1. HashMap集合(HashMap<Student,String>)的案例
HashMap<Student,String>
键:Student
要求:如果两个对象的成员变量值都相同,则为同一个对象。
值:String
HashMap是最常用的Map集合,它的键值对在存储时要根据键的哈希码来确定值放在哪里。
HashMap 中键作为对象必须重写Object的hashCode()方法和equals()方法
HashMap 底层是哈希表,哈希表的实现依赖于hashCode()方法和equals()方法
2. 代码示例:
(1)Student.java,如下:
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 7 public Student() { 8 super(); 9 } 10 11 public Student(String name, int age) { 12 super(); 13 this.name = name; 14 this.age = age; 15 } 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getAge() { 26 return age; 27 } 28 29 public void setAge(int age) { 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public int hashCode() { 35 final int prime = 31; 36 int result = 1; 37 result = prime * result + age; 38 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 39 return result; 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 44 if (this == obj) 45 return true; 46 if (obj == null) 47 return false; 48 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 49 return false; 50 Student other = (Student) obj; 51 if (age != other.age) 52 return false; 53 if (name == null) { 54 if (other.name != null) 55 return false; 56 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 57 return false; 58 return true; 59 } 60 61 }
(2)测试类HashMapDemo4,如下:
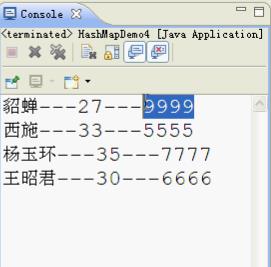
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 /* 7 * HashMap<Student,String> 8 * 键:Student 9 * 要求:如果两个对象的成员变量值都相同,则为同一个对象。 10 * 值:String 11 */ 12 public class HashMapDemo4 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 // 创建集合对象 15 HashMap<Student, String> hm = new HashMap<Student, String>(); 16 17 // 创建学生对象 18 Student s1 = new Student("貂蝉", 27); 19 Student s2 = new Student("王昭君", 30); 20 Student s3 = new Student("西施", 33); 21 Student s4 = new Student("杨玉环", 35); 22 Student s5 = new Student("貂蝉", 27); 23 24 // 添加元素 25 hm.put(s1, "8888"); 26 hm.put(s2, "6666"); 27 hm.put(s3, "5555"); 28 hm.put(s4, "7777"); 29 hm.put(s5, "9999"); 30 31 // 遍历 32 Set<Student> set = hm.keySet(); 33 for (Student key : set) { 34 String value = hm.get(key); 35 System.out.println(key.getName() + "---" + key.getAge() + "---" 36 + value); 37 } 38 } 39 }
运行结果,如下:
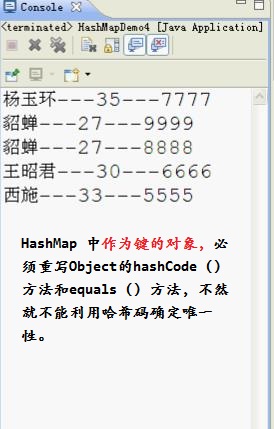
Student作为键对象,重写Object的hashCode()方法和equals()方法,(代码如上),重新运行结果,如下: