『PyTorch × TensorFlow』第十七弹_ResNet快速实现
要点
- 神经网络逐层加深有Degradiation问题,准确率先上升到饱和,再加深会下降,这不是过拟合,是测试集和训练集同时下降的
- 提出了残差结构,这个结构解决了深层网络训练误差反而提升的情况,使得网络理论上可以无限深
- bottleneck网络结构,注意Channel维度变化:
,宛如一个中间细两端粗的瓶颈,所以称为“bottleneck”。这种结构相比VGG,早已经被证明是非常效的,能够更好的提取图像特征。
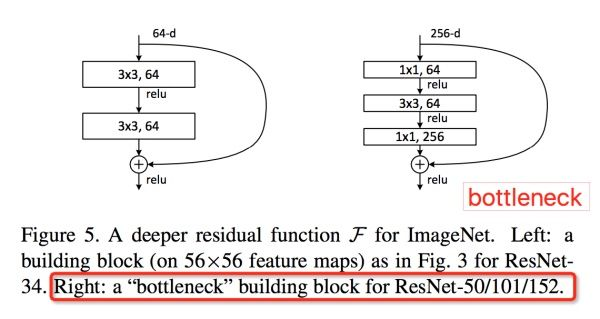
残差结构
截取代码如下,
@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs,depth,depth_bottleneck,stride,
outputs_collections=None,scope=None):
"""
核心残差学习单元
输入tensor给出一个直连部分和残差部分加和的输出tensor
:param inputs: 输入tensor
:param depth: Block类参数,输出tensor通道
:param depth_bottleneck: Block类参数,中间卷积层通道数
:param stride: Block类参数,降采样步长
3个卷积只有中间层采用非1步长去降采样。
:param outputs_collections: 节点容器collection
:return: 输出tensor
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope,'bottleneck_v2',[inputs]) as sc:
# 获取输入tensor的最后一个维度(通道)
depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(),min_rank=4)
# 对输入正则化处理,并激活
preact = slim.batch_norm(inputs,activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,scope='preact')
'shortcut直连部分'
if depth == depth_in:
# 如果输入tensor通道数等于输出tensor通道数
# 降采样输入tensor使之宽高等于输出tensor
shortcut = subsample(inputs,stride,'shortcut')
else:
# 否则,使用尺寸为1*1的卷积核改变其通道数,
# 同时调整宽高匹配输出tensor
shortcut = slim.conv2d(preact,depth,[1,1],stride,
normalizer_fn=None,activation_fn=None,
scope='shortcut')
'residual残差部分'
residual = slim.conv2d(preact,depth_bottleneck,[1,1],stride=1,scope='conv1')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual,depth_bottleneck,3,stride=stride,scope='conv2')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual,depth,[1,1],stride=1,scope='conv3')
output = shortcut + residual
return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,sc.name,output)
逻辑流程如下,
批正则化数据
shortcut分量处理:调整输入tensor使之和输出tensor深度一致,宽高一致
residual分量处理:1*1/1卷积->3*3/自定步长(所以上面需要调整shortcut宽高)卷积->1*1/1卷积
shortcut + residual 作为最终输出,注意是加,不是concat。
代码
之前一直对变量作用域的实际功效比较不解(虽然介绍文章看了很多)特别是reuse属性搭配上后,这节网络结构较为复杂,图结构生成方式很混乱,也和自己粗心有关,运行时出了一些变量重复的错,修改过程中对变量作用域的理解深入了。所谓的reuse或者重名什么的和变量生成函数没有关系,只要同一个生成函数不同生成次数时指定不同的name就完全没问题,重点是在计算图的位置要不一样。如果是同一个计算图位置重复生成(初始化)的话要注明reuse=True。
实际例子中作者采用了一些写起来显得麻烦但是提高了效率的架构方式,比如conv2d_same的实现,和网络结束部分的全局平均池化,都为了效率放弃了最简单的写法。
网络结构如下,
# Author : Hellcat
# Time : 2017/12/14
import math
import time
from datetime import datetime
import collections
import tensorflow as tf
slim = tf.contrib.slim
class Block(collections.namedtuple('Block',['scope','unit_fn','args'])):
"""
使用collections.namedtuple设计ResNet基本模块组的name tuple,并用它创建Block的类
只包含数据结构,不包含具体方法。
定义一个典型的Block,需要输入三个参数:
scope:Block的名称
unit_fn:ResNet V2中的残差学习单元生成函数
args:Block的args(输出深度,瓶颈深度,瓶颈步长)
"""
def subsample(inputs,factor,scope=None):
"""
如果factor为1,则不做修改直接返回inputs;如果不为1,则使用
slim.max_pool2d最大池化来实现,通过1*1的池化尺寸,factor作步长,实
现降采样。
:param inputs: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels]
:param factor: 采样因子
:param scope: 域名
:return: 采样结果
"""
if factor == 1:
return inputs
else:
return slim.max_pool2d(inputs,[1,1],stride=factor,scope=scope)
def conv2d_same(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride,scope=None):
"""
卷积层实现,有更简单的写法,这样做其实是为了提高效率
:param inputs: 输入tensor
:param num_outputs: 输出通道
:param kernel_size: 卷积核尺寸
:param stride: 卷积步长
:param scope: 节点名称
:return: 输出tensor
"""
if stride == 1:
return slim.conv2d(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride=1,padding='SAME',scope=scope)
else:
pad_total = kernel_size - 1
pad_beg = pad_total // 2
pad_end = pad_total - pad_beg
inputs = tf.pad(inputs,[[0,0],[pad_beg,pad_end],
[pad_beg,pad_end],[0,0]])
return slim.conv2d(inputs,num_outputs,kernel_size,stride=stride,
padding='VALID',scope=scope)
@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_block_dense(net,blocks,outputs_collections=None):
"""
示例,Block('block1',bottleneck,[(256,64,1)]*2 + [(256,64,2)])
:param net: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height, width, channels].
