Android的静默安装似乎是一个很有趣很诱人的东西,但是,用普通做法,如果手机没有root权限的话,似乎很难实现静默安装,因为Android并不提供显示的Intent调用,一般是通过以下方式安装apk:
|
1
2
3
|
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); intent.setDataAndType(Uri.fromFile(file), "application/vnd.android.package-archive"); startActivity(intent); |
但是,这并没有真正的实现静默安装,因为有用户界面,会让用户知道。那么,怎么在后台悄悄的安装APK呢?只能试图去看看Android系统源码正常安装APK的过程,我这边下载的源码是Android5.0系统的,5个G的大小,但是可能由于Android5.0有一些安全方面的更新,跟之前的版本还是有一定的差距的,但是,学会一个之后再去学另一个相似的过程,那就简单许多了,就像学会了C语言,再学Java,也并非什么难事。
Android系统把所有的Permission(权限)依据其潜在风险划分为四个等级,即"normal"、 "dangerous"、
"signature"、 "signatureOrSystem"。APK的安装对应的权限是
INSTALL_PACKAGES,权限等级属于后两者。所以,最终想实现APK的静默安装,必然需要一些特殊的处理,执行安装的这个进程,须为系统进程。
那么,我们就来看看Android自身是如何实现安装APK的。安装的命令是pm install...
我们定位到系统源码的/frameworks/base/cmds/pm/src/com/android/commands/pm/Pm.java这个文件,他实现了pm命令,我们看runInstall方法,这就是APK的安装过程。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
|
private void runInstall() { int installFlags = 0; int userId = UserHandle.USER_ALL; String installerPackageName = null; String opt; String originatingUriString = null; String referrer = null; String abi = null; while ((opt=nextOption()) != null) { if (opt.equals("-l")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_FORWARD_LOCK; } else if (opt.equals("-r")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING; } else if (opt.equals("-i")) { installerPackageName = nextOptionData(); if (installerPackageName == null) { System.err.println("Error: no value specified for -i"); return; } } else if (opt.equals("-t")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_ALLOW_TEST; } else if (opt.equals("-s")) { // Override if -s option is specified. installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL; } else if (opt.equals("-f")) { // Override if -s option is specified. installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_INTERNAL; } else if (opt.equals("-d")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_ALLOW_DOWNGRADE; } else if (opt.equals("--originating-uri")) { originatingUriString = nextOptionData(); if (originatingUriString == null) { System.err.println("Error: must supply argument for --originating-uri"); return; } } else if (opt.equals("--referrer")) { referrer = nextOptionData(); if (referrer == null) { System.err.println("Error: must supply argument for --referrer"); return; } } else if (opt.equals("--abi")) { abi = checkAbiArgument(nextOptionData()); } else if (opt.equals("--user")) { userId = Integer.parseInt(nextOptionData()); } else { System.err.println("Error: Unknown option: " + opt); return; } } if (userId == UserHandle.USER_ALL) { userId = UserHandle.USER_OWNER; installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_ALL_USERS; } final Uri verificationURI; final Uri originatingURI; final Uri referrerURI; if (originatingUriString != null) { originatingURI = Uri.parse(originatingUriString); } else { originatingURI = null; } if (referrer != null) { referrerURI = Uri.parse(referrer); } else { referrerURI = null; } // Populate apkURI, must be present final String apkFilePath = nextArg(); System.err.println(" pkg: " + apkFilePath); if (apkFilePath == null) { System.err.println("Error: no package specified"); return; } // Populate verificationURI, optionally present final String verificationFilePath = nextArg(); if (verificationFilePath != null) { System.err.println(" ver: " + verificationFilePath); verificationURI = Uri.fromFile(new File(verificationFilePath)); } else { verificationURI = null; } LocalPackageInstallObserver obs = new LocalPackageInstallObserver(); try { VerificationParams verificationParams = new VerificationParams(verificationURI, originatingURI, referrerURI, VerificationParams.NO_UID, null); mPm.installPackageAsUser(apkFilePath, obs.getBinder(), installFlags, installerPackageName, verificationParams, abi, userId); //注意!!最终就是调用这个方法来进行安装的 synchronized (obs) { while (!obs.finished) { try { obs.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } if (obs.result == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) { System.out.println("Success"); } else { System.err.println("Failure [" + installFailureToString(obs) + "]"); } } } catch (RemoteException e) { System.err.println(e.toString()); System.err.println(PM_NOT_RUNNING_ERR); } } |
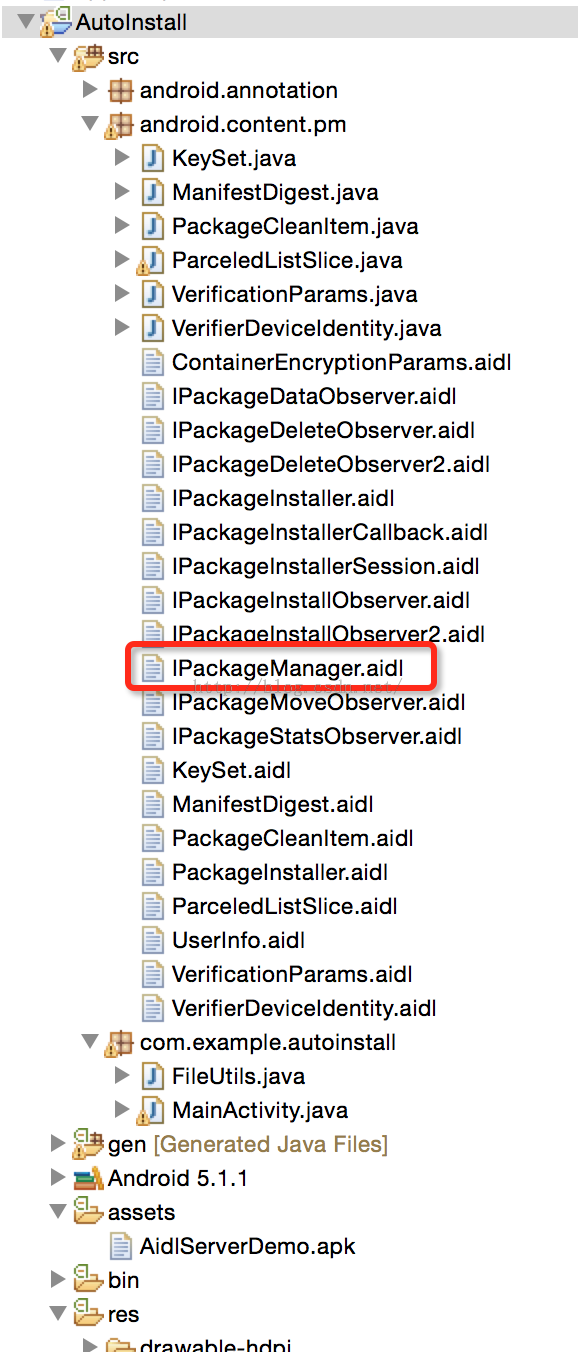
知道了这个过程之后,就大概知道怎么做了。既然系统底层把这个API屏蔽了,那就想办法去绕过这层屏蔽,来使用它。首先想到的就是使用AIDL,不知道AIDL这东西的,先问度娘去吧~~在上面的代码中,最终实现安装的那一句话,mPm.installPackageAsUser(...),mPm是个什么东西?不难发现,IPackageManager类型,那么这个类从哪里来?搜寻一下,位于/frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/pm这个包底下,拷贝到我们工程目录底下,包名不能变,只拷贝这一个文件的话,一定是不行了,会报其他的一些aidl找不到,相应地也拷贝过来。Android5.0中,aidl改动还是比较大的,所以要拷贝很多东西过来,还要进行一些改动...我也是花了挺久才改到他没报错。
最终,工程的目录如下所示~~
那么,如何来使用它呢?
