可以使用HttpClient这个调用Web API,下面是HttpClient的定义,列举了一些常用的方法,其中还有一些没有列举,包括重载的方法。
public class HttpClient : HttpMessageInvoker { public HttpClient(); public HttpClient(HttpMessageHandler handler); //统一资源标识符 (URI) 的基地址 public Uri BaseAddress { get; set; } //获取或设置请求超时前等待的毫秒数 public TimeSpan Timeout { get; set; } //发送异步GET请求 public Task<HttpResponseMessage> GetAsync(Uri requestUri); //发送异步POST请求 public Task<HttpResponseMessage> PostAsync(Uri requestUri, HttpContent content); //发生异步请求,可以指定HTTP动作 public Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request); }
HttpClient的使用
上面几个方法GetAsync、PostAsync、SendAsync的返回值类型都是Task<HttpResponseMessage>,可以调用Task<TResult>.Result属性获得类型为HttpResponseMessage的实例。HttpResponseMessage的Content属性有一个异步方法ReadAsStringAsync可以获得响应消息体的内容(服务端传过来的字符串),使用ReadAsAsync<T>方法已获得反序列化后的CLR类型数据。
例:读取字符串。
为了看清返回类型,客户端每个方法的调用返回值赋给一个强类型的变量,方便观察返回值和理解,也可以将返回值变量赋给一个var类型的变量。
客户端:
public static void TestClient() { string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.GetAsync(url); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<string> contentStr = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); contentStr.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(contentStr.Result); } Console.ReadLine(); }
服务端:
public class TestApiController : ApiController { public IHttpActionResult Get() { return Ok("hello web api client"); } }
路由配置:
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute( name: "DefaultApi", routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}", defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional } );
例:获得实体,并序列化显示
调用响应的Content.ReadAsAsync<T>方法获得实体。
客户端:
public static void TestClient() { string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi/1"; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.GetAsync(url); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<DataModel> model = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<DataModel>(); model.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(model.Result,Formatting.Indented)); } Console.ReadLine(); }
服务端(路由配置同上):
public IHttpActionResult Get(int id = 1) { DataModel model = new DataModel { Id = id, Field1Name = "f1", Field2Name = "f2", DT = DateTime.Now }; return Ok(model); }
返回结果:
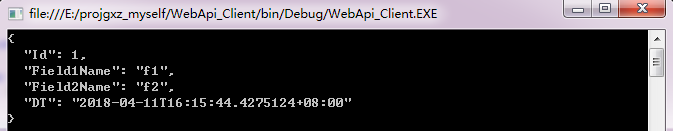
例:客户端向服务端传递复杂数据。
使用SendAsync方法,但是注意无法发送GET和HEAD请求。下面的例子向服务端发送PUT请求,并且将发送给服务端的数据放入了请求消息的消息体中,为了让服务端获取消息体内容的格式信息以便其选择多媒体格式化器绑定模型,将HttpContent.Headers.ContentType设置为application/json类型,因为向请求消息体中写入的是JSON格式的字符串。
客户端:
public static void TestClient() { string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; var modelRequest = new { Id = 1, Field1Name = "1name", Field2Name = "2name", DT = DateTime.Now }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { using (HttpContent content = new StringContent(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(modelRequest))) { content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"); using (HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Put, url)) { request.Content = content; Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.SendAsync(request); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<DataModel> model = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<DataModel>(); model.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(model.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } } } Console.ReadLine(); }
服务端:
public IHttpActionResult Put(DataModel model) { return Ok(model); }
路由:
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute( name: "DefaultApi", routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}", defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
例:将数据写入请求消息体的方式
有几种方式为HttpRequestMessage.Content属性赋值,可以使用FormUrlEncodedContent、StringContent,他们都派生自ByteArrayContent。FormUrlEncodedContent指定的多媒体格式为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,如果将写入请求消息体的内容格式设置为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,即HttpContent.Headers.ContentType = application/x-www-form-urlencoded,可以正常传递数据,不设置就默认指定为application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型。
客户端调用
