生成数据的时候,把数值类型float64改为改为float32
Softmax Regression Example
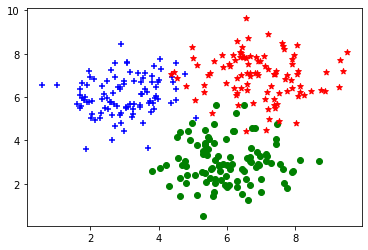
生成数据集, 看明白即可无需填写代码
'+' 从高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(3, 6, 1, 1, 0).
'o' 从高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(6, 3, 1, 1, 0)
'*' 从高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(7, 7, 1, 1, 0)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation, rc
from IPython.display import HTML
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
dot_num = 100
x_p = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num)
x_p = np.float32(x_p) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y_p = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num)
y_p = np.float32(y_p) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y = np.ones(dot_num)
y = np.float32(y) # 转换为 float32
C1 = np.array([x_p, y_p, y]).T
x_n = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num)
x_n = np.float32(x_n) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y_n = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num)
y_n = np.float32(y_n) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y = np.zeros(dot_num)
y = np.float32(y) # 转换为 float32
C2 = np.array([x_n, y_n, y]).T
x_b = np.random.normal(7., 1, dot_num)
x_b = np.float32(x_b) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y_b = np.random.normal(7., 1, dot_num)
y_b = np.float32(y_b) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
y = np.ones(dot_num)*2
y = np.float32(y) # 转换为 float32
C3 = np.array([x_b, y_b, y]).T
plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+')
plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o')
plt.scatter(C3[:, 0], C3[:, 1], c='r', marker='*')
data_set = np.concatenate((C1, C2, C3), axis=0)
np.random.shuffle(data_set)
建立模型
建立模型类,定义loss函数,定义一步梯度下降过程函数
填空一:在__init__构造函数中建立模型所需的参数
填空二:实现softmax的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数)
epsilon = 1e-12
class SoftmaxRegression():
def __init__(self):
'''============================='''
#todo 填空一,构建模型所需的参数 self.W, self.b 可以参考logistic-regression-exercise
'''============================='''
self.W = tf.Variable(shape=[2, 3], dtype=tf.float32,
initial_value=tf.random.uniform(shape=[2,3], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1))
self.b = tf.Variable(shape=[1, 3], dtype=tf.float32,initial_value=tf.zeros(shape=[1,3]))
self.trainable_variables = [self.W, self.b]
@tf.function
def __call__(self, inp):
logits = tf.matmul(inp, self.W) + self.b # shape(N, 3)
pred = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
return pred
@tf.function
def compute_loss(pred, label):
label = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(label, dtype=tf.int32), dtype=tf.float32, depth=3)
'''============================='''
#输入label shape(N, 3), pred shape(N, 3)
#输出 losses shape(N,) 每一个样本一个loss
#todo 填空二,实现softmax的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数)
'''============================='''
losses = -tf.reduce_mean(label*tf.math.log(pred+epsilon))
loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(label,axis=1), tf.argmax(pred, axis=1)), dtype=tf.float32))
return loss, accuracy
@tf.function
def train_one_step(model, optimizer, x, y):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
pred = model(x)
loss, accuracy = compute_loss(pred, y)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
return loss, accuracy
实例化一个模型,进行训练
model = SoftmaxRegression()
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
x1, x2, y = list(zip(*data_set))
x = list(zip(x1, x2))
for i in range(1000):
loss, accuracy = train_one_step(model, opt, x, y)
if i%50==49:
print(f'loss: {loss.numpy():.4}\t accuracy: {accuracy.numpy():.4}')
loss: 0.3221 accuracy: 0.36
loss: 0.2854 accuracy: 0.7067
loss: 0.2592 accuracy: 0.81
loss: 0.2397 accuracy: 0.84
loss: 0.2246 accuracy: 0.8633
loss: 0.2125 accuracy: 0.88
loss: 0.2025 accuracy: 0.8833
loss: 0.1941 accuracy: 0.89
loss: 0.187 accuracy: 0.8867
loss: 0.1808 accuracy: 0.8867
loss: 0.1754 accuracy: 0.8833
loss: 0.1705 accuracy: 0.8867
loss: 0.1662 accuracy: 0.89
loss: 0.1623 accuracy: 0.8933
loss: 0.1588 accuracy: 0.8933
loss: 0.1556 accuracy: 0.8967
loss: 0.1526 accuracy: 0.8967
loss: 0.1499 accuracy: 0.8967
loss: 0.1474 accuracy: 0.9
loss: 0.1451 accuracy: 0.9
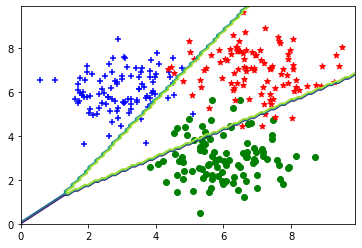
结果展示,无需填写代码
plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+')
plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o')
plt.scatter(C3[:, 0], C3[:, 1], c='r', marker='*')
x = np.arange(0., 10., 0.1)
y = np.arange(0., 10., 0.1)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
inp = np.array(list(zip(X.reshape(-1), Y.reshape(-1))), dtype=np.float32)
print(inp.shape)
Z = model(inp)
Z = np.argmax(Z, axis=1)
Z = Z.reshape(X.shape)
plt.contour(X,Y,Z)
plt.show()
(10000, 2)