首先我们来看看spring官方文档对这个注解的解释:
The
@Profileannotation allows you to indicate that a component is eligible for registration when one or more specified profiles are active
这个注解可以根据当前的环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件的功能
结合之前的一些知识,做一个例子,在我们开发的时候,可能在开发的时候连接的是开发环境的数据库,在测试的时候连接测试环境,生产环境连接的是生产数据库,不同环境下使用的数据库是不同的,如何动态的切换数据源的注入呢?
配置类讲解
首先看一下配置类MainConfigProfile类
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.EmbeddedValueResolverAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver;
import com.atguigu.bean.Yellow;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
/**
* Profile:
* Spring为我们提供的可以根据当前环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件的功能;
*
* 开发环境、测试环境、生产环境;
* 数据源:(/A)(/B)(/C);
*
*
* @Profile:指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,不指定,任何环境下都能注册这个组件
*
* 1)、加了环境标识的bean,只有这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是default环境
* 2)、写在配置类上,只有是指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能开始生效
* 3)、没有标注环境标识的bean在,任何环境下都是加载的;
*/
@PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfProfile implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware{
@Value("${db.user}")
private String user;
private StringValueResolver valueResolver;
private String driverClass;
@Bean
public Yellow yellow(){
return new Yellow();
}
@Profile("test")
@Bean("testDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceTest(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"); // 测试库
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean("devDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud"); // 开发库
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean("prodDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceProd(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/scw_0515"); // 生产库
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Override
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.valueResolver = resolver;
driverClass = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}");
}
}
在配置类中我们注入了三个Bean,分别对应测试环境、开发环境、生产环境。
我们知道数据源的注入需要四大金刚:user、password、driver、url。
注意:这里,三种环境连接的都不是相同的数据库,我们这里只以url作为区分。每个环境下的url是不同的。
其他三个参数,我们都配置在类路径下的db.properties中,如下
db.user=root
db.password=123456
db.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
这里结合之前我学习的知识点,使用不同的方式注入db.properties中的值
使用是加载资源文件,这个用法可参阅:Spring中使用@Value和@PropertySource为属性赋值
@PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties")
那如何为
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
这两句中的方法赋值呢?
第一个我们构造了一个
private String user;属性,然后在属性上通过@Value("${db.user}")然后再
dataSource.setUser(user);就拿到值了。
其次呢,
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{...}我们在方法上添加了一个参数,在参数前加上了@Value("${db.password}")便可以从资源文件db.properties中拿到值,赋给这个参数
小结:以上是@Value的用法,可参考上面的链接
进行到这里,我们换一种方式,来取得资源文件中的driverClass,
我们可以通过实现EmbeddedValueResolverAware接口,spring中有很多aware接口,是提供给我们使用spring底层功能的途径。
这里的EmbeddedValueResolverAware就是值解析器 ,实现该接口,即实现其抽象方法
@Override
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.valueResolver = resolver;
driverClass = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}");
}
在容器启动的时候 ,这个方法会被调用,
我们定义 了一个属性,用以接收方法中参数的值,也即StringValueResolver resolver
private StringValueResolver valueResolver;
然后解析
driverClass = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}");
并赋值给我们自定义的属性driverClass。这样这个属性就拿到了资源文件中的值
以上和@Profile没有太大的关系,但可以很好的复习
另外我们还在配置类中,定义 了一个叫做yellow的bean。
测试,并激活对应的环境
首先我们全部不加入@Profile注解
测试一下,观察控制台输出,该方法我们就称为测试方法1
package com.atguigu.test;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.atguigu.bean.Yellow;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConfigOfProfile;
public class IOCTest_Profile {
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
mainConfigOfProfile
yellow
testDataSource
devDataSource
prodDataSource
可以看到包含配置类本身所有的bean都被注入到了ioc容器中。
现在打开所有的@Profile注释
比如现在我们是在dev即开发环境下,如何只激活@Bean("devDataSource")这个组件呢?
