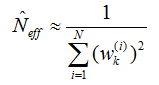gmapping
源码:git搜索 gmapping 下面两个即是:
gmapping 原理很简单,通过“l粒子滤波"实现定位。具体通过粒子与已经产生的地图进行scanMatch,矫正里程计误差实现。 在定位的同时,每次经过map_update_interval_时间,进行地图更新 updateMap(*scan)。相对cartographer,缺少闭环,所以计算量很小,实测,局部地图比carto清晰,质量较好。下面对代码进行梳理(梳理导航相关代码跟着laser走,会比较清晰)
代码梳理
1> ros 部分 (代码为简化版,方便梳理 ... 表示有省略代码)
gmapping/src/main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "slam_gmapping");
SlamGMapping gn;
gn.startLiveSlam();
ros::spin();
return(0);
}
gmapping/src/slam_gmapping.cpp
void SlamGMapping::startLiveSlam()
{
... // 订阅激光数据
scan_filter_->registerCallback(boost::bind(&SlamGMapping::laserCallback, this, _1));
}
void SlamGMapping::laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& scan)
{
// We can't initialize the mapper until we've got the first scan
if(!got_first_scan_)
{
if(!initMapper(*scan))
return;
}
GMapping::OrientedPoint odom_pose;
if(addScan(*scan, odom_pose))// addscan:对新激光,结合里程计数据进行粒子滤波矫正得出最新位置
{ // 以下通过getBestParticle的位置(即,当前激光位置)和里程计最终,算出map-to-odom,发布出去
GMapping::OrientedPoint mpose = gsp_->getBestParticleIndex().pose;
tf::Transform laser_to_map = tf::Transform(mpose...);
tf::Transform odom_to_laser = tf::Transform(odom_pose...);
map_to_odom_ = (odom_to_laser * laser_to_map).inverse();
// 当满足 一定时间间隔 更新地图
if(!got_map_ || (scan->header.stamp - last_map_update) > map_update_interval_)
{
updateMap(*scan);
last_map_update = scan->header.stamp;
}
}
总结:其实以上便是gmapping主要程序框架,通过激光数据和odom数据,进行粒子滤波计算,不断更新自己的位置,同时间断的进行更新地图运算。具体实现函数为:addScan(scan, odom_pose) 和 updateMap(scan);两个函数之间通过变量best(gsp_获得)连接(best是通过粒子滤波得到的最优粒子,也就是SLAM轨迹最优位置)。具体相关代码如下:gmapping/src/slam_gmapping.cpp (核心结构代码)
GMapping::GridSlamProcessor* gsp_;
void SlamGMapping::laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& scan)
{
if(addScan(*scan, odom_pose))// addscan:对新激光,结合里程计数据进行粒子滤波矫正得出最新位置
{
...
// 当满足 一定时间间隔 更新地图
if(!got_map_ || (scan->header.stamp - last_map_update) > map_update_interval_)
{
updateMap(*scan);
last_map_update = scan->header.stamp;
}
}
}
bool SlamGMapping::addScan(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan, GMapping::OrientedPoint& gmap_pose)
{
return gsp_->processScan(reading);
}
void SlamGMapping::updateMap(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan)
{
GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::Particle best = gsp_->getParticles()[gsp_->getBestParticleIndex()];
//以下 得到机器人最优的携带地图路径,重新计算栅格单元的概率.
for(GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::TNode* n = best.node;
n;
n = n->parent)
{
... updateMap();
}
}
int GridSlamProcessor::getBestParticleIndex() const{
unsigned int bi=0;
double bw=-std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_particles.size(); i++)
if (bw<m_particles[i].weightSum){
bw=m_particles[i].weightSum;
bi=i;
}
return (int) bi;
}
updateMap
gmapping/src/slam_gmapping.cpp
通过粒子滤波得到的best_particle (一条最优路径。)建图。
void SlamGMapping::updateMap(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan)
{
GMapping::ScanMatcher matcher; // 定义matcher 并设置参数,为地图更新做准备
matcher.setLaserParameters(scan.ranges.size(), &(laser_angles_[0]),
gsp_laser_->getPose());
matcher.setlaserMaxRange(maxRange_);
matcher.setusableRange(maxUrange_);
matcher.setgenerateMap(true);
if(!got_map_) { // 如果没有地图,便初始化一个地图
map_.map.info.resolution = delta_;
map_.map.info.origin.position.x = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.position.y = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.position.z = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.orientation.x = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.orientation.y = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.orientation.z = 0.0;
map_.map.info.origin.orientation.w = 1.0;
}
GMapping::Point center;
center.x=(xmin_ + xmax_) / 2.0; // xmin,max ,ymin max 地图边界坐标 center 中心坐标
center.y=(ymin_ + ymax_) / 2.0;
GMapping::ScanMatcherMap smap(center, xmin_, ymin_, xmax_, ymax_,
delta_);// detla 分辨率
GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::Particle best = gsp_->getParticles()[gsp_->getBestParticleIndex()];
//以下 得到机器人最优的携带地图路径,重新计算栅格单元的概率.