:param blocks: 是之前定义的Block的class的列表
:param outputs_collections: 收集各个end_points的collections
:return: Output tensor
"""
for block in blocks:
with tf.variable_scope(block.scope,'block',[net]) as sc:
for i,unit in enumerate(block.args):
with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i+1), values=[net]):
# 示例:(256,64,1)
unit_depth,unit_depth_bottleneck,unit_stride = unit
net = block.unit_fn(net,
depth=unit_depth,
depth_bottleneck=unit_depth_bottleneck,
stride=unit_stride)
net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,sc.name,net)
'''
这个方法会返回本次添加的tensor对象,
意义是为tensor添加一个别名,并收集进collections中
实现如下
if collections:
append_tensor_alias(outputs,alias)
ops.add_to_collections(collections,outputs)
return outputs
据说本方法位置已经被转移到这里了,
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import utils
utils.collect_named_outputs()
'''
return net
@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs,depth,depth_bottleneck,stride,
outputs_collections=None,scope=None):
"""
核心残差学习单元
输入tensor给出一个直连部分和残差部分加和的输出tensor
:param inputs: 输入tensor
:param depth: Block类参数,输出tensor通道
:param depth_bottleneck: Block类参数,中间卷积层通道数
:param stride: Block类参数,降采样步长
3个卷积只有中间层采用非1步长去降采样。
:param outputs_collections: 节点容器collection
:return: 输出tensor
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope,'bottleneck_v2',[inputs]) as sc:
# 获取输入tensor的最后一个维度(通道)
depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(),min_rank=4)
# 对输入正则化处理,并激活
preact = slim.batch_norm(inputs,activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,scope='preact')
'shortcut直连部分'
if depth == depth_in:
# 如果输入tensor通道数等于输出tensor通道数
# 降采样输入tensor使之宽高等于输出tensor
shortcut = subsample(inputs,stride,'shortcut')
else:
# 否则,使用尺寸为1*1的卷积核改变其通道数,
# 同时调整宽高匹配输出tensor
shortcut = slim.conv2d(preact,depth,[1,1],stride,
normalizer_fn=None,activation_fn=None,
scope='shortcut')
'residual残差部分'
residual = slim.conv2d(preact,depth_bottleneck,[1,1],stride=1,scope='conv1')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual,depth_bottleneck,3,stride=stride,scope='conv2')
residual = slim.conv2d(residual,depth,[1,1],stride=1,scope='conv3')
output = shortcut + residual
return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,sc.name,output)
def resnet_arg_scope(is_training=True,
weight_decay=0.0001, # L2权重衰减速率
batch_norm_decay=0.997, # BN的衰减速率
batch_norm_epsilon=1e-5, # BN的epsilon默认1e-5
batch_norm_scale=True): # BN的scale默认值
batch_norm_params = { # 定义batch normalization(标准化)的参数字典
'is_training': is_training,
# 是否是在训练模式,如果是在训练阶段,将会使用指数衰减函数(衰减系数为指定的decay),
# 对moving_mean和moving_variance进行统计特性的动量更新,也就是进行使用指数衰减函数对均值和方
# 差进行更新,而如果是在测试阶段,均值和方差就是固定不变的,是在训练阶段就求好的,在训练阶段,
# 每个批的均值和方差的更新是加上了一个指数衰减函数,而最后求得的整个训练样本的均值和方差就是所
# 有批的均值的均值,和所有批的方差的无偏估计
'zero_debias_moving_mean': True,
# 如果为True,将会创建一个新的变量对 'moving_mean/biased' and 'moving_mean/local_step',
# 默认设置为False,将其设为True可以增加稳定性
'decay': batch_norm_decay, # Decay for the moving averages.