我们写个测试类
package com.atguigu.test;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.atguigu.bean.Yellow;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConfigOfProfile;
public class IOCTest_Profile {
//1、使用命令行动态参数: 在虚拟机参数位置加载 -Dspring.profiles.active=test
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
//2、代码的方式激活某种环境;
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//1、创建一个applicationContext
//2、设置需要激活的环境
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev"); // 这里可以写多个值,
//3、注册主配置类
applicationContext.register(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
//4、启动刷新容器
applicationContext.refresh();
String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class);
for (String string : namesForType) {
System.out.println(string);
}
Yellow bean = applicationContext.getBean(Yellow.class);
System.out.println(bean);
applicationContext.close();
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
// String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
// for (String name : definitionNames) {
// System.out.println(name);
// }
}
}
控制台打印:
devDataSource
com.atguigu.bean.Yellow@27ce24aa // 没有被@Profile修饰。
观察可以发现,确实只有开发环境的bean被注入了ioc容器中,
这里还有另外一种激活@Profile注解 的方式。
测试方法1:
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
然后运行该方法,不过需要在运行时候加上虚拟机参数。=后面是我们需要激活的环境,多个值用逗号分隔开。
-Dspring.profiles.active=test
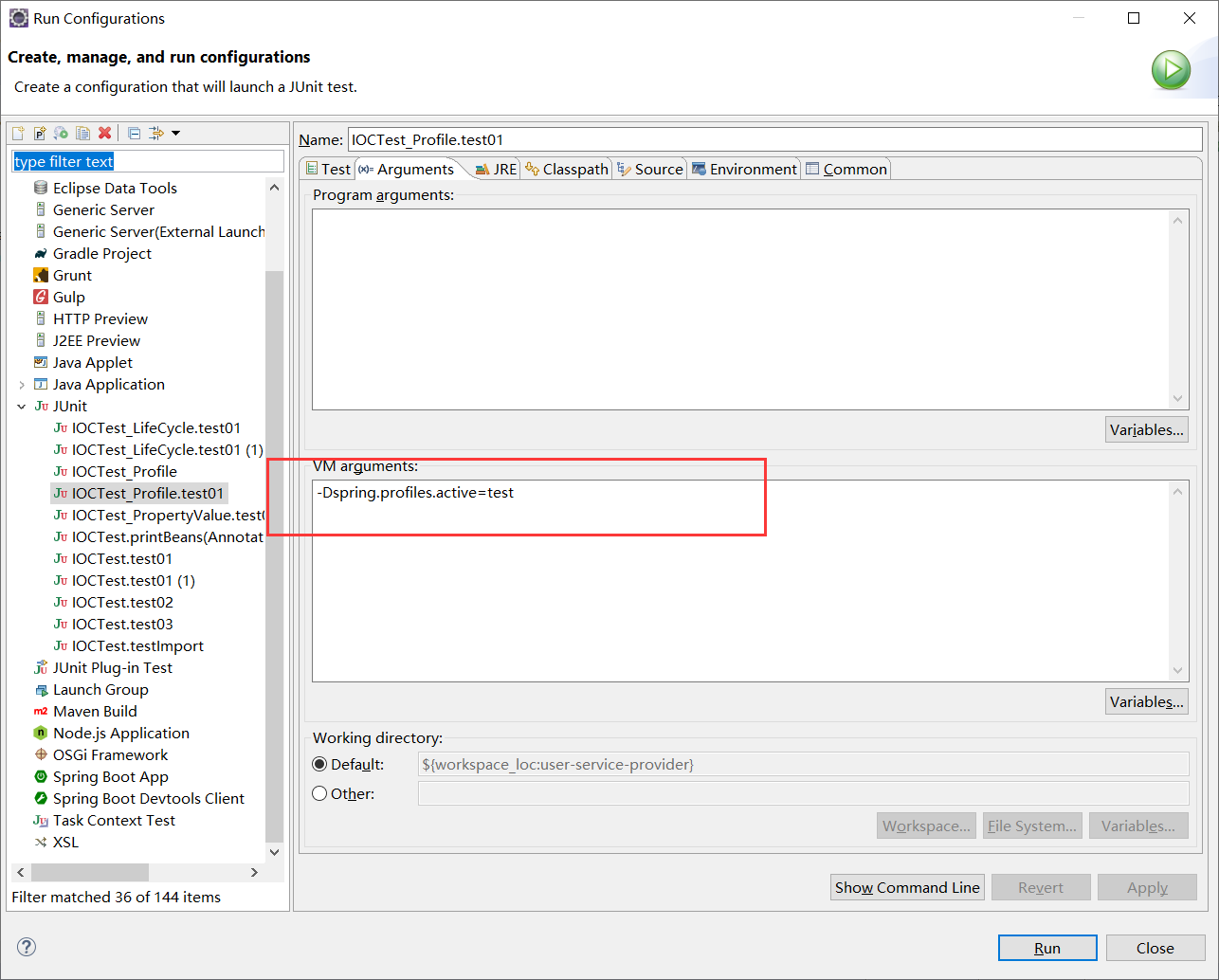
打印一下输出:
mainConfigOfProfile
yellow
testDataSource //测试环境被注入
@Profile注解 使用在类上,
保持配置类不变,我们在该配置类上加上@Profile("prod")
我们在来运行测试方法1(前面有提),控制台并没有输出,这表示配置类中的bean都没有被注入进容器中,
可以这样思考:@Profile注解标注在类上,如果你没有指定激活该环境,自然该配置类整个都不会被加载,配置类中的Bean(即使如Yellow,没有被@Profile注解),也不会被注入进容器中,
那我们以同样的方式,来正确的激活该环境后呢?(如何激活环境,参考前文)
控制台打印输出
mainConfigOfProfile
yellow
prodDataSource
这显然与我们预料的是一致的。
Tips
如果环境都没有被激活,那@Profile("default")会被激活,也就是说,默认就是default环境。