Fork版本项目地址:SSD
参考自集智专栏
一、SSD基础
在分类器基础之上想要识别物体,实质就是 用分类器扫描整张图像,定位特征位置 。这里的关键就是用什么算法扫描,比如可以将图片分成若干网格,用分类器一个格子、一个格子扫描,这种方法有几个问题:
问题1 : 目标正好处在两个网格交界处,就会造成分类器的结果在两边都不足够显著,造成漏报(True Negative)。
问题2 : 目标过大或过小,导致网格中结果不足够显著,造成漏报。
针对第一点,可以采用相互重叠的网格。比如一个网格大小是 32x32 像素,那么就网格向下移动时,只动 8 个像素,走四步才完全移出以前的网格。针对第二点,可以采用大小网格相互结合的策略,32x32 网格扫完,64x64 网格再扫描一次,16x16 网格也再扫一次。
但是这样会带来其他问题——我们为了保证准确率, 对同一张图片扫描次数过多,严重影响了计算速度 ,造成这种策略 无法做到实时标注 。
为了快速、实时标注图像特征,对于整个识别定位算法,就有了诸多改进方法。
一个最基本的思路是,合理使用卷积神经网络的内部结构,避免重复计算。用卷积神经网络扫描某一图片时,实际上卷积得到的结果已经存储了不同大小的网格信息,这一过程实际上已经完成了我们上一部分提出的改进措施,如下图所示,我们发现前几层卷积核的结果更关注细节,后面的卷积层结果更加关注整体:

对于问题1,如果一个物体位于两个格子的中间,虽然两边都不一定足够显著,但是两边的基本特征如果可以合理组合的话,我们就不需要再扫描一次。而后几层则越来越关注整体,对问题2,目标可能会过大过小,但是特征同样也会留下。也就是说,用卷积神经网络扫描图像过程中,由于深度神经网络本身就有好几层卷积、实际上已经反复多次扫描图像,以上两个问题可以通过合理使用卷积神经网络的中间结果得到解决。
在 SSD 算法之前,MultiBox,FastR-CNN 法都采用了两步的策略,即第一步通过深度神经网络,对潜在的目标物体进行定位,即先产生Box;至于Box 里面的物体如何分类,这里再进行第二步计算。此外第一代的 YOLO 算法可以做到一步完成计算加定位,但是结构中采用了全连接层,而全连接层有很多问题,并且正在逐步被深度神经网络架构“抛弃”。

二、TF_SSD项目中网络的结构
回到项目中,以VGG300(/nets/ssd_vgg_300.py)为例,大体思路就是,用VGG 深度神经网络的前五层,并额外多加几层结构,最后提取其中几层进过卷积后的结果,进行网格搜索,找目标特征。对应到函数里,转化为三个大部分,原网络结构、添加网络结构、SSD处理结构:
def ssd_net(inputs,
num_classes=SSDNet.default_params.num_classes,
feat_layers=SSDNet.default_params.feat_layers,
anchor_sizes=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_sizes,
anchor_ratios=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_ratios,
normalizations=SSDNet.default_params.normalizations,
is_training=True,
dropout_keep_prob=0.5,
prediction_fn=slim.softmax,
reuse=None,
scope='ssd_300_vgg'):
"""SSD net definition.
"""
# if data_format == 'NCHW':
# inputs = tf.transpose(inputs, perm=(0, 3, 1, 2))
# End_points collect relevant activations for external use.
"""
net = layers_lib.repeat(
inputs, 2, layers.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 2, layers.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool5')
"""
end_points = {}
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'ssd_300_vgg', [inputs], reuse=reuse):
######################################
# 前五个 Blocks,首先照搬 VGG16 架构 #
# 注意这里使用 end_points 标注中间结果 #
######################################
# ——————————————————Original VGG-16 blocks.———————————————————————
net = slim.repeat(inputs, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
end_points['block1'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1')
# Block 2.
net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
end_points['block2'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
# Block 3.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
end_points['block3'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3')
# Block 4.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
end_points['block4'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4')
# Block 5.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
end_points['block5'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='pool5') # 池化层步长由2修改到三
####################################
# 后六个 Blocks,使用额外卷积层 #
####################################
# ————————————Additional SSD blocks.——————————————————————
# Block 6: let's dilate the hell out of it!
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [3, 3], rate=6, scope='conv6')
end_points['block6'] = net
net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
# Block 7: 1x1 conv. Because the fuck.
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [1, 1], scope='conv7')
end_points['block7'] = net
net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
# Block 8/9/10/11: 1x1 and 3x3 convolutions stride 2 (except lasts).
end_point = 'block8'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))
net = slim.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block9'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block10'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block11'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
######################################
# 每个中间层 end_points 返回中间结果 #
# 将各层预测结果存入列表,返回给优化函数 #
######################################
# Prediction and localisations layers.
predictions = []
logits = []
localisations = []
# feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
for i, layer in enumerate(feat_layers):
with tf.variable_scope(layer + '_box'):
p, l = ssd_multibox_layer(end_points[layer],
num_classes,
anchor_sizes[i],
anchor_ratios[i],
normalizations[i])
"""
框的数目等于anchor_sizes[i]和anchor_ratios[i]的长度和
anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),
(45., 99.),
(99., 153.),
(153., 207.),
(207., 261.),
(261., 315.)]
anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]]
normalizations=[20, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
"""
predictions.append(prediction_fn(p)) # prediction_fn=slim.softmax
logits.append(p)
localisations.append(l)
return predictions, localisations, logits, end_points
ssd_net.default_image_size = 300
在整个函数最后,给出了ssd_arg_scope函数,用于约束网络中的超参数设定,用法脚本头中已经给了:
Usage:
with slim.arg_scope(ssd_vgg.ssd_vgg()):
outputs, end_points = ssd_vgg.ssd_vgg(inputs)
def ssd_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0005, data_format='NHWC'):
"""Defines the VGG arg scope.
Args:
weight_decay: The l2 regularization coefficient.
Returns:
An arg_scope.
"""
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
weights_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(),
biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d],
padding='SAME',
data_format=data_format):
with slim.arg_scope([custom_layers.pad2d,
custom_layers.l2_normalization,
custom_layers.channel_to_last],
data_format=data_format) as sc:
return sc
a、超参数设定
实际上原程序中超参数作为一个class属性给出的,我们现在不关心这个class的信息,仅仅将其包含超参数设定的部分提取出来,提升对上面网络的理解,
SSDParams = namedtuple('SSDParameters', ['img_shape',
'num_classes',
'no_annotation_label',
'feat_layers',
'feat_shapes',
'anchor_size_bounds',
'anchor_sizes',
'anchor_ratios',
'anchor_steps',
'anchor_offset',
'normalizations',
'prior_scaling'
])
class SSDNet(object):
default_params = SSDParams(
img_shape=(300, 300),
num_classes=21,
no_annotation_label=21,
feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11'],
feat_shapes=[(38, 38), (19, 19), (10, 10), (5, 5), (3, 3), (1, 1)],
anchor_size_bounds=[0.15, 0.90],
# anchor_size_bounds=[0.20, 0.90],
anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),
(45., 99.),
(99., 153.),
(153., 207.),
(207., 261.),
(261., 315.)],
anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]],
anchor_steps=[8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],
anchor_offset=0.5,
normalizations=[1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1], # 控制SSD层处理时是否预先沿着HW正则化
prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]
)
b、SSD处理结构
# Prediction and localisations layers.
predictions = []
logits = []
localisations = []
# feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
for i, layer in enumerate(feat_layers):
with tf.variable_scope(layer + '_box'):
p, l = ssd_multibox_layer(end_points[layer], # <-----SSD处理
num_classes,
anchor_sizes[i],
anchor_ratios[i],
normalizations[i])
predictions.append(prediction_fn(p)) # prediction_fn=slim.softmax
logits.append(p)
localisations.append(l)
return predictions, localisations, logits, end_points
在网络架构的最后,会对选取的特征层外接新的卷积处理(上面代码),处理函数如下:
def tensor_shape(x, rank=3):
"""Returns the dimensions of a tensor.
Args:
image: A N-D Tensor of shape.
Returns:
A list of dimensions. Dimensions that are statically known are python
integers,otherwise they are integer scalar tensors.
"""
if x.get_shape().is_fully_defined():
return x.get_shape().as_list()
else:
# get_shape返回值,with_rank相当于断言assert,是否rank为指定值
static_shape = x.get_shape().with_rank(rank).as_list()
# tf.shape返回张量,其中num解释为"The length of the dimension `axis`.",axis默认为0
dynamic_shape = tf.unstack(tf.shape(x), num=rank)
# list,有定义的给数字,没有的给tensor
return [s if s is not None else d
for s, d in zip(static_shape, dynamic_shape)]
def ssd_multibox_layer(inputs,
num_classes,
sizes,
ratios=[1],
normalization=-1,
bn_normalization=False):
"""Construct a multibox layer, return a class and localization predictions.
