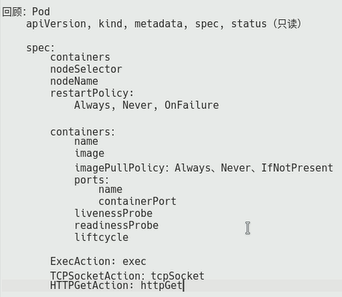
Pod控制器:
ReplicaSet: 帮助用户管理无状态的pod资源,并确保pod可以精确反应用户所定义的目标数量
主要有三个资源:
1、用户期望的pod副本,即由replicaset管控的pod副本数量
2、标签选择器,即ReplicaSet判断pod归自己管理的依据;
3、pod模板:假如现存的pod数量不够副本中定义的pod数量,就需要根据pod模板去创建新的pod
Deployment:工作在ReplicaSet之上,Deployment不直接控制pod,而是直接控制ReplicaSet从而控制pod;
DaemonSet:用于确保集群中的每一个节点只运行一个特定的pod副本,通常是实现系统级别的后台任务;
Deployment和DaemonSet都是无状态的,同时他们必须的守护进程类的,必须持续的运行在后台,
Job:
Cronjob:
StatefulSet: 实现管理有状态应用,且每一个pod副本都是被单独来管理的,拥有者pod自己独有的标识和独有的数据集,如果新的pod副本替代老的pod,需要做很多初始化操作;
StatefulSet可能是有数据有持久化存储的
ReplicaSet(简称rs)简单示例:
# kubectl explain rs
KIND: ReplicaSet VERSION: apps/v1 DESCRIPTION: ReplicaSet ensures that a specified number of pod replicas are running at any given time. FIELDS: apiVersion <string> APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string> Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object> If the Labels of a ReplicaSet are empty, they are defaulted to be the same as the Pod(s) that the ReplicaSet manages. Standard object's metadata. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object> Spec defines the specification of the desired behavior of the ReplicaSet. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status status <Object> Status is the most recently observed status of the ReplicaSet. This data may be out of date by some window of time. Populated by the system. Read-only. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
# kubectl explain rs.spec //查看spec
KIND: ReplicaSet VERSION: apps/v1 RESOURCE: spec <Object> DESCRIPTION: Spec defines the specification of the desired behavior of the ReplicaSet. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status ReplicaSetSpec is the specification of a ReplicaSet. FIELDS: minReadySeconds <integer> Minimum number of seconds for which a newly created pod should be ready without any of its container crashing, for it to be considered available. Defaults to 0 (pod will be considered available as soon as it is ready) replicas <integer> Replicas is the number of desired replicas. This is a pointer to distinguish between explicit zero and unspecified. Defaults to 1. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicationcontroller/#what-is-a-replicationcontroller selector <Object> -required- Selector is a label query over pods that should match the replica count. Label keys and values that must match in order to be controlled by this replica set. It must match the pod template's labels. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels/#label-selectors template <Object> Template is the object that describes the pod that will be created if insufficient replicas are detected. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicationcontroller#pod-template
# kubectl explain rs.spec.template //查看spec中的template,是pod的模板
KIND: ReplicaSet VERSION: apps/v1 RESOURCE: template <Object> DESCRIPTION: Template is the object that describes the pod that will be created if insufficient replicas are detected. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicationcontroller#pod-template PodTemplateSpec describes the data a pod should have when created from a template FIELDS: //下面是定义pod中的metadata和spec metadata <Object> Standard object's metadata. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object> Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
# kubectl explain rs.spec.template.spec //包含很多字段

1 KIND: ReplicaSet 2 VERSION: apps/v1 3 4 RESOURCE: template <Object> 5 6 DESCRIPTION: 7 Template is the object that describes the pod that will be created if 8 insufficient replicas are detected. More info: 9 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicationcontroller#pod-template 10 11 PodTemplateSpec describes the data a pod should have when created from a 12 template 13 14 FIELDS: 15 metadata <Object> 16 Standard object's metadata. More info: 17 https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata 18 19 spec <Object> 20 Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: 21 https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status 22 23 [root@kmaster manifests]# kubectl explain rs.spec.template.spec 24 KIND: ReplicaSet 25 VERSION: apps/v1 26 27 RESOURCE: spec <Object> 28 29 DESCRIPTION: 30 Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: 31 https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status 32 33 PodSpec is a description of a pod. 34 35 FIELDS: 36 activeDeadlineSeconds <integer> 37 Optional duration in seconds the pod may be active on the node relative to 38 StartTime before the system will actively try to mark it failed and kill 39 associated containers. Value must be a positive integer. 40 41 affinity <Object> 42 If specified, the pod's scheduling constraints 43 44 automountServiceAccountToken <boolean> 45 AutomountServiceAccountToken indicates whether a service account token 46 should be automatically mounted. 