1. 引入。 先上代码
1 // 本事件通信类应该支持一个事件的上半部、下半部方法的注册,以及cancel_event方法的注册。(或者不采用注册,而借助信号与槽)
2 // 外界可以通过本类对外提供的wake_event接口触发本类的do_event方法的执行。
3 // do_event方法内部如果需要等待资源,则可以调用wait_resource方法进行等待,外界使用wake_resource方法通知资源到位。
4
5 class indev_event_waiter{
6
7 boost::condition_variable cond;
8 boost::mutex mutex;
9
10 int step;
11
12 int event_t;
13 void* p_event_t; //
14
15 int wait_event(){
16 // 等待消息队列,取出事件类型
17
18 }
19
20 int wait_resource(){
21 boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex> lock(mutex);
22 cond.wait(lock);
23 }
24
25
26 public:
27 indev_event_waiter(int state): step(state){
28
29
30 }
31
32 void do_event_loop_thread(const int &id)
33 {
34 while(1)
35 {
36 switch(step)
37 {
38
39 case s_start_init:
40 {
41 // 资源初始化
42
43
44 step = s_waitevent;
45 break;
46 }
47
48 case s_waitevent:
49 {
50 event_t = wait_event(); // 等待外部调用wake_event()方法
51 step = s_dofunc_part_up;
52 break;
53 }
54
55 case s_dofunc_part_up: // 执行事件的上半部
56 {
57 // 在这里添加事件的上半部的处理函数
58 // ...
59
60 // 可选方案:
61 // 借助信号与槽机制,将事件的上半部的处理函数作为槽函数,在此处维护一个信号或其引用?
62
63 step = s_wait_resource;
64 break;
65 }
66
67 case s_wait_resource:
68 {
69 int type = wait_resource(); // 等待外部调用wake_resource()方法
70
71 if(type == t_resource_for_funcpartdown_gotready){
72 step = s_dofunc_part_down;
73 }
74 else if(type == t_cancel_funcpartdown){
75 step = s_waitevent;
76 }
77
78 break;
79 }
80 case s_dofunc_part_down: // 执行事件的下半部
81 {
82 // 在这里添加事件的下半部的处理函数
83 // ...
84
85 // 事件的下半部分完成以后,重新回到等待下一轮事件的状态。
86 step = s_waitevent;
87 break;
88 }
89
90 default:
91 break;
92 }
93 }
94 }
95
96
97 #if 1
98 void create_event_loop(){
99
100 // 这里应该执行获取消息队列中的消息(可以是,事件类型 或 纯数据,或者兼有),
101 // 然后执行对应的事件,事件进行异步处理(单独放在一个线程)
102 // 比如:获取到事件类型,然后执行状态机的对应动作。event_invoke(EVENT_STOP) 这种。
103
104 boost::thread t(do_event_loop_thread, 1);
105 t.detach();
106
107 }
108 #endif
109
110 void wake_event(int event_t){
111 // 这里应该执行向消息队列发送消息,同时传递事件类型
112
113
114 }
115
116 void wake_resource(int type){
117 //唤醒资源的同时,可以传递消息。以便唤醒资源后执行不同的操作。
118 }
119
120 void cancel_funcpartdown(){ // 取消执行当前事件的下半部
121 wake_resource(t_cancel_funcpartdown);
122
123 }
124
125 };
这里产生了编译报错,104行是引发报错所在行: 本类的do_event_loop_thread成员函数不可以直接作为新创建线程的线程函数的实体。
解决办法:虽然本类的该非静态成员函数隐含了this指针,但我们仍需显示传入this指针。
下面展示解决方案的代码:
1:
创建线程,使用bind技术,来解决和上述demo一样的编译问题
