知识点:
1、事务的隔离级别和事务的传播行为
2、配置声明式事务(XML方式和注解方式)
3、事务不生效的情况
一、Spring事务配置
在项目开发过程中经常会使用事务来确保数据的一致性。根据网上的资料整理一下在spring中配置事务的几种方式。无论是哪种方式都需要在配置文件中配置连接池和事务管理器,代码如下。
<!-- 读取配置文件 --> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:database.properties</value> <value>classpath:service.properties</value> </list> </property> <property name="fileEncoding" value="UTF-8" /> <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="false" /> </bean> <!--连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${db.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${db.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${db.password}" /> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean>
1、声明式事务管理
1.1 基于AspectJ的XML方式的配置 这是我觉得最好的方式,基于aop配置,当新增的方法要使用事务管理时,无需修改代码。首先在配置文件xml中引入aop和tx的命名空间
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd"
1.2 然后在xml中加入aop的配置。下面的配置就是在services的切入点上应用txAdvice的增强,services的切入点就是ymy.com.service.impl包下的所有方法应用txAdvice的增强。
然后txAdvice是在所有以create,add,delete,update,change开头的方法上加上事务管理。
<!-- 定义事务通知 (事务的增强)--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!-- 定义方法的过滤规则 --> <tx:attributes> <!-- 所有方法都使用事务 --> <!-- propagation:事务传播行为 isolation:事务隔离 read-only:只读 rollback-for:发生哪些异常回滚 no-rollback-for:发生哪些异常不回滚 timeout:过期信息 --> <tx:method name="create*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="change*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 定义AOP配置 配置切面 --> <aop:config> <!-- 定义一个切入点 --> <aop:pointcut id="services" expression="execution (* ymy.com.service.impl.*.*(..))" /> <!-- 对切入点和事务的通知,进行适配 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="services"/> </aop:config>
采用这种方式配置,当方法是按照事务定义的规则命名时,都会加入事务管理。
2、基于注解事务管理
这种方式是我觉得最简单的,第二推荐。要采用注解的方式,需要在配置文件中开启注解事务。在默认情况下<tx:annotation-driven/>会自动使用名为"transactionManager"的事务管理器。
所以如果用户的事务管理器id为"transactionManager",则可以进一步将①处的配置简化为<tx:annotation-driven/>
<tx:annotation-driven/>还有另外两个属性:
proxy-target-class: 如果为true,则Spring将通过创建子类来代理业务类;如果为false,则使用基于接口的代理。如果使用子类代理,则需要导入CGLib.jar类库。
order: 如果业务类除事务切面外,还需要织入其他切面,则通过该属性可以控制事务切面在目标连接点的织入顺序。
<!-- 开启注解事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
在使用时只需在对应的类上添加注解@Transactional即可
@Service
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
) public class TaskService implements ITaskService { }
二、Spring事务详解
1、MySQL事务知识
2、Spring事务有7种传播行为

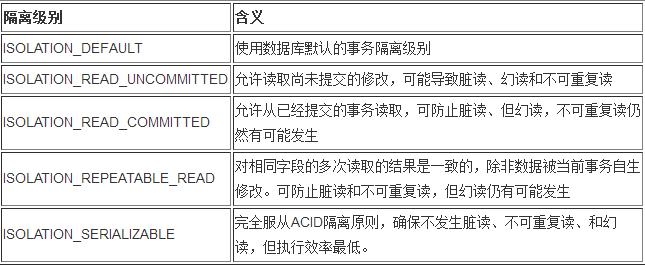
3、Spring事务的隔离级别
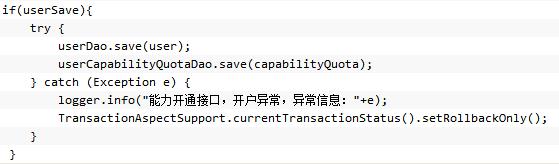
4、Spring事务回滚的注意点