for(GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::TNode* n = best.node;
n;
n = n->parent)
{
if(!n->reading)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Reading is NULL");
continue;
}
//以下是updateMap主要函数
matcher.invalidateActiveArea(); //有效区域还没计算,等待计算。
matcher.computeActiveArea(smap, n->pose, &((*n->reading)[0])); //计算有效区域
matcher.registerScan(smap, n->pose, &((*n->reading)[0]));//匹配扫描,根据Bresenham算法确 定激光扫过的单元格,进行改良跟新
}
// the map may have expanded, so resize ros message as well
if(map_.map.info.width != (unsigned int) smap.getMapSizeX() || map_.map.info.height != (unsigned int) smap.getMapSizeY()) {
// NOTE: The results of ScanMatcherMap::getSize() are different from the parameters given to the constructor
// so we must obtain the bounding box in a different way
GMapping::Point wmin = smap.map2world(GMapping::IntPoint(0, 0));
GMapping::Point wmax = smap.map2world(GMapping::IntPoint(smap.getMapSizeX(), smap.getMapSizeY()));
xmin_ = wmin.x; ymin_ = wmin.y;
xmax_ = wmax.x; ymax_ = wmax.y;
map_.map.info.width = smap.getMapSizeX();
map_.map.info.height = smap.getMapSizeY();
map_.map.info.origin.position.x = xmin_;
map_.map.info.origin.position.y = ymin_;
map_.map.data.resize(map_.map.info.width * map_.map.info.height);
}
// 跟新地图栅格值
for(int x=0; x < smap.getMapSizeX(); x++)
{
for(int y=0; y < smap.getMapSizeY(); y++)
{
/// @todo Sort out the unknown vs. free vs. obstacle thresholding
GMapping::IntPoint p(x, y);
double occ=smap.cell(p);
if(occ < 0)
map_.map.data[MAP_IDX(map_.map.info.width, x, y)] = -1;
else if(occ > occ_thresh_)
{
//map_.map.data[MAP_IDX(map_.map.info.width, x, y)] = (int)round(occ*100.0);
map_.map.data[MAP_IDX(map_.map.info.width, x, y)] = 100;
}
else
map_.map.data[MAP_IDX(map_.map.info.width, x, y)] = 0;
}
}
got_map_ = true;
//make sure to set the header information on the map
map_.map.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
map_.map.header.frame_id = tf_.resolve( map_frame_ );
sst_.publish(map_.map);
}
// scanmatcher/scanmatcher.cpp 简化版程序
double ScanMatcher::registerScan(ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings){
IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp); // 得到激光起始点世界坐标
// 遍历每条激光线
for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++)
if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r>m_usableRange) continue;
Point phit=lp;
phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle);
phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle);
IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit);
map.cell(p1).update(true,phit);
}
addScan
粒子滤波伪代码:参考概率机器人 英文版
粒子滤波流程:
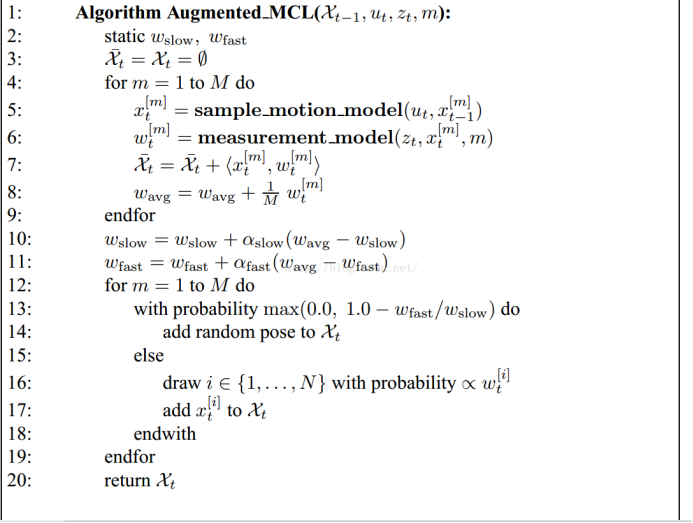
运动模型:

处理计算过程:

主要过程:
-
scanMath 得到每个粒子的权重 it—>weight (当前匹配结果+之前路径权重)和it—> weightSUM,以及Neff作为判断是否需要重采样的依据
-
updateTreeWeights: 把当前weight值根据parent关系传递给之前节点。如上图所示:parent weight = sum(child weight)
-
如果需要重采样,则根据一定规则,删除一些权重较低的粒子,并增加一些权重较大粒子。如果不需要重采样,则跟新父子关系,产生新的节点即可。
顶层代码如下:
gmapping/src/slam_gmapping.cpp
bool SlamGMapping::addScan(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan, GMapping::OrientedPoint& gmap_pose)
{
// GMapping wants an array of doubles...