var list = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>> { new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Field21", "f1"), new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Field22", "f2") }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { using (HttpContent content = new FormUrlEncodedContent(list)) { content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"); using (HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, url)) { request.Content = content; Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.SendAsync(request); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<Model2> model = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model2>(); model.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(model.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } } } Console.ReadLine();
服务器:
public IHttpActionResult Post(Model2 model) { return Ok(model); } public class Model2 { public string Field21 { get; set; } public string Field22 { get; set; } }
运行结果:
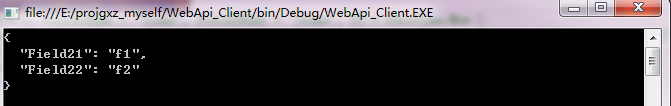
如果将上述客户端代码的content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
改为:content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"),则服务端无法正常为操作参数赋值:
此外FormUrlEncodedContent不适合传递集合或数据模型中属性为集合类型的实体。如下面的实体类型,若服务端接收的参数类型为Model1,则不适合使用FormUrlEncodedContent。而应使用StringContent
public class Model1 { public List<Model2> List1 { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } public class Model2 { public string Field21{get;set;} public string Field22{get;set;} }
例:使用HttpClientExtensions
HttpClientExtensions提供了HttpClient的扩展方法,PostAsJsonAsync<T>可以将实体T序列化为JSON格式放入请求消息体中,同样地PutAsJsonAsync也如此,只不过前者发送POST请求后者发送PUT请求。另外,他们的重载方法可以指定多媒体格式化器。
客户端:
string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; List<Model2> model2List = new List<Model2> { new Model2 { Field21 = "f1", Field22 = "f2" }, new Model2 { Field21 = "f21", Field22 = "f22" } }; Model1 model = new Model1 { Name = "集合", List1 = model2List }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.PostAsJsonAsync(url,model); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<Model1> models = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model1>(); models.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(models.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } Console.ReadLine();
服务端:
public IHttpActionResult Post(Model1 model) { return Ok(model); } public class Model1 { public List<Model2> List1 { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } public class Model2 { public string Field21 { get; set; } public string Field22 { get; set; } }
结果:
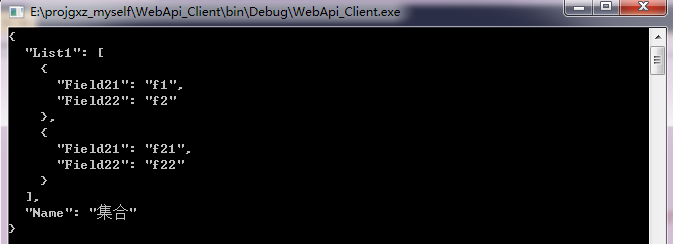
指定格式化器,下面例子指定了JSON格式化器,也可以指定BSON格式化器。
string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; List<Model2> model2List = new List<Model2> { new Model2 { Field21 = "f1", Field22 = "f2" }, new Model2 { Field21 = "f21", Field22 = "f22" } }; Model1 model = new Model1 { Name = "集合", List1 = model2List }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.PostAsync(url, model, new JsonMediaTypeFormatter()); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<Model1> models = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model1>(); models.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(models.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } Console.ReadLine();
指定BSON格式化器,并且解析响应时也要指定为BOSN格式化器,同时需要注意的是,Web API默认配置没有包含BSON格式化器,所以要在服务端添加BSON格式化器。
string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; List<Model2> model2List = new List<Model2> { new Model2 { Field21 = "f1", Field22 = "f2" }, new Model2 { Field21 = "f21", Field22 = "f22" } }; Model1 model = new Model1 { Name = "集合", List1 = model2List }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.PostAsync(url, model, new BsonMediaTypeFormatter()); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Task<Model1> models = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model1>(new List<BsonMediaTypeFormatter> { new BsonMediaTypeFormatter() }); models.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(models.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } Console.ReadLine();
---------------------------------------------------------------------
转载与引用请注明出处。
时间仓促,水平有限,如有不当之处,欢迎指正。