1 #include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
2
3 #include <boost/bind.hpp>
4 #include <iostream>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 #include <unistd.h>
8
9 class Count
10 {
11 public:
12 Count();
13 void addCount();
14 void getCount();
15 void mainThread();
16
17 void print(int i);
18 private:
19 typedef boost::mutex::scoped_lock slock;
20 boost::mutex mutex; //for count
21 //boost::condition cond;
22 int count;
23 };
24
25 Count::Count()
26 {
27 this->count = 0;
28 }
29
30 void Count::addCount()
31 {
32
33 while(1)
34 {
35 cout<<"--11111--"<<endl;
36 sleep(1);
37
38 slock lock(this->mutex);
39 this->count++;
40 }
41 }
42
43 void Count::getCount()
44 {
45 cout<<"--22222--"<<endl;
46
47 slock lock(this->mutex);
48 this->print(this->count);
49 }
50
51 void Count::mainThread()
52 {
53 boost::thread thrd1(boost::bind(&Count::addCount, this));
54 thrd1.detach();
55 }
56
57 void Count::print(int i)
58 {
59 cout << "i = "<< i << endl;
60 }
61
62 int main()
63 {
64 Count object;
65 object.mainThread();
66 object.getCount();
67
68 sleep(6);
69 cout << "Process END!"<< endl;
70 return 0;
71 }
2:
创建线程组,使用bind技术,来解决一样的编译问题
1 #include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
2 #include <boost/bind.hpp>
3 #include <iostream>
4 using namespace std;
5 #include <unistd.h>
6 #include <sys/types.h>
7 #include <stdio.h>
8 #include <sys/syscall.h>
9
10 pid_t gettid()
11 {
12 return syscall(SYS_gettid); /*这才是内涵*/
13 }
14
15 class CTestThread
16 {
17 public:
18 CTestThread(int nNum):m_nThreadNum(nNum){}
19 ~CTestThread(){}
20
21 void TestThread(){
22 printf("Thread ID %ld -- Thread Num: %d
", gettid(), m_nThreadNum);
23 }
24
25 void BeginThread(){
26 threadGroups.create_thread(boost::bind(&CTestThread::TestThread, this));
27 }
28 private:
29 int m_nThreadNum;
30 boost::thread_group threadGroups;
31 };
32 int main(void)
33 {
34
35 CTestThread t1(11);
36 CTestThread t2(22);
37 CTestThread t3(33);
38 CTestThread t4(44);
39
40 t1.BeginThread();
41 t2.BeginThread();
42 t3.BeginThread();
43 t4.BeginThread();
44
45 while(1){
46 sleep(5);
47 cout << "pause" << endl;
48 }
49
50
51 return 0;
52 }
bind技术,看这里,参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/benxintuzi/p/4862129.html
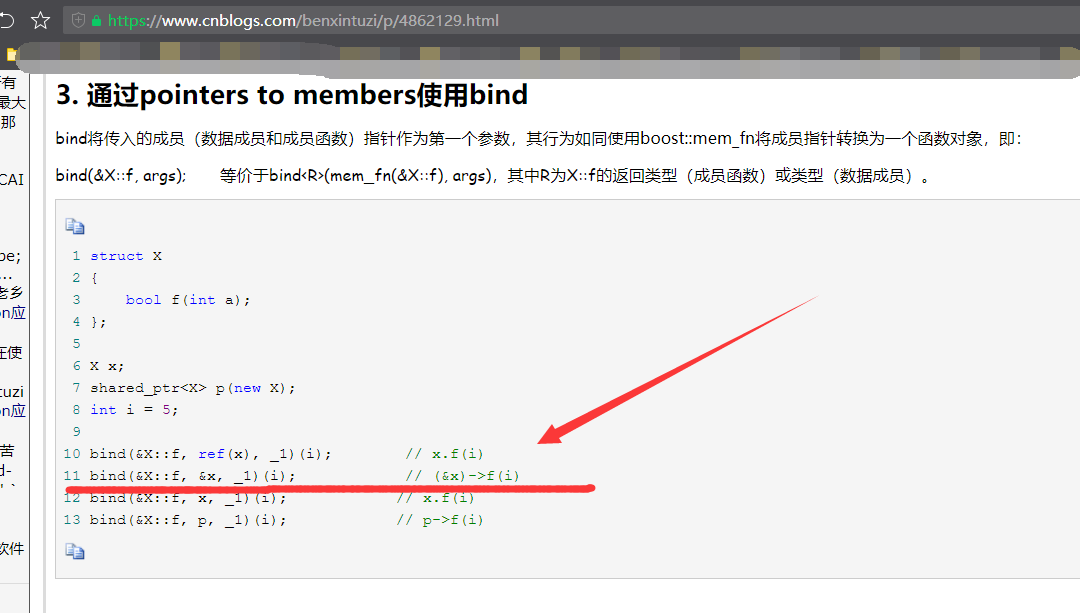
本次用到的知识点就是上述划红线处。
.