声明:原创作品,转载注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vestinfo/
六、flex和bison相结合。
test.l
test.y
编译:
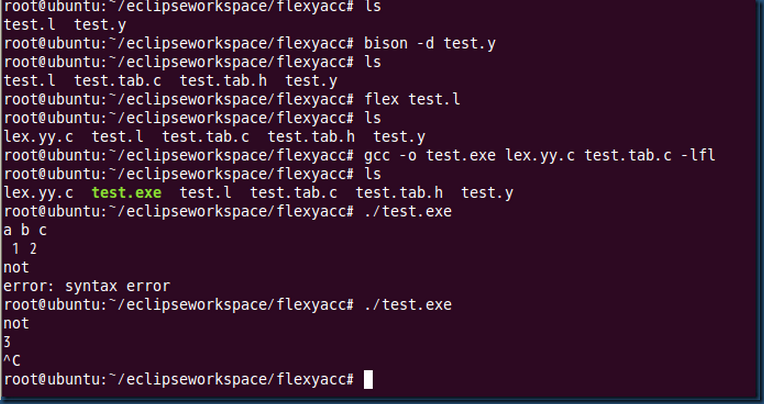
七、文件信息分析。
tset.l分析test.txt文件中的关键词(即test.y中的token标记),遇到token返回给test.y,test.y判断
是否符合一定语法,符合则进行相应动作。
test.l
test.y
%{
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char* string;
#define YYSTYPE string
%}
%token NAME EQ AGE
%%
file : record file
| record
;
record : NAME EQ AGE {
printf("%s is %s years old!!!\n", $1, $3); }
;
%%
int main()
{
extern FILE* yyin;
if(!(yyin = fopen("test.txt", "r")))
{
perror("cannot open parsefile:");
return -1;
}
yyparse();
fclose(yyin);
return 0;
}
int yyerror(char *msg)
{
printf("Error encountered: %s \n", msg);
}
test.txt
编译
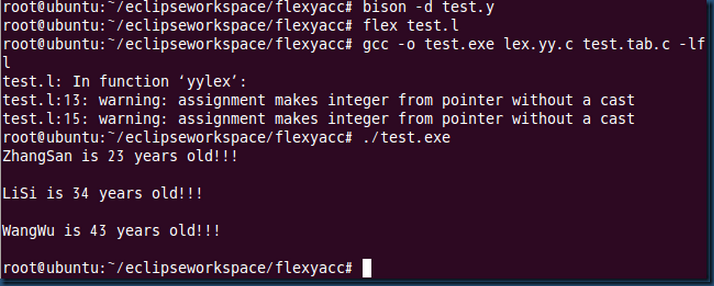
token定义的标记的类型及union的使用。
token定义的标记的类型默认为int 且 默认赋值从258开始。如上面的例子,在生成的头文件
test.tab.h中有如下预编译,
/* Tokens. */
#ifndef YYTOKENTYPE
# define YYTOKENTYPE
/* Put the tokens into the symbol table, so that GDB and other debuggers
know about them. */
enum yytokentype {
NAME = 258,
EQ = 259,
AGE = 260
};
#endif
如果想将token标记定义为其他类型呢?首先将类型定义在联合中,
%union {
char *str;
int num;
struct { int num1; int num2; } dnum;
}
然后,如下定义,
%token <str> K_HOST K_ERROR %token <str> WORD PATH STRING %token <num> NUM %token <dnum> DNUM
补充 :$$ $1 $2….
Each symbol in a bison rule has a value; the value of the target symbol (the one to the
left of the colon) is called $$ in the action code, and the values on the right are numbered
$1, $2, and so forth, up to the number of symbols in the rule.
$$——表示冒号的左边符号;$1——冒号右边第一个;$2——冒号右边第二个,依此类推。
如record : NAME EQ AGE { printf("%s is %s years old!!!\n", $1, $3); } ;
匹配NAME EQ AGE后,$1即NAME所表示的内容,$3即AGE所表示的内容。