- 1、先获取系统服务android.os.ServiceManager,这个又是隐藏的,怎么办?考验Java水平的时候到了~~没错,用反射机制,来获取ServiceManager类,以及该类里面的方法;
- 2、有了服务之后,我们就要去拿到IPackageManager这个对象;
- 3、调用IPackageManager里面的installPackage方法进行安装;
实现代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
|
package com.example.autoinstall; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.pm.IPackageInstallObserver2; import android.content.pm.IPackageManager; import android.content.pm.VerificationParams; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } /** * Button点击事件 * @param view */ public void install(View view) { String path = ""; if (FileUtils.isSdcardReady()) { path = FileUtils.getSdcardPath(); } else { path = FileUtils.getCachePath(this); } String fileName = path + "/AidlServerDemo.apk"; File file = new File(fileName); try { if(!file.exists()) copyAPK2SD(fileName); Uri uri = Uri.fromFile(new File(fileName)); // 通过Java反射机制获取android.os.ServiceManager Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("android.os.ServiceManager"); Method method = clazz.getMethod("getService", String.class); IBinder iBinder = (IBinder) method.invoke(null, "package"); IPackageManager ipm = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(iBinder); @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") VerificationParams verificationParams = new VerificationParams(null, null, null, VerificationParams.NO_UID, null); // 执行安装(方法及详细参数,可能因不同系统而异) ipm.installPackage(fileName, new PackageInstallObserver(), 2, null, verificationParams, ""); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } // 用于显示结果 class PackageInstallObserver extends IPackageInstallObserver2.Stub { @Override public void onUserActionRequired(Intent intent) throws RemoteException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onPackageInstalled(String basePackageName, int returnCode, String msg, Bundle extras) throws RemoteException { //returnCode<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">为1,就是安装成功</span> } }; /** * 拷贝assets文件夹的APK插件到SD * * @param strOutFileName * @throws IOException */ private void copyAPK2SD(String strOutFileName) throws IOException { FileUtils.createDipPath(strOutFileName); InputStream myInput = this.getAssets().open("AidlServerDemo.apk"); OutputStream myOutput = new FileOutputStream(strOutFileName); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int length = myInput.read(buffer); while (length > 0) { myOutput.write(buffer, 0, length); length = myInput.read(buffer); } myOutput.flush(); myInput.close(); myOutput.close(); } } |
每个版本的系统源码里面的aidl可能会不一样,所以具体调用的方法和参数,还得根据实际情况而定,需要去仔细阅读Pm.java这个文件的源码。
在其他版本可能只需要拷贝这4个文件:PackageManager.java、 IPackageDeleteObserver.aidl 、IPackagerInstallObserver.aidl、 IPackageMoveObserver.aidl
然后,还需在配置清单文件里面添加INSTALL_PACKAGE权限
|
1
|
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES"/> |
然后把该应用的uid设置为系统级别的,在manifest标签下添加以下属性
|
1
|
android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system" |
仅仅这样的话,还是没法实现静默安装,因为系统并不认为你这个app是系统级别的应用,所以,还应该对该应用的APK进行系统签名(注意:不是那个静默安装的APK,是这个实现静默安装程序的APK)。签名过程如下:
总共需要三个文件:
- 1、SignApk.jar %系统源码%/out/host/linux-x86/framework/signapk.jar
- 2、platform.x509.pem %系统源码%/build/target/product/security/platform.x509.pem
- 3、platform.pk8 %系统源码%/build/target/product/security/platform.pk8
打开终端,执行命令 java -jar SignApk.jar platform.x509.pem platform.pk8 未签名APK 签名后APK,例如
java -jar SignApk.jar platform.x509.pem platform.pk8 AutoInstall.apk AutoInstall_new.apk
之后,把签名过后的APK安装到手机上,打开,点击静默安装,在去程序页看看,发现安装成功~~
本文主要是提供了一种实现静默安装的思路,但是具体怎么做到兼容各个系统,举一反三,