以前其实是写过@Condtional注解的笔记的,这里附上链接:
Spring中的@conditional注解
但已经忘记的差不多了,所以今天再重新学习下,可以互补着学习
@Contional:按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器中注册bean
首先准备一个person实体类,具体代码不列了,前几篇博文中都有。
要使用@Condtional注解,必须实现Conditon接口,并实现其抽象方法mathes,也即用来判断条件的。
然后是准备配置类:
@Configuration
public class MainConfig2 {
//如果系统是windows,给容器中注册("bill")
//如果是linux系统,给容器中注册("linus")
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})
@Bean("bill")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)
@Bean("linus")
public Person person02(){
return new Person("linus", 48);
}
}
//判断是否windows系统
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if(property.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//判断是否linux系统
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
/**
* ConditionContext:判断条件能使用的上下文(环境)
* AnnotatedTypeMetadata:注释信息
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// TODO是否linux系统
//1、能获取到ioc使用的beanfactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//2、获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
//3、获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
//4、获取到bean定义的注册类
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
//可以判断容器中的bean注册情况,也可以给容器中注册bean
boolean definition = registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");
if(property.contains("linux")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
写一个测试类,当前我们的环境是Windows10的环境,所以配置类中第二个显然是不满足的。
package com.atguigu.test;
import java.util.Map;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import com.atguigu.bean.Blue;
import com.atguigu.bean.Person;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConfig;
import com.atguigu.config.MainConfig2;
public class IOCTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
@Test
public void test03(){
String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
//动态获取环境变量的值;Windows 10
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println(property);
for (String name : namesForType) {
System.out.println(name);
}
Map<String, Person> persons = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(persons);
}
}
打印出结果:
Windows 10 // 系统环境
bill // 第二个@Bean("linus")没有被注册进来
现在我们再改变一下系统环境
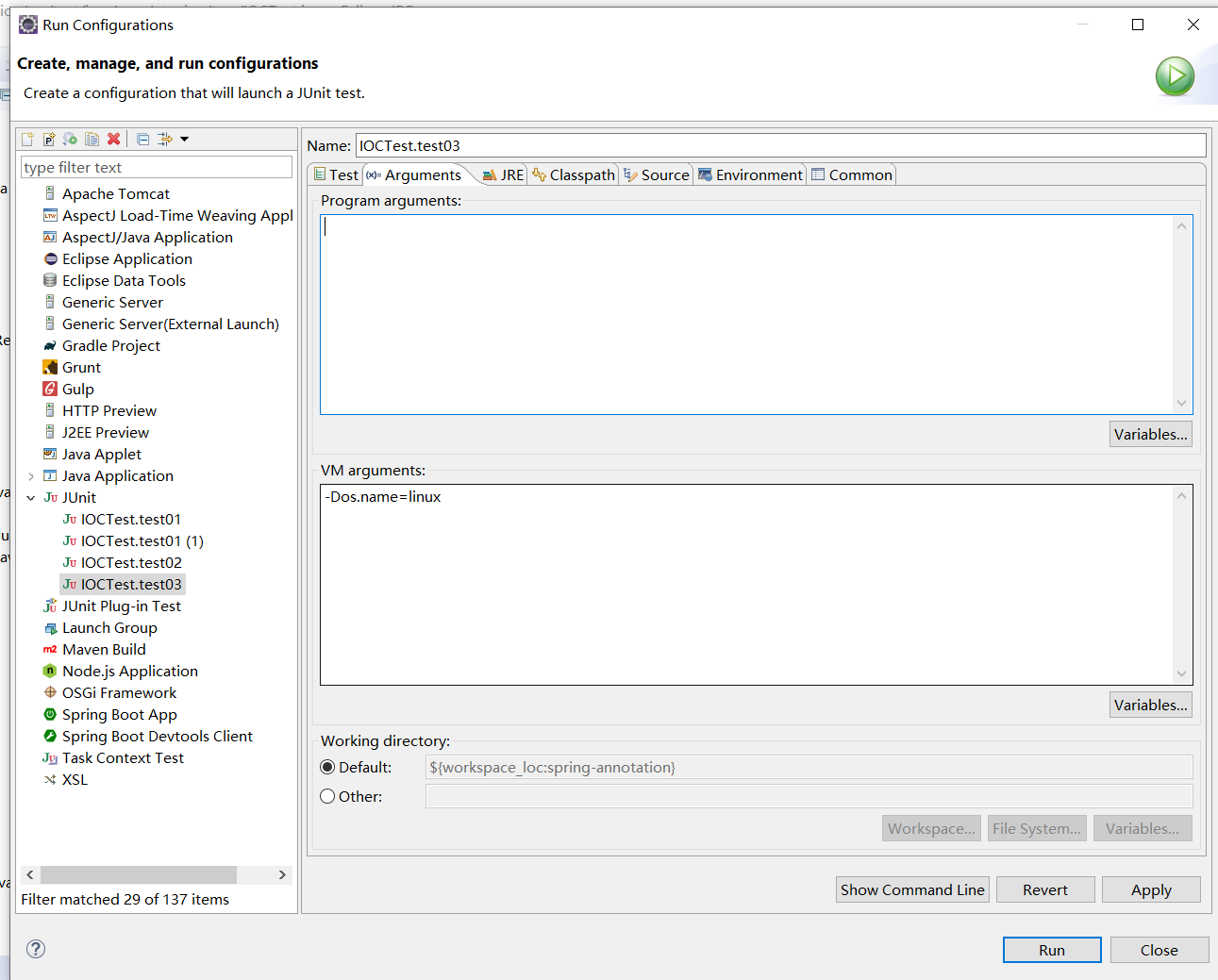
注意看虚拟机参数,这样我们的系统环境就会被识别为linux
点击Run运行,
linux // 系统环境
linus // linus被注册进来
需要注意的是:这个@Conditonal注解,也可以注解在类上,表示:类中组件统一设置。满足当前条件,这个类中配置的所有bean注册才能生效;
至于LinuxCondition和WindowsConditon这两个用来判断条件是否成立的类,可以参看文章开头给的链接。