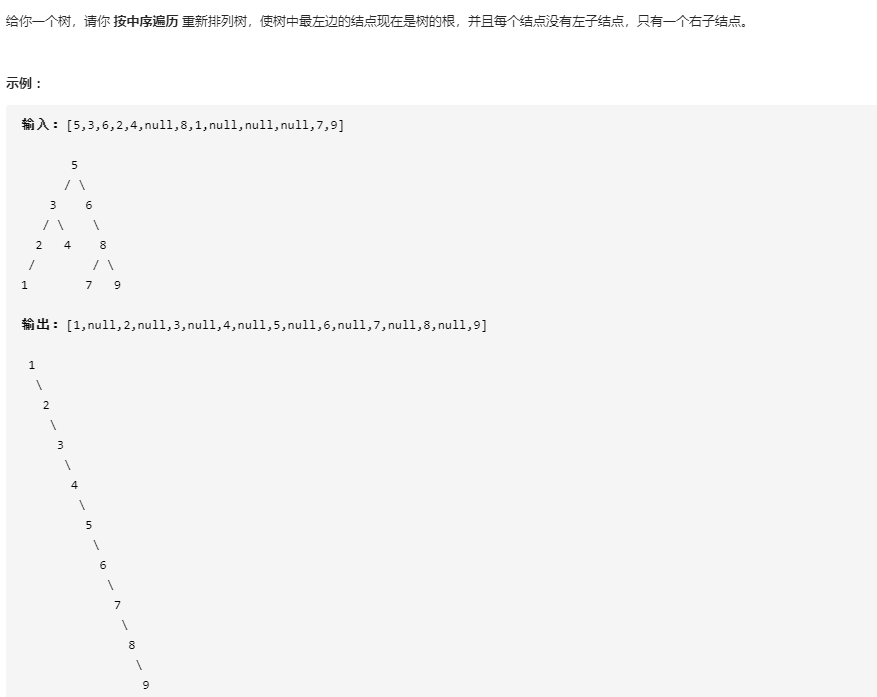
老实说这题自己都不知道怎么做出来的。。然后写完提交然后成功了。。然后看自己写的东西看了好一会儿才明白。。汗。。做的头有点晕
class Solution { public TreeNode increasingBST(TreeNode root) { if (root==null)return null; TreeNode rt = new TreeNode(); find(rt,root); return rt.right; } public static TreeNode find(TreeNode root,TreeNode current){ TreeNode trr = new TreeNode(current.val); if (current.left != null){ root = find(root, current.left); } root.right = trr; root = trr; if (current.right != null){ root = find(root,current.right); } return root; } }
JZ68 这题感觉主要的点就在于查找左右两边是否存在q或者p,如果均成功就代表该点是结果,因为如果q,p在一边的话就只有一个会返回成功

class Solution { TreeNode result; public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { find(root,p,q); return result; } public boolean find(TreeNode node,TreeNode p, TreeNode q){ if (node == null)return false; boolean left = find(node.left, p, q); boolean right = find(node.right, p, q); if ( (left&&right) || ((node.val == p.val || node.val == q.val)&&(left||right)) ){ result = node; } return left || right || ((node.val == p.val || node.val == q.val)); } }
JZ17 这题和897是同一个题,但是要求不能使用额外的存储空间,解法应该是如下
class Solution { TreeNode treeNode ; TreeNode current; public TreeNode convertBiNode(TreeNode root) { if (root==null)return null; find(root); return treeNode; } public void find(TreeNode node){ if (node == null)return; find(node.left); //处理当前 if (current == null){ treeNode = node; current = treeNode; }else { current.right = node; current = current.right; } current.left = null; find(node.right); } }
95 不同的二叉搜索树