"""
net = inputs
if normalization > 0:
net = custom_layers.l2_normalization(net, scaling=True)
# Number of anchors.
num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)
# Location.
num_loc_pred = num_anchors * 4 # 每一个框有四个坐标
loc_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_loc_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
scope='conv_loc') # 输出C表示不同框的某个坐标
# 强制转换为NHWC
loc_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(loc_pred)
# NHW(num_anchors+4)->NHW,num_anchors,4
loc_pred = tf.reshape(loc_pred,
tensor_shape(loc_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, 4])
# Class prediction.
num_cls_pred = num_anchors * num_classes # 每一个框都要计算所有的类别
cls_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_cls_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
scope='conv_cls') # 输出C表示不同框的对某个类的预测
# 强制转换为NHWC
cls_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(cls_pred)
# NHW(num_anchors+类别)->NHW,num_anchors,类别
cls_pred = tf.reshape(cls_pred,
tensor_shape(cls_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, num_classes])
return cls_pred, loc_pred
根据是否正则化的的参数,对特征层进行L2正则化(空间维度C上正则化),具体流程见下节
然后并行的在选定特征层后面加上两个卷积,一个输出通道为num_anchors×4,一个输出通道为num_anchors×类别数
将两个卷积的输出格维度各自扩展一维,排序转换为:[NHW,num_anchors,4] 和 [NHW,num_anchors,类别]
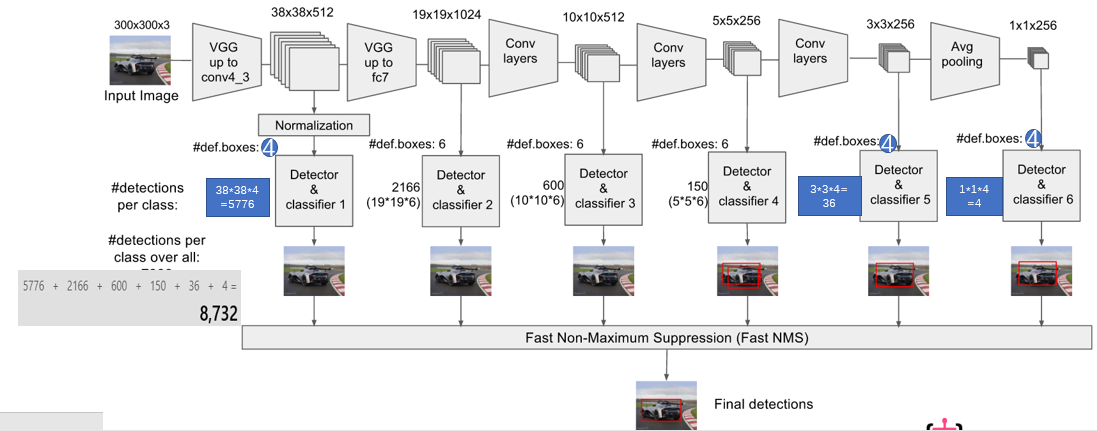
此时我们可以知道网络结构函数的返回的意义了:各个指定层SSD处理后输出的框对类别的概率,各个指定层SSD处理后输出的框坐标修正,各个指定层SSD处理后输出的框对类别的原始输出,所有中间层的end_point。
c、custom_layers.l2_normalization:特征层L2正则化
首先在特征层维度进行正则化,过程见nn.l2_normalize,然后对每一个层取一个scale因子,对各个层放缩调整(因子是可学习的),最后返回这个调整后的特征
@add_arg_scope
def l2_normalization(
inputs,
scaling=False,
scale_initializer=init_ops.ones_initializer(),
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
data_format='NHWC',
trainable=True,
scope=None):
"""Implement L2 normalization on every feature (i.e. spatial normalization).
Should be extended in some near future to other dimensions, providing a more
flexible normalization framework.
Args:
inputs: a 4-D tensor with dimensions [batch_size, height, width, channels].
scaling: whether or not to add a post scaling operation along the dimensions
which have been normalized.
scale_initializer: An initializer for the weights.
reuse: whether or not the layer and its variables should be reused. To be
able to reuse the layer scope must be given.
variables_collections: optional list of collections for all the variables or
a dictionary containing a different list of collection per variable.
outputs_collections: collection to add the outputs.
data_format: NHWC or NCHW data format.
trainable: If `True` also add variables to the graph collection
`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
Returns:
A `Tensor` representing the output of the operation.
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
scope, 'L2Normalization', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
inputs_shape = inputs.get_shape()
inputs_rank = inputs_shape.ndims
dtype = inputs.dtype.base_dtype
# 在C上做l2标准化
if data_format == 'NHWC':
# norm_dim = tf.range(1, inputs_rank-1)
norm_dim = tf.range(inputs_rank-1, inputs_rank)
params_shape = inputs_shape[-1:]
elif data_format == 'NCHW':
# norm_dim = tf.range(2, inputs_rank)
norm_dim = tf.range(1, 2)
params_shape = (inputs_shape[1])
# Normalize along spatial dimensions.
outputs = nn.l2_normalize(inputs, norm_dim, epsilon=1e-12)
