1、类别值属性的数值化
1.1 StringIndexer
StringIndexer将标签的字符串列编码为标签索引列。索引[0, numLabels)按标签频率排序,因此最常用的标签获得索引0。如果输入列是数字,我们将其转换为字符串并索引字符串值。
val df: DataFrame = spark.createDataFrame(
Seq((0, "a"), (1, "b"), (2, "c"), (3, "a"), (4, "a"), (5, "c")))
.toDF("id", "features")
// *- 4-数据查看
df.printSchema()
df.show(false)
// *- 5-引入StringIndexer转换
// .setInputCol() --输入列的名字---features---一般的情况下输入一定是来源于上一个输出
// .setOutputCol() ---用户自定义的输出,用户可以自己随便定义
val strIndex: StringIndexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("strIndexerOutput")
//fit在操作的时候实际上是会形成model,有了model才能对数据进行转换
val indexerModel: StringIndexerModel = strIndex.fit(df)
//transform是用于在一个DataFrame转化为另外一个DataFrame
val strResult: DataFrame = indexerModel.transform(df)
// *- 6-查看结果
strResult.show(false)
1.2 IndexToString
对称的StringIndexer,IndexToString将一列标签索引映射回包含原始标签作为字符串的列。
// 分类问题--好西瓜0+坏西瓜1----0好西瓜1坏西瓜
//IndexToString的过程中不能随意的转换,必须将原来的类别型的数据对应过来了
//maps a column of indices back to a new column of corresponding string values.
val indexer: IndexToString = new IndexToString()
.setLabels(indexerModel.labels)
.setInputCol("strIndexerOutput") //需要将strIndexerOutput反转回去称为abc
.setOutputCol("indexer")
indexer.transform(strResult).show(false)
// +---+--------+----------------+-------+
// |id |features|strIndexerOutput|indexer|
// +---+--------+----------------+-------+
// |0 |a |0.0 |a |
// |1 |b |2.0 |b |
// |2 |c |1.0 |c |
// |3 |a |0.0 |a |
// |4 |a |0.0 |a |
// |5 |c |1.0 |c |
// +---+--------+----------------+-------+
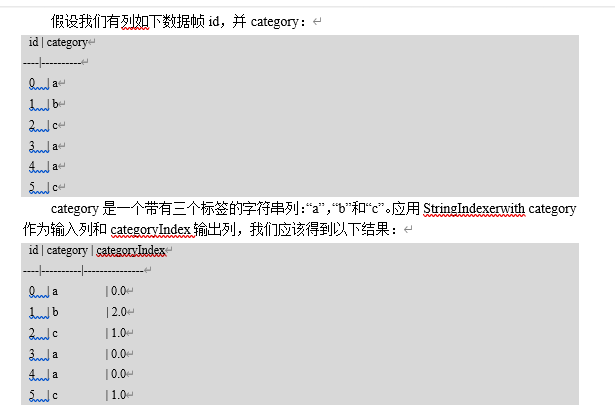
1.3 onehotcoder
val df = spark.createDataFrame(Seq(
(0, "a"),
(1, "b"),
(2, "c"),
(3, "a"),
(4, "a"),
(5, "c")
)).toDF("id", "category")
val indexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("category")
.setOutputCol("categoryIndex")
.fit(df)
val indexed = indexer.transform(df)
val encoder = new OneHotEncoder()
.setInputCol("categoryIndex")
.setOutputCol("categoryVec")
val encoded = encoder.transform(indexed)
encoded.select("id", "categoryVec").show()
}
}
结果:
+---+-------------+
| id| categoryVec|
+---+-------------+
| 0|(2,[0],[1.0])|
| 1| (2,[],[])|
| 2|(2,[1],[1.0])|
| 3|(2,[0],[1.0])|
| 4|(2,[0],[1.0])|
| 5|(2,[1],[1.0])|
+---+-------------+
2、连续值属性的离散化
Binarizer二值化
// *- 1-准备环境
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("stringIndexerOperation").setMaster("local[*]")
val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession.builder().config(conf).getOrCreate()
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN")
// 2-准备数据
val data = Array((0, 0.1), (1, 0.8), (2, 0.2))
val df: DataFrame = spark.createDataFrame(data).toDF("id","features")
// 3-使用二值化的方法进行转换
val binarizer: Binarizer = new Binarizer()
.setInputCol("features") // 想要转化为列名
.setOutputCol("biFeatures") // 随意输入
.setThreshold(0.5) // 二值化的边界