这题的关键在于理解二叉搜索树任何一个节点其左边须小于当前节点,右边大于当前节点。对应的数组中的话就是任何一个元素其左边的所有元素都是其左子树的节点,右边的都是其右子树的节点。所以当前元素代表的节点i的node的所有情况是 List(node) = List(node(left ~ i-1))×List(node(i+1 ~ right)) 所以递归遍历left-righr即可解决此题 。这儿注意当递归到left小于right的时候需要 添加一个null,目的是为了获取到边界节点
public static List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) { List<TreeNode> treeNodes = generateTrees(0, n); return treeNodes; } public static List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int left,int right){ List<TreeNode> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (left>right){ result.add(null); return result; } for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) { List<TreeNode> leftNodes = generateTrees(left, i - 1); List<TreeNode> rightNodes = generateTrees(i+1, right ); for (TreeNode leftNode : leftNodes) { for (TreeNode rightNode : rightNodes) { TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(i); treeNode.left = leftNode; treeNode.right = rightNode; result.add(treeNode); } } } return result; }
96 和上题一模一样

除了上题的解法外,根据这种求第N个输入的解应该是可以考虑是否可以用动态规划来做。涉及到动态规划感觉自己基本稳跪,所以最后还是看了下官方解析。这个题的递推关键在于
1.是每个元素为根节点的所有存在可能是左边的子节点情况存在数量×右边子节点情况存在数量 这儿注意 数量一样数字所能组成的可能情况是一致的 比如 123 ,234,345,589 都存在的情况数量是一样的
2.第N个元素所有存在情况是从1一直到第N个元素为根节点所有存在的可能之和
其实这两个规律在上题已经发现了,然后根据这个就可以找到递推式
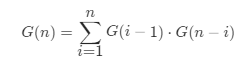
这儿注意dp[0] 设置为1的作用是 当i和j相等时 例如 1,2,3,4 遍历到以4为根节点时左边所有的情况数量需要乘1而不是0
public static int numTrees(int n) { int[] dp = new int[n+1]; dp[0] = dp[1] = 1; for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i ; j++) { dp[i] += dp[j-1]*dp[i-j]; } } return dp[n]; }
98 验证有效二叉搜索树

二叉搜索树中序遍历是递增
int min; public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { min = Integer.MIN_VALUE; return isValidBSTs(root); } public boolean isValidBSTs(TreeNode root) { if (root.left != null && !isValidBSTs(root.left)){ return false; } if (root.val<=min){ return false; }else { min = root.val; } if (root.right != null && !isValidBSTs(root.right)){ return false; } return true; }
105 通过前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树 (这题让我等非科班学生又学到了)
通过中序遍历 + 前序遍历/后序遍历可以 确定一颗唯一二叉树
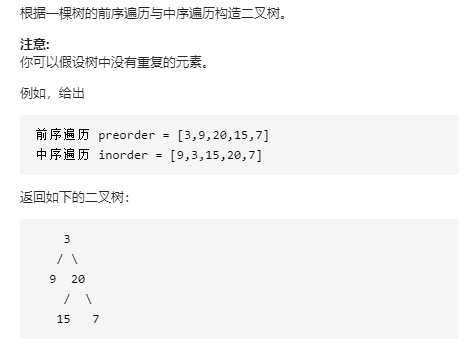
关键点应该如下的推导
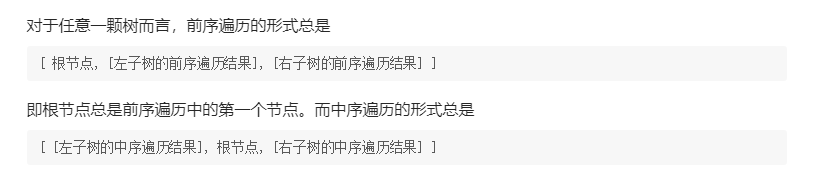
这儿注意两个点
- 左子树和右子树不管是什么遍历方法,其数量应该是完全一致的
- 前序遍历的第一个节点为根节点,同理后续遍历的最后一个节点为根节点
根据这两个性质就可以递归的进行构建,注意递归的边界则是 当前节点没有左右子节点,也就是 前序或者中序当前结果范围里都只有一个元素 ,例如 [9],[9] 此时前序或者中序遍历结果根节点都是9,左右子树都为空,此时再进行递归的时候计算左子树或者右子树的右范围时为0,右范围还是当前索引也就是0,而左范围按照规律应该加1,此时left>right,则可以退出,可以结合代码分析
Map<Integer,Integer> indexMap; public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { if (preorder.length == 0)return null; indexMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { indexMap.put(inorder[i],i); } TreeNode build = build(preorder, inorder, 0, preorder.length-1, 0, inorder.length-1); return build; } public TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int preLeft,int preEnd,int inLeft,int inRight){ if (preLeft > preEnd) return null; //构造当前根节点 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preLeft]); //当前根节点的左子节点为构造出的左子树的根节点 Integer index = indexMap.get(root.val); root.left = build(preorder,inorder,preLeft+1,preLeft+(index-inLeft),inLeft,index-1); root.right = build(preorder,inorder,preLeft+(index-inLeft)+1,preEnd,index+1,inRight); return root; }
106 中序遍历与后续遍历确定二叉树 基本与上题分析一致
Map<Integer,Integer> indexMap; public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) { if (postorder.length == 0)return null; indexMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { indexMap.put(inorder[i],i); } TreeNode build = build(postorder, inorder, 0, postorder.length-1, 0, inorder.length-1); return build; } public TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int preLeft,int preEnd,int inLeft,int inRight){ if (preLeft > preEnd) return null; //构造当前根节点 TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preEnd]); //当前根节点的左子节点为构造出的左子树的根节点 Integer index = indexMap.get(root.val); root.left = build(preorder,inorder,preLeft,preEnd-1-(inRight-index),inLeft,index-1); root.right = build(preorder,inorder,preEnd-(inRight-index),preEnd-1,index+1,inRight); return root; }
113 路径总和

大致原理的写法应该就是如下,但是我这样写效率比较低
List<List<Integer>> result; int target; public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { result = new ArrayList<>(); target = targetSum; find(root,""); return result; } public void find(TreeNode root,String str){ if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ int total = root.val; String[] split = str.split(","); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (String s : split) { if (s.equals(""))continue; Integer integer = Integer.valueOf(s); list.add(integer); total+=integer; } if (total == target){ list.add(root.val); result.add(list); } } if (root.left != null){ find(root.left,str+","+root.val); } if (root.right != null){ find(root.right,str+","+root.val); } }
重新优化了下写法,然后好了很多
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result; LinkedList<Integer> current; int pre; int target; public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null)return result; pre = 0; current = new LinkedList<>(); target = targetSum; find(root); return result; } public void find(TreeNode root){ current.add(root.val); pre+=root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ if (pre == target){ ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(current); result.add(integers); } } if (root.left != null){ find(root.left); } if (root.right != null){ find(root.right); } pre-=root.val; current.pollLast(); } }
114 二叉树展开为链表 类似的题好像做了不少了,解题方法都差不多
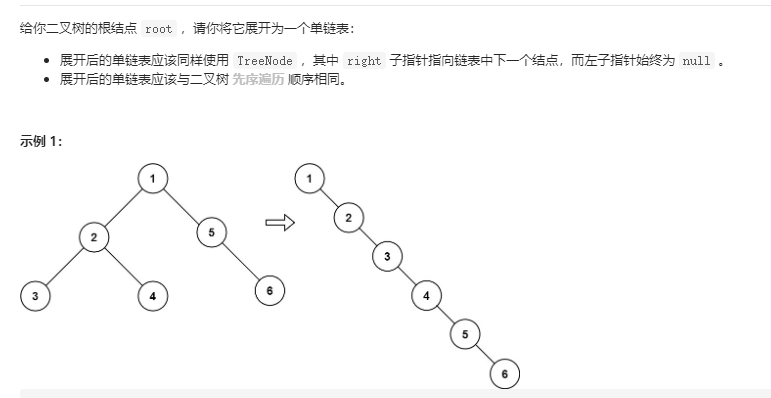
TreeNode roots; TreeNode current; public void flatten(TreeNode root) { fill(root); } public void fill(TreeNode node){ TreeNode left = node.left,right = node.right; node.left = node.right = null; if (roots == null){ roots = node; current = node; }else { current.right = node; current = current.right; } if (left != null){ fill(left); } if (right != null){ fill(right); } }