面向流(BIO)与面向缓冲(NIO)
Java NIO和IO之间第一个最大的区别是,IO是面向流的,NIO是面向缓冲区的。 Java IO面向流意味着每次从流中读一个或多个字节,直至读取所有字节,它们没有被缓存在任何地方。此外,它不能前后移动流中的数据。如果需要前后移动从流中读取的数据,需要先将它缓存到一个缓冲区。 Java NIO的缓冲导向方法略有不同。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动。这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性。但是,还需要检查是否该缓冲区中包含所有您需要处理的数据。而且,需确保当更多的数据读入缓冲区时,不要覆盖缓冲区里尚未处理的数据。
一、传统的BIO
BIO(Blocking I/O)即同步阻塞I/O,在NIO出现之前主要使用BIO及新建线程的方式来解决并发请求,但这样很容易因线程瓶颈而造成限制。下面是BIO的经典编程模型(主要代码):
{ ExecutorService executor = Excutors.newFixedThreadPollExecutor(100);//线程池 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(); serverSocket.bind(8088); while(!Thread.currentThread.isInturrupted()){//当前线程未中断 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); executor.submit(new ConnectIOnHandler(socket));//为新的连接创建新的线程 } class ConnectIOnHandler extends Thread{ private Socket socket; public ConnectIOnHandler(Socket socket){ this.socket = socket; } public void run(){ while(!Thread.currentThread.isInturrupted()&&!socket.isClosed()){死循环处理读写事件 String someThing = socket.read()....//读取数据 if(someThing!=null){ ......//处理数据 socket.write()....//写数据 } } } }
之所已使用多线程,因为accept()、read()、write()三个函数都是同步阻塞的,当一个连接存在的时候,系统是阻塞的,所以利用多线程让cpu处理更多的申请。多线程的本质:
- 利用cpu的多核特性
- 当I/O阻塞系统,但cpu空闲的时候,可以利用多线程使用cpu资源
现在的多线程一般都使用线程池,可以让线程的创建和回收成本相对较低。在活动连接数不是特别高(小于单机1000)的情况下,这种模型是比较不错的,可以让每一个连接专注于自己的I/O并且编程模型简单,也不用过多考虑系统的过载、限流等问题。线程池本身就是一个天然的漏斗,可以缓冲一些系统处理不了的连接或请求。但当处理百万级的连接时,使用这种模型肯定是不实际的,让cpu去创建这么多的线程是不可能的。
二、优秀的NIO
‘优秀’是当今很流行的一个词,可以十分恰当的形容NIO在java中的重要性。从JDK1.4开始,Java提供了一系列改进的输入/输出处理的新特性,被统称为NIO(即New I/O)。新增了许多用于处理输入输出的类,这些类都被放在java.nio包及子包下,并且对原java.io包中的很多类进行改写,新增了满足NIO的功能。NIO采用内存映射文件的方式来处理输入输出,NIO将文件或文件的一段区域映射到内存中,这样就可以像访问内存一样访问文件了。NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用的方式完全不同, NIO支持面向缓冲区(Buffer)的、基于通道(Channel)的IO操作。NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
NIO中的三个重要组件:
1. 缓冲区Buffer
缓冲区有直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区之分(关于两者的区别可以看这里),它实际上也是一段内存空间。在NIO库中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的。在读取数据时,它是直接读到缓冲区中的; 在写入数据时,它也是写入到缓冲区中的。流程如下图:
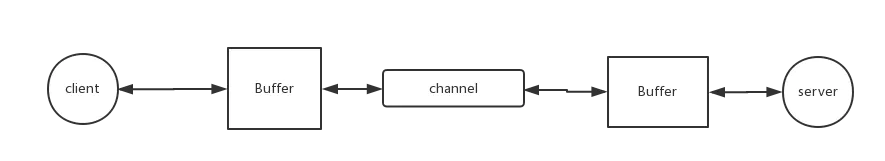
2. 通道Channel
Channel(通道)表示到实体如硬件设备、文件、网络套接字或可以执行一个或多个不同I/O操作的程序组件的开放的连接。
Channel和传统IO中的Stream很相似。主要区别为:通道是双向的,通过一个Channel既可以进行读,也可以进行写;而Stream只能进行单向操作,通过一个Stream只能进行读或者写,比如InputStream只能进行读取操作,OutputStream只能进行写操作;通道是一个对象,通过它可以读取和写入数据,当然了所有数据都通过Buffer对象来处理。我们永远不会将字节直接写入通道中,相反是将数据写入包含一个或者多个字节的缓冲区。同样不会直接从通道中读取字节,而是将数据从通道读入缓冲区,再从缓冲区获取这个字节。
3.选择器Selector
Selector类是NIO的核心类,Selector(选择器)选择器提供了选择已经就绪的任务的能力。Selector会不断的轮询注册在上面的所有channel,如果某个channel为读写等事件做好准备,那么就处于就绪状态,通过Selector可以不断轮询发现出就绪的channel,进行后续的IO操作。一个Selector能够同时轮询多个channel。这样,一个单独的线程就可以管理多个channel,从而管理多个网络连接。这样就不用为每一个连接都创建一个线程,同时也避免了多线程之间上下文切换导致的开销。
与Selector有关的一个关键类是SelectionKey,一个SelectionKey表示一个到达的事件,这2个类构成了服务端处理业务的关键逻辑。关于SelectionKey的详细介绍可以参考这篇博文
三、NIO编程
客户端代码:
public class Client { ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); public void start() throws IOException{ //打开socket通道 SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open(); sc.configureBlocking(false); sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",3400)); //创建选择器 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //将channel注册到selector中 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (true){ selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); System.out.println("keys:"+keys.size()); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); //判断此通道上是否在进行连接操作 