binarizer.transform(df).show(false) // 继承transform所以这还需要transform

Bucketier分箱
// 2-准备数据
val data = Array(-0.5, -0.3, 0.0, 0.2)
val df: DataFrame = spark.createDataFrame(data.map(Tuple1.apply)).toDF("features")
// 3-使用分箱的方法进行转换
// 请注意,如果您不知道目标列的上限和下限,则应添加Double.NegativeInfinity和Double.PositiveInfinity作为拆分的边界,以防止可能超出Bucketizer边界异常。
val splits = Array(Double.NegativeInfinity, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5, Double.PositiveInfinity)
val bucketizer: Bucketizer = new Bucketizer()
.setSplits(splits)
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("bucket")
bucketizer.transform(df).show(false)
// +--------+------+
// |features|bucket|
// +--------+------+
// |-0.5 |1.0 |
// |-0.3 |1.0 |
// |0.0 |2.0 |
// |0.2 |2.0 |
// +--------+------+
QuantileDiscretizer 分位数分箱(不容易控制区间)
val data = Array((0, 18.0), (1, 19.0), (2, 8.0), (3, 5.0), (4, 2.2))
var df = spark.createDataFrame(data).toDF("id", "hour")
val discretizer = new QuantileDiscretizer()
.setInputCol("hour")
.setOutputCol("result")
.setNumBuckets(3)
val result = discretizer
.fit(df)
.transform(df)
result.show()
+---+----+------+
| id|hour|result|
+---+----+------+
| 0|18.0| 2.0|
| 1|19.0| 2.0|
| 2| 8.0| 1.0|
| 3| 5.0| 1.0|
| 4| 2.2| 0.0|
3、特征组合
VectorAssembler是一个变换器,它将给定的列表组合到一个向量列中。将原始特征和由不同特征变换器生成的特征组合成单个特征向量非常有用,以便训练ML模型,如逻辑回归和决策树。 VectorAssembler接受以下输入列类型:所有数字类型,布尔类型和矢量类型。在每一行中,输入列的值将按指定的顺序连接到一个向量中。

// * 1-准备环境
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("stringIndexerOperation").setMaster("local[*]")
val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession.builder().config(conf).getOrCreate()
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN")
// * 2-准备数据
val dataset = spark.createDataFrame(
// * 3-解析数据
Seq((0, 18, 1.0, Vectors.dense(0.0, 10.0, 0.5), 1.0))
).toDF("id", "hour", "mobile", "userFeatures", "clicked")
// * 4-VectorAssemble转换
val assembler: VectorAssembler = new VectorAssembler()
.setInputCols(Array("hour", "mobile", "userFeatures"))
.setOutputCol("features")
// * 5-得到结果
assembler.transform(dataset).show(false)
结果:[[18.0,1.0,0.0,10.0,0.5],1.0]
4、数值型数据标准化和归一化
4.1标准化

val dataFrame = spark.createDataFrame(Seq(
(0, Vectors.dense(1.0, 0.5, -1.0)),
(1, Vectors.dense(2.0, 1.0, 1.0)),
(2, Vectors.dense(4.0, 10.0, 2.0))
)).toDF("id", "features")
println("StandardScaler")
val std: StandardScaler = new StandardScaler()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("stand_features")
.setWithStd(true)
.setWithMean(true)
std.fit(dataFrame).transform(dataFrame).show(false)
println("minMaxScaler")
4.2归一化
MinMaxScaler 归一到[0,1]
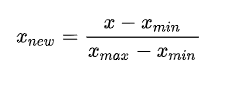
val minMaxScaler: MinMaxScaler = new MinMaxScaler()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("min_features")
minMaxScaler
.fit(dataFrame)
.transform(dataFrame)
.show(false)
MaxAbsScaler 归一到[-1,1]
val maxAbsScaler: MaxAbsScaler = new MaxAbsScaler()
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("min_features")
maxAbsScaler
.fit(dataFrame)
.transform(dataFrame)
.show(false)
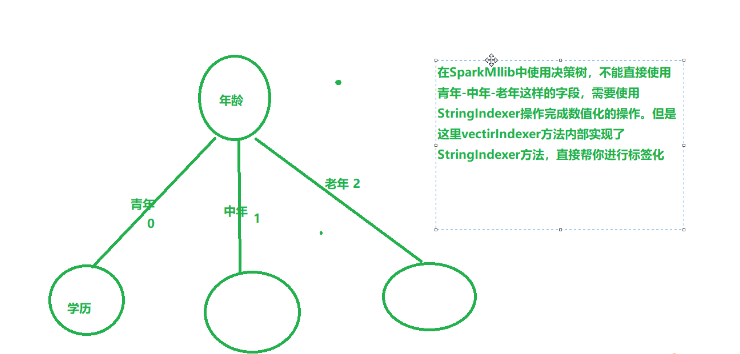
5、VectorIndexer特征索引
VectorIndexer是对数据集特征向量中的类别(离散值)特征(index categorical features categorical features )进行编号。
它能够自动判断那些特征是离散值型的特征,并对他们进行编号,具体做法是通过设置一个maxCategories,特征向量中某一个特征不重复取值个数小于maxCategories,则被重新编号为0~K(K<=maxCategories-1)。某一个特征不重复取值个数大于maxCategories,则该特征视为连续值,不会重新编号(不会发生任何改变)
- VectorIndexer是将向量索引化
- 定义一个类别值的最大值,超过类别值的最大值,视为连续值属性
- 否则就是离散值的属性,对于离散值的属性,会对每一个特征的所有的取值进行stringindexer的操作
- 如:age:100种取值
- vectorIndexer(20)设定类别值取值大于20种的视为连续值,上面的年龄就是连续值
- 用途:
- 在决策树和提升树算法中,能够确定类别特征指标,VectorIndexer可以提升这些算法的性能
- 在决策树和提升树算法中,能够确定类别特征指标,VectorIndexer可以提升这些算法的性能
// * 3-数据解析
val df: DataFrame = spark.read.format("libsvm").load(datapath)
// label+features
// * 4-VectorIndexer
val vecIndexer: VectorIndexer = new VectorIndexer()
.setMaxCategories(20)
.setInputCol("features")
.setOutputCol("vec_features")
// * 5-输出
vecIndexer.fit(df).transform(df).show(false)
- example:
+-------------------------+-------------------------+
|features |vec_features |
+-------------------------+-------------------------+
|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,5.0,7.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,1.0,1.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,5.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,1.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[4.0,7.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[4.0,3.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,4.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,0.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[9.0,5.0,7.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[9.0,1.0,1.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,5.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[2.0,1.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,4.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,0.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[8.0,4.0,9.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[8.0,0.0,2.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,6.0,2.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[3.0,2.0,0.0])|
|(3,[0,1,2],[5.0,9.0,2.0])|(3,[0,1,2],[5.0,4.0,0.0])|
+-------------------------+-------------------------+
结果分析:特征向量包含3个特征,即特征0,特征1,特征2。如Row=1,对应的特征分别是2.0,5.0,7.0.被转换为2.0,1.0,1.0。
我们发现只有特征1,特征2被转换了,特征0没有被转换。这是因为特征0有6中取值(2,3,4,5,8,9),多于前面的设置setMaxCategories(5)
,因此被视为连续值了,不会被转换。
特征1中,(4,5,6,7,9)-->(0,1,2,3,4,5)
特征2中, (2,7,9)-->(0,1,2)
输出DataFrame格式说明(Row=1):
3个特征 特征0,1,2 转换前的值
|(3, [0,1,2], [2.0,5.0,7.0])
3个特征 特征1,1,2 转换后的值
|(3, [0,1,2], [2.0,1.0,1.0])