# Additional scaling.
if scaling:
# 从collections获取变量
scale_collections = utils.get_variable_collections(
variables_collections, 'scale')
# 创建变量,shape=C的层数
scale = variables.model_variable('gamma',
shape=params_shape,
dtype=dtype,
initializer=scale_initializer,
collections=scale_collections,
trainable=trainable)
if data_format == 'NHWC':
outputs = tf.multiply(outputs, scale)
elif data_format == 'NCHW':
scale = tf.expand_dims(scale, axis=-1)
scale = tf.expand_dims(scale, axis=-1)
outputs = tf.multiply(outputs, scale)
# outputs = tf.transpose(outputs, perm=(0, 2, 3, 1))
# 为outputs添加别名,并将之收集进collection,返回原节点
return utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,
sc.original_name_scope, outputs)
至此,网络结构的介绍就完成了,下一节我们将关注目标检测模型的关键技术之一:定位框的生成,并串联本节,理解整个SSD网络的生成过程。
附录、相关实现
custom_layers.channel_to_last:NHWC转化
@add_arg_scope # 层可以被slim.arg_scope设定
def channel_to_last(inputs,
data_format='NHWC',
scope=None):
"""Move the channel axis to the last dimension. Allows to
provide a single output format whatever the input data format.
Args:
inputs: Input Tensor;
data_format: NHWC or NCHW.
Return:
Input in NHWC format.
"""
with tf.name_scope(scope, 'channel_to_last', [inputs]):
if data_format == 'NHWC':
net = inputs
elif data_format == 'NCHW':
net = tf.transpose(inputs, perm=(0, 2, 3, 1))
return net
custom_layers.pad2d:2D-tensor填充
@add_arg_scope # 层可以被slim.arg_scope设定
def pad2d(inputs,
pad=(0, 0),
mode='CONSTANT',
data_format='NHWC',
trainable=True,
scope=None):
"""2D Padding layer, adding a symmetric padding to H and W dimensions.
Aims to mimic padding in Caffe and MXNet, helping the port of models to
TensorFlow. Tries to follow the naming convention of `tf.contrib.layers`.
Args:
inputs: 4D input Tensor;
pad: 2-Tuple with padding values for H and W dimensions;(填充的宽度)
mode: Padding mode. C.f. `tf.pad`
data_format: NHWC or NCHW data format.
"""
with tf.name_scope(scope, 'pad2d', [inputs]):
# Padding shape.
if data_format == 'NHWC':
paddings = [[0, 0], [pad[0], pad[0]], [pad[1], pad[1]], [0, 0]]
elif data_format == 'NCHW':
paddings = [[0, 0], [0, 0], [pad[0], pad[0]], [pad[1], pad[1]]]
net = tf.pad(inputs, paddings, mode=mode)
return net
slim的vgg_16
def vgg_16(inputs,
num_classes=1000,
is_training=True,
dropout_keep_prob=0.5,
spatial_squeeze=True,
scope='vgg_16'):
"""Oxford Net VGG 16-Layers version D Example.
Note: All the fully_connected layers have been transformed to conv2d layers.
To use in classification mode, resize input to 224x224.
Args:
inputs: a tensor of size [batch_size, height, width, channels].
num_classes: number of predicted classes.
is_training: whether or not the model is being trained.
dropout_keep_prob: the probability that activations are kept in the dropout
layers during training.
spatial_squeeze: whether or not should squeeze the spatial dimensions of the
outputs. Useful to remove unnecessary dimensions for classification.
scope: Optional scope for the variables.
Returns:
the last op containing the log predictions and end_points dict.
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope, 'vgg_16', [inputs]) as sc:
end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'
# Collect outputs for conv2d, fully_connected and max_pool2d.
with arg_scope(
[layers.conv2d, layers_lib.fully_connected, layers_lib.max_pool2d],
outputs_collections=end_points_collection):
net = layers_lib.repeat(
inputs, 2, layers.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 2, layers.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4')
net = layers_lib.repeat(net, 3, layers.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
net = layers_lib.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool5')
# Use conv2d instead of fully_connected layers.
net = layers.conv2d(net, 4096, [7, 7], padding='VALID', scope='fc6')
net = layers_lib.dropout(
net, dropout_keep_prob, is_training=is_training, scope='dropout6')
net = layers.conv2d(net, 4096, [1, 1], scope='fc7')
net = layers_lib.dropout(
net, dropout_keep_prob, is_training=is_training, scope='dropout7')
net = layers.conv2d(
net,
num_classes, [1, 1],
activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None,
scope='fc8')
# Convert end_points_collection into a end_point dict.
end_points = utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection)
if spatial_squeeze:
net = array_ops.squeeze(net, [1, 2], name='fc8/squeezed')
end_points[sc.name + '/fc8'] = net
return net, end_points
vgg_16.default_image_size = 224
不常用API记录
nn.l2_normalize:L2正则化层
slim.repeat:重复层快速构建
Tensor.get_shape().with_rank(rank).as_list():加类似断言的shape获取函数
tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers.utils.collect_named_outputs:变量添加进collections,并取别名