断点续传基本原理
HTTP协议中与断点续传相关的HTTP头为:Range和Content-Range标头,断点续传实现流程:
1)客户端请求下载一个文件,文件的总长度为n;已经下载了一部分文件,长度为m(单位KB)
2) 客户端主动暂停下载或网络中断,客户端请求继续下载,HTTP请求标头设置为:
Range:bytes=m-
3) 服务端收到断点续传请求,从文件的m位置开始传输,HTTP响应头设置为:
Content-Range:bytes m-n/n,服务端返回的HTTP状态码是206。
HTTP请求与响应实例(使用wireshark抓取HTTP报文):
第一次请求的请求头:
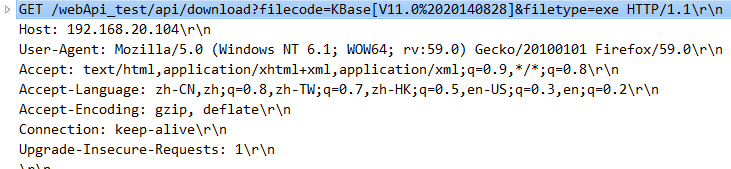
暂停后,再次请求的请求头:

某次暂停后再次发起的请求和返回的响应头:
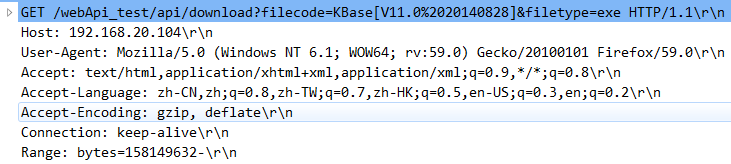
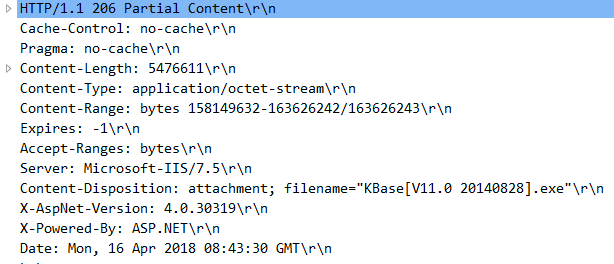
Web API提供了对上述标头的支持:
HttpRequestMessage.Headers.Range:设置请求头的Range标头,Range的类型是RangeHeaderValue,RangeHeaderValue有一个类型为ICollection<RangeItemHeaderValue>的属性Ranges,RangeItemHeaderValue有两个类型为long的属性From和To,这两个属性分别表达了请求数据的开始和结束位置。
HttpResponseHeaders.AcceptRanges属性设置Accept-Ranges标头,HttpResponseMessage.Content属性的Headers属性设置响应内容标头,q其类型为HttpContentHeaders,HttpContentHeaders.ContentDisposition属性设置Content-Disposition标头值,ContentDisposition属性类型为ContentDispositionHeaderValue,可使用ContentDispositionHeaderValue.FileName设置文件名。HttpContentHeaders.ContentTypes属性设置Content-Type标头。HttpContentHeaders.ContentRangese设置响应的消息体的数据范围。
二、示例
Get请求,调用url:http://localhost/webApi_test/api/download?filecode=KBase[V11.0%2020140828]&filetype=exe
1使用StreamContent向消息体中写数据
使用StreamContent适合将磁盘文件流直接“挂”到响应流,对于那种数据源是另一个服务,或者数据来自本地磁盘,但是无法将文件流直接挂到响应流(可能对文件要进行编码转换或加密解密等操作)的情形不适合使用StreamContent,因为直接将流“挂”到响应流,可以实现对服务器缓存的控制,已实现在服务器和客户端之间建立一个管道,一点一点地,源源不断将数据传送给客户端,而不必一次将数据都读入内存,这样极大的节省了内存,同时也使得传输大文件成为了可能。
控制器及操作:
public class DownloadController : ApiController { public HttpResponseMessage Get([FromUri]Input input) { string filePath = string.Format(@"D:工具软件{0}.{1}", input.FileCode, input.FileType); string fileName = Path.GetFileName(filePath); DiskFileProvider fileProvider = new DiskFileProvider(filePath); long entireLength = fileProvider.GetLength(); ContentInfo contentInfo = GetContentInfoFromRequest(entireLength, this.Request); Stream partialStream = fileProvider.GetPartialStream(contentInfo.From); HttpContent content = new StreamContent(partialStream, 1024); return SetResponse(content, contentInfo, entireLength,fileName); } }
获得请求信息,包括:文件的总长度,请求数据的额范围,是否支持多个范围。
private ContentInfo GetContentInfoFromRequest(long entireLength, HttpRequestMessage request) { var contentInfo = new ContentInfo { From = 0, To = entireLength - 1, IsPartial = false, Length = entireLength }; RangeHeaderValue rangeHeader = request.Headers.Range; if (rangeHeader != null && rangeHeader.Ranges.Count != 0) { //仅支持一个range if (rangeHeader.Ranges.Count > 1) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); } RangeItemHeaderValue range = rangeHeader.Ranges.First(); if (range.From.HasValue && range.From < 0 || range.To.HasValue && range.To > entireLength - 1) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); } contentInfo.From = range.From ?? 0; contentInfo.To = range.To ?? entireLength - 1; contentInfo.IsPartial = true; contentInfo.Length = entireLength; if (range.From.HasValue && range.To.HasValue) { contentInfo.Length = range.To.Value - range.From.Value + 1; } else if (range.From.HasValue) { contentInfo.Length = entireLength - range.From.Value; } else if (range.To.HasValue) { contentInfo.Length = range.To.Value + 1; } } return contentInfo; }
设置响应,对上述介绍的响应内容标头字段进行合理的设置。
private HttpResponseMessage SetResponse(HttpContent content, ContentInfo contentInfo, long entireLength,string fileName) { HttpResponseMessage response = new HttpResponseMessage(); //设置Accept-Ranges:bytes response.Headers.AcceptRanges.Add("bytes"); //设置传输部分数据时,如果成功,那么状态码为206 response.StatusCode = contentInfo.IsPartial ? HttpStatusCode.PartialContent : HttpStatusCode.OK; //设置响应内容 response.Content = content; //Content-Disposition设置为attachment,指示浏览器客户端弹出下载框。 response.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition = new ContentDispositionHeaderValue("attachment"); //设置下载文件的文件名 response.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName = fileName; //设置Content-Type:application/octet-stream response.Content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/octet-stream"); //设置响应消息内容长度 response.Content.Headers.ContentLength = contentInfo.Length; if (contentInfo.IsPartial) { //设置响应内容的起始位置 response.Content.Headers.ContentRange = new ContentRangeHeaderValue(contentInfo.From, contentInfo.To, entireLength); } return response; }
