简单说: 底层原理就是采用数组加链表:

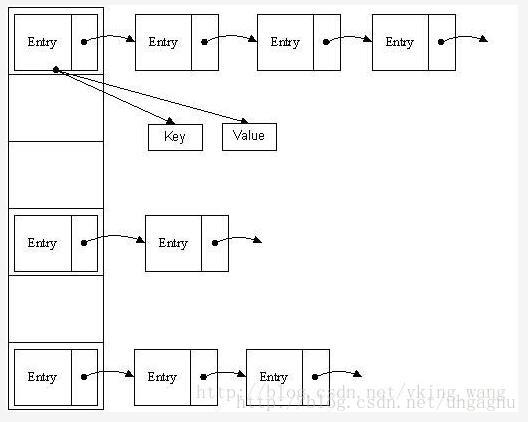
两张图片很清晰地表明存储结构:
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,大致是这样实现:
// 存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode(); // 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
// 取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); //null总是放在数组的第一个链表中
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//遍历链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//如果key在链表中已存在,则替换为新value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); //参数e, 是Entry.next
//如果size超过threshold,则扩充table大小。再散列
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
get()
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
//先定位到数组元素,再遍历该元素处的链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
null key的存取
null key总是存放在Entry[]数组的第一个元素。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
private V getForNullKey() {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
再散列rehash过程
当哈希表的容量超过默认容量时,必须调整table的大小。当容量已经达到最大可能值时,那么该方法就将容量调整到Integer.MAX_VALUE返回,这时,需要创建一张新表,将原表的映射到新表中。
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
//重新计算index
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}