double* ranges_double = new double[scan.ranges.size()];
GMapping::RangeReading reading(scan.ranges.size(),
ranges_double,
gsp_laser_,
scan.header.stamp.toSec());
reading.setPose(gmap_pose);
return gsp_->processScan(reading);
}
gridfastslam/gridslamprocessor_tree.cpp
bool GridSlamProcessor::processScan(const RangeReading & reading, int 0 = 0){
/**retireve the position from the reading, and compute the odometry*/
m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose=reading.getPose();
//write the state of the reading and update all the particles using the motion model
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
OrientedPoint& pose(it->pose);
pose=m_motionModel.drawFromMotion(it->pose, relPose, m_odoPose);
} // 通过里程计计算新粒子运动后的位置
...
// 算出里程计在这个周期内跑了多远
OrientedPoint move=relPose-m_odoPose;
move.theta=atan2(sin(move.theta), cos(move.theta));
m_linearDistance+=sqrt(move*move);
m_angularDistance+=fabs(move.theta);
//下次迭代开始
m_odoPose=relPose;
bool processed=false;
// 如果里程计大于某个阈值,就处理一批激光数据。可参照视觉SLAM关键帧的内在含义
if ( m_linearDistance>m_linearThresholdDistance
|| m_angularDistance>m_angularThresholdDistance){
//把激光雷达数据转换成openslam_gmapping可以读懂的格式
double * plainReading = new double[m_beams];
for(unsigned int i=0; i<m_beams; i++){
plainReading[i]=reading[i];
}
//为每个粒子进行scanMatch,计算出每个粒子的最优位姿
scanMatch(plainReading);
updateTreeWeights(false);//由于scanmatch之中对粒子的权重进行了更新,各个粒子的轨迹上的累计权重 都需要重新计算
resample(plainReading, adaptParticles);
updateTreeWeights(false);
m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose; //update the past pose for the next iteration
m_linearDistance=0;
m_angularDistance=0;
m_count++;
processed=true;
//keep ready for the next step
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
it->previousPose=it->pose;
}
}
return processed;
}
scanMatch(plainReading);
struct TNode{
OrientedPoint pose: the pose of the robot in the trajectory
double weight: the weight of the particle at that point in the trajectory
double accWeight: the cumulative weight of the particle
TNode* parent: the parent node in the tree
int childs: the number of childs
};
/**This class defines a particle of the filter. Each particle has a map, a pose, a weight and retains the current node in the trajectory tree*/
struct Particle{
ScanMatcherMap map;
OrientedPoint pose;
/** The pose of the robot at the previous time frame (used for computing thr odometry displacements) */
OrientedPoint previousPose;
double weight;
double weightSum; /** The cumulative weight of the particle */
double gweight;
int previousIndex;/** The index of the previous particle in the trajectory tree */
TNode* node; /** Entry to the trajectory tree */
};
/**Just scan match every single particle.If the scan matching fails, the particle gets a default likelihood.*/
inline void GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch(const double* plainReading){
// sample a new pose from each scan in the reference
double sumScore=0;
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
m_matcher.likelihoodAndScore(s, l, it->map, it->pose, plainReading); //l is the likelihood
sumScore+=score;
it->weight+=l;
it->weightSum+=l;
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.computeActiveArea(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
}
}
updateTreeWeights(false);
void GridSlamProcessor::updateTreeWeights(bool weightsAlreadyNormalized){
if (!weightsAlreadyNormalized) { normalize();}
resetTree(); //整个tree,所有参数置0
propagateWeights();
}
inline void GridSlamProcessor::normalize(){ // 各个particle的weight值标准化,得到m_weights,用于propagateWeights
//normalize the log m_weights
double gain=1./(m_obsSigmaGain*m_particles.size());
double lmax= -std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
lmax=it->weight>lmax?it->weight:lmax;
}
m_weights.clear();
double wcum=0;
for (std::vector<Particle>::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
m_weights.push_back(exp(gain*(it->weight-lmax)));
wcum+=m_weights.back();
//cout << "l=" << it->weight<< endl;
}
m_neff=0; // 离散度计算,作为是否重采样的判断参数
for (std::vector<double>::iterator it=m_weights.begin(); it!=m_weights.end(); it++){
*it=*it/wcum;
double w=*it;
m_neff+=w*w;
}
m_neff=1./m_neff;
}
double GridSlamProcessor::propagateWeights(){ //每个粒子通过当前weight值,向其parent传递。
double lastNodeWeight=0;
double aw=0; // sum of the weights in the
std::vector<double>::iterator w=m_weights.begin();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
double weight=*w;
aw+=weight;
TNode * n=it->node;
n->accWeight=weight;
lastNodeWeight+=propagateWeight(n->parent,n->accWeight);
w++;
}
if (fabs(aw-1.0) > 0.0001 || fabs(lastNodeWeight-1.0) > 0.0001) {
cerr << "root->accWeight=" << lastNodeWeight << " sum_leaf_weights=" << aw << endl;
assert(0);
}
return lastNodeWeight;
}
double propagateWeight(GridSlamProcessor::TNode* n, double weight){
if (!n) return weight;
double w=0;
n->visitCounter++;
n->accWeight+=weight; //所有childs 的weight都传递来
if (n->visitCounter==n->childs){ //迭代向前传递
w=propagateWeight(n->parent,n->accWeight);
}
assert(n->visitCounter<=n->childs);
return w;
}
resample(plainReading, adaptParticles);
//原理:粒子集对目标分布的近似越差,则权重的方差越大。因此用Neff作为权重值离差的量度/
//很多粒子的权重都变得很小,可以忽略了,只有少数粒子的权重比较大。并且粒子权值的方差随着时间增大,状态空间中的有效粒子数较少。
//随着无效采样粒子数目的增加,使得大量的计算浪费在对估计后验滤波概率分布几乎不起作用的粒子上,使得估计性能下降,
inline bool GridSlamProcessor::resample(const double* plainReading, int adaptSize, const RangeReading* ){
bool hasResampled = false;
TNodeVector oldGeneration;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_particles.size(); i++){
oldGeneration.push_back(m_particles[i].node);
}
if (m_neff<m_resampleThreshold*m_particles.size()){ //m_resampleThreshold =.5
uniform_resampler<double, double> resampler;
m_indexes=resampler.resampleIndexes(m_weights, adaptSize);
ParticleVector temp;
unsigned int j=0;
std::vector<unsigned int> deletedParticles; //this is for deleteing the particles which have been resampled away.
// cerr << "Existing Nodes:" ;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_indexes.size(); i++){
while(j<m_indexes[i]){
deletedParticles.push_back(j); // delete nodes
j++;
}
if (j==m_indexes[i]) j++;
// find the children of m_indexes[i] node
Particle & p=m_particles[m_indexes[i]];
TNode* node=0;
TNode* oldNode=oldGeneration[m_indexes[i]];
node=new TNode(p.pose, 0, oldNode, 0);
node->reading=0;
temp.push_back(p);
temp.back().node=node;
temp.back().previousIndex=m_indexes[i];
}
while(j<m_indexes.size()){
deletedParticles.push_back(j);
j++;
}
for (unsigned int i=0; i<deletedParticles.size(); i++){
delete m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node; //delete nodes
m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node=0;
}
//Copying Particles and Registering scans...