数据源访问接口:
public interface IFileProvider { bool Exists(); Stream GetPartialStream(long offset); long GetLength(); }
数据源接口实现
public class DiskFileProvider : IFileProvider,IDisposable { private Stream fileStream; private string filePath; public DiskFileProvider(string filePath) { try { this.filePath = filePath; this.fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read,FileShare.Read); } catch (Exception ex) { } } public bool Exists() { return File.Exists(filePath); } public Stream GetPartialStream(long offset) { if (offset > 0) { fileStream.Seek(offset, SeekOrigin.Begin); } return fileStream; } public long GetLength() { return fileStream.Length; } public void Dispose() { if(fileStream!=null)fileStream.Close(); } }
数据模型:请求参数模型和请求数据信息模型
public class Input { public string FileCode { set; get; } public string FileType { set; get; } } public class ContentInfo { public long From {set;get;} public long To { set; get; } public bool IsPartial { set; get; } public long Length { set; get; } }
2使用PushStreamContent
为了使用PushStreamContent需要对IFileProvider进行改造,如下:
public interface IFileProvider { long Offset{set;get;} bool Exists(); Stream GetPartialStream(long offset); Task WriteToStream(Stream outputStream, HttpContent content, TransportContext context); long GetLength(); }
可以发现与原来的接口相比较多了Offset属性和WriteToStream方法。
下面是IFileProvider接口的实现,为了使用PushStreamContent,实现接口的WriteToStream方法,这里需要注意:
PushStreamContent构造函数有几个重载的方法,他们的共同特点是含有委托类型的参数。而本文采用了有返回值的参数,经实践发现采用无返回值的参数,会随机地生成一条windows警告日志。另外调用FileStream.Read函数时,其参数都是int类型的,但是FileStream.Length却是long类型的,在使用时就需要转型,不要将FileStream.Length,而应在(int)Math.Min(length, (long)buffer.Length)这部分执行转型,这样如果FileStream.Length真的比int类型的最大值还大,那么也不会因为转型而出现错误。
public class ByteToStream : IFileProvider { private string filePath; public long Offset{set;get;} public ByteToStream(string filePath) { try { this.filePath = filePath; } catch (Exception ex) { } } public bool Exists() { return File.Exists(filePath); } public Stream GetPartialStream(long offset) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public long GetLength() { using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { return fileStream.Length; } } public async Task WriteToStream(Stream outputStream, HttpContent content, TransportContext context) { try { var buffer = new byte[1024000]; using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { fileStream.Seek(Offset, SeekOrigin.Begin); long length = fileStream.Length; var bytesRead = 1; while (length > 0 && bytesRead > 0) { bytesRead = fileStream.Read(buffer, 0, (int)Math.Min(length, (long)buffer.Length)); await outputStream.WriteAsync(buffer, 0, bytesRead); length -= bytesRead; } } } catch (HttpException ex) { return; } finally { outputStream.Close(); } }
}
控制器操作相应地变为:
public HttpResponseMessage Get([FromUri]Input input) { string filePath = string.Format(@"D:工具软件{0}.{1}", input.FileCode, input.FileType); string fileName = Path.GetFileName(filePath); IFileProvider fileProvider = new ByteToStream(filePath); long entireLength = fileProvider.GetLength(); ContentInfo contentInfo = GetContentInfoFromRequest(entireLength, this.Request); Func<Stream, HttpContent, TransportContext, Task> onStreamAvailable = fileProvider.WriteToStream; HttpContent content = new PushStreamContent(onStreamAvailable); return SetResponse(content, contentInfo, entireLength,fileName); }
---------------------------------------------------------------------
转载与引用请注明出处。
时间仓促,水平有限,如有不当之处,欢迎指正。