# 该参数能够衡量使用指数衰减函数更新均值方差时,更新的速度,取值通常在0.999-0.99-0.9之间,值
# 越小,代表更新速度越快,而值太大的话,有可能会导致均值方差更新太慢,而最后变成一个常量1,而
# 这个值会导致模型性能较低很多.另外,如果出现过拟合时,也可以考虑增加均值和方差的更新速度,也
# 就是减小decay
'epsilon': batch_norm_epsilon, # 就是在归一化时,除以方差时,防止方差为0而加上的一个数
'scale': batch_norm_scale,
'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
# force in-place updates of mean and variance estimates
# 该参数有一个默认值,ops.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,当取默认值时,slim会在当前批训练完成后再更新均
# 值和方差,这样会存在一个问题,就是当前批数据使用的均值和方差总是慢一拍,最后导致训练出来的模
# 型性能较差。所以,一般需要将该值设为None,这样slim进行批处理时,会对均值和方差进行即时更新,
# 批处理使用的就是最新的均值和方差。
#
# 另外,不论是即使更新还是一步训练后再对所有均值方差一起更新,对测试数据是没有影响的,即测试数
# 据使用的都是保存的模型中的均值方差数据,但是如果你在训练中需要测试,而忘了将is_training这个值
# 改成false,那么这批测试数据将会综合当前批数据的均值方差和训练数据的均值方差。而这样做应该是不
# 正确的。
}
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay), # 权重正则器设置为L2正则
weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm, # 标准化器设置为BN
normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm],**batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d],padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
return arg_sc
def resnet_v2(inputs,
blocks,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
include_root_block=True,
reuse=None,
scope=None):
"""
网络结构主函数
:param inputs: 输入tensor
:param blocks: Block类列表
:param num_classes: 输出类别数
:param global_pool: 是否最后一层全局平均池化
:param include_root_block: 是否最前方添加7*7卷积和最大池化
:param reuse: 是否重用
:param scope: 整个网络名称
:return:
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope,'resnet_v2',[inputs],reuse=reuse) as sc:
# 字符串,用于命名collection名字
end_points_collecion = sc.original_name_scope + 'end_points'
print(end_points_collecion)
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,bottleneck,stack_block_dense],
# 为新的收集器取名
outputs_collections=end_points_collecion):
net = inputs
if include_root_block:
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d],
activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None):
# 卷积:2步长,7*7核,64通道
net = conv2d_same(net,64,7,stride=2,scope='conv1')
# 池化:2步长,3*3核
net = slim.max_pool2d(net,[3,3],stride=2,scope='pool1')
# 至此图片缩小为1/4
# 读取blocks数据结构,生成残差结构
net = stack_block_dense(net,blocks)
net = slim.batch_norm(net,
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
scope='postnorm')
if global_pool:
# 全局平均池化,效率比avg_pool更高
# 即对每个feature做出平均池化,使每个feature输出一个值
net = tf.reduce_mean(net,[1,2],name='pool5',keep_dims=True)
if num_classes is not None:
net = slim.conv2d(net,num_classes,[1,1],
activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None,
scope='logits')
# 将collection转化为dict
end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collecion)
if num_classes is not None:
# 为dict添加节点
end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net,scope='predictions')
return net, end_points
def resnet_v2_152(inputs,
num_classes=None,
global_pool=True,
reuse=None,
scope='resnet_v2_152'):
blocks = [
# 输出深度,瓶颈深度,瓶颈步长
Block('block1',bottleneck,[(256,64,1)]*2 + [(256,64,2)]),
Block('block2',bottleneck,[(512,128,1)]*7 + [(512,128,2)]),
Block('block3',bottleneck,[(1024,256,1)]*35 + [(1024,256,2)]),
Block('block4',bottleneck,[(2048,512,1)]*3)
]
return resnet_v2(inputs,blocks,num_classes,global_pool,
include_root_block=True,reuse=reuse,scope=scope)
#-------------------评测函数---------------------------------
# 测试152层深的ResNet的forward性能
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
batch_size = 32
height,width = 224,224
inputs = tf.random_uniform([batch_size,height,width,3])
with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=False)):
# 1000分类
net,end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs,1000)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
num_batches = 100
time_tensorflow_run(sess,net,'Forward')
# forward计算耗时相比VGGNet和Inception V3大概只增加了50%,是一个实用的卷积神经网络。
和上节同理,不贴时耗。