m_particles.clear();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=temp.begin(); it!=temp.end(); it++){
it->setWeight(0);
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
m_particles.push_back(*it);//
}
hasResampled = true;
} else {
int index=0;
TNodeVector::iterator node_it=oldGeneration.begin();
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){
//create a new node in the particle tree and add it to the old tree
TNode* node=0;
node=new TNode(it->pose, 0.0, *node_it, 0);
node->reading=0;
it->node=node;
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
it->previousIndex=index;
index++;
node_it++;
}
}
return hasResampled;
}
/*Implementation of the above stuff*/
template <class Particle, class Numeric>
std::vector<unsigned int> uniform_resampler<Particle, Numeric>:: resampleIndexes(const std::vector<Particle>& particles, int nparticles) const{
Numeric cweight=0; //compute the cumulative weights
unsigned int n=0;
for (typename std::vector<Particle>::const_iterator it=particles.begin(); it!=particles.end(); ++it){
cweight+=(Numeric)*it;
n++;
}
if (nparticles>0) n=nparticles;
Numeric interval = cweight/n; //compute the interval 4.5
Numeric target=interval*::drand48(); //compute the initial target weight ::drand48() [0,1)之间保留4位小数的随机数
cweight=0; //compute the resampled indexes
std::vector<unsigned int> indexes(n);
n=0;
unsigned int i=0;
for (typename std::vector<Particle>::const_iterator it=particles.begin(); it!=particles.end(); ++it, ++i){
cweight+=(Numeric)* it;
while(cweight>target){
indexes[n++]=i;
target+=interval;
}
}
return indexes;
}
/* test code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float particles[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
float interval = 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10;
interval /= 10.0;
float target = interval*0.9;
int n = 10;
std::vector<float> indexes(n);
cout << "interval:" << interval << " target:" <<target << endl;
float cweight = 0;
n = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++ )
{
cweight += particles[i];
while(cweight > target)
{
indexes[n++] = i;
target += interval;
cout <<cweight << " index " << n << " : " << i << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
*/
resample code
more weight , more possible
[template <class Particle, class Numeric>
std::vector<unsigned int> uniform_resampler<Particle, Numeric>:: resampleIndexes(const std::vector<Particle>& particles, int nparticles) const{
Numeric cweight=0;]()
//compute the cumulative weights
unsigned int n=0;
for (typename std::vector<Particle>::const_iterator it=particles.begin(); it!=particles.end(); ++it){
cweight+=(Numeric)*it;
n++;
}
if (nparticles>0) n=nparticles;
//compute the interval
Numeric interval=cweight/n;
//compute the initial target weight
Numeric target=interval*::drand48();
//compute the resampled indexes
cweight=0;
std::vector<unsigned int> indexes(n);
n=0;
unsigned int i=0;
for (typename std::vector<Particle>::const_iterator it=particles.begin(); it!=particles.end(); ++it, ++i){
cweight+=(Numeric)* it;
while(cweight>target){
indexes[n++]=i;
target+=interval;
}
}
return indexes;
}
resample
inline bool GridSlamProcessor::resample(const double* plainReading, int adaptSize, const RangeReading* reading){
unsigned int j=0;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_indexes.size(); i++){
//cerr << " " << m_indexes[i];
while(j<m_indexes[i]){
deletedParticles.push_back(j);
j++;
}
if (j==m_indexes[i]) j++;
Particle & p=m_particles[m_indexes[i]];
TNode* node=0;
TNode* oldNode=oldGeneration[m_indexes[i]];
//cerr << i << "->" << m_indexes[i] << "B("<<oldNode->childs <<") ";
node=new TNode(p.pose, 0, oldNode, 0);
//node->reading=0;
node->reading=reading;
//cerr << "A("<<node->parent->childs <<") " <<endl;
temp.push_back(p);
temp.back().node=node;
temp.back().previousIndex=m_indexes[i];
}
while(j<m_indexes.size()){
deletedParticles.push_back(j);
j++;
}
// cerr << endl;
std::cerr << "Deleting Nodes:";
for (unsigned int i=0; i<deletedParticles.size(); i++){
std::cerr <<" " << deletedParticles[i];
delete m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node;
m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node=0;
}
std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl;
//END: BUILDING TREE
std::cerr << "Deleting old particles..." ;
m_particles.clear();
std::cerr << "Done" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Copying Particles and Registering scans...";
for (ParticleVector::iterator it=temp.begin(); it!=temp.end(); it++){
it->setWeight(0);
m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea();
m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading);
m_particles.push_back(*it);
}
std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl;
hasResampled = true;
}
return hasResampled;
}