if (key.isConnectable()){ sc.finishConnect(); //注册写操作 sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); System.out.println("server connected..."); break; }else if (key.isWritable()){ System.out.println("please input message:"); String message = scanner.nextLine(); writeBuffer.clear(); writeBuffer.put(message.getBytes()); //将缓冲区各标志复位,因为向里面put了数据标志被改变要想从中读取数据发向服务器,就要复位 writeBuffer.flip(); sc.write(writeBuffer); //注册写操作,每个chanel只能注册一个操作,最后注册的一个生效 //如果你对不止一种事件感兴趣,那么可以用“位或”操作符将常量连接起来 //int interestSet = SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE; //使用interest集合 sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE | SelectionKey.OP_READ); }else if(key.isReadable()){ System.out.print("receive message:"); SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //将缓冲区清空以备下次读取 readBuffer.clear(); int num = client.read(readBuffer); System.out.println(new String(readBuffer.array(),0, num)); //注册写操作,下一次写 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { new Client().start(); } }
服务器代码:
/** * nio是面向缓冲区的 * bio是面向流的 * @author zmrwego * @descreption * @create 2018-10-15 **/ public class Server { private Selector selector; private ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//调整缓冲区大小为1024字节 private ByteBuffer sendBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); String str; public void start() throws IOException{ //打开服务器套接字通道 ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ssc.configureBlocking(false); //服务器配置为非阻塞 即异步IO ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(3400)); //绑定本地端口 //创建选择器 selector = Selector.open(); ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//ssc注册到selector准备连接 //无限判断当前线程状态,如果没有中断,就一直执行while内容。 while(! Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){ selector.select(); //select()方法返回的值表示有多少个 Channel 可操作 Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = keys.iterator(); while (keyIterator.hasNext()){//处理客户端连接 SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next(); if (!key.isValid()){ continue; } if (key.isAcceptable()){ accept(key); } if(key.isReadable()){ read(key); } if (key.isWritable()){ write(key); } keyIterator.remove(); //移除当前的key } } } private void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{ SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); this.readBuffer.clear();//清除缓冲区,准备接受新数据 int numRead; try{ numRead = socketChannel.read(this.readBuffer); }catch (IOException e){ key.cancel(); socketChannel.close(); return; } str = new String(readBuffer.array(),0,numRead); System.out.println(str); socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); } private void write(SelectionKey key) throws IOException, ClosedChannelException{ SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); System.out.println("write:"+str); sendBuffer.clear(); sendBuffer.put(str.getBytes()); sendBuffer.flip();//反转,由写变为读 channel.write(sendBuffer); //注册读操作 下一次进行读 channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ); } private void accept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel clientChannel = ssc.accept(); clientChannel.configureBlocking(false); clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println("a new client connected "+clientChannel.getRemoteAddress()); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("sever start..."); new Server().start(); } }