47 48 containers <[]Object> -required- 49 List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be 50 added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be 51 updated. 52 53 dnsConfig <Object> 54 Specifies the DNS parameters of a pod. Parameters specified here will be 55 merged to the generated DNS configuration based on DNSPolicy. 56 57 dnsPolicy <string> 58 Set DNS policy for the pod. Defaults to "ClusterFirst". Valid values are 59 'ClusterFirstWithHostNet', 'ClusterFirst', 'Default' or 'None'. DNS 60 parameters given in DNSConfig will be merged with the policy selected with 61 DNSPolicy. To have DNS options set along with hostNetwork, you have to 62 specify DNS policy explicitly to 'ClusterFirstWithHostNet'. 63 64 enableServiceLinks <boolean> 65 EnableServiceLinks indicates whether information about services should be 66 injected into pod's environment variables, matching the syntax of Docker 67 links. Optional: Defaults to true. 68 69 ephemeralContainers <[]Object> 70 List of ephemeral containers run in this pod. Ephemeral containers may be 71 run in an existing pod to perform user-initiated actions such as debugging. 72 This list cannot be specified when creating a pod, and it cannot be 73 modified by updating the pod spec. In order to add an ephemeral container 74 to an existing pod, use the pod's ephemeralcontainers subresource. This 75 field is alpha-level and is only honored by servers that enable the 76 EphemeralContainers feature. 77 78 hostAliases <[]Object> 79 HostAliases is an optional list of hosts and IPs that will be injected into 80 the pod's hosts file if specified. This is only valid for non-hostNetwork 81 pods. 82 83 hostIPC <boolean> 84 Use the host's ipc namespace. Optional: Default to false. 85 86 hostNetwork <boolean> 87 Host networking requested for this pod. Use the host's network namespace. 88 If this option is set, the ports that will be used must be specified. 89 Default to false. 90 91 hostPID <boolean> 92 Use the host's pid namespace. Optional: Default to false. 93 94 hostname <string> 95 Specifies the hostname of the Pod If not specified, the pod's hostname will 96 be set to a system-defined value. 97 98 imagePullSecrets <[]Object> 99 ImagePullSecrets is an optional list of references to secrets in the same 100 namespace to use for pulling any of the images used by this PodSpec. If 101 specified, these secrets will be passed to individual puller 102 implementations for them to use. For example, in the case of docker, only 103 DockerConfig type secrets are honored. More info: 104 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod 105 106 initContainers <[]Object> 107 List of initialization containers belonging to the pod. Init containers are 108 executed in order prior to containers being started. If any init container 109 fails, the pod is considered to have failed and is handled according to its 110 restartPolicy. The name for an init container or normal container must be 111 unique among all containers. Init containers may not have Lifecycle 112 actions, Readiness probes, Liveness probes, or Startup probes. The 113 resourceRequirements of an init container are taken into account during 114 scheduling by finding the highest request/limit for each resource type, and 115 then using the max of of that value or the sum of the normal containers. 116 Limits are applied to init containers in a similar fashion. Init containers 117 cannot currently be added or removed. Cannot be updated. More info: 118 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/init-containers/ 119 120 nodeName <string> 121 NodeName is a request to schedule this pod onto a specific node. If it is 122 non-empty, the scheduler simply schedules this pod onto that node, assuming 123 that it fits resource requirements. 124 125 nodeSelector <map[string]string> 126 NodeSelector is a selector which must be true for the pod to fit on a node. 127 Selector which must match a node's labels for the pod to be scheduled on 128 that node. More info: 129 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/ 130 131 overhead <map[string]string> 132 Overhead represents the resource overhead associated with running a pod for 133 a given RuntimeClass. This field will be autopopulated at admission time by 134 the RuntimeClass admission controller. If the RuntimeClass admission 135 controller is enabled, overhead must not be set in Pod create requests. The 136 RuntimeClass admission controller will reject Pod create requests which 137 have the overhead already set. If RuntimeClass is configured and selected 138 in the PodSpec, Overhead will be set to the value defined in the 139 corresponding RuntimeClass, otherwise it will remain unset and treated as 140 zero. More info: 141 https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/20190226-pod-overhead.md This 142 field is alpha-level as of Kubernetes v1.16, and is only honored by servers 143 that enable the PodOverhead feature. 144 145 preemptionPolicy <string> 146 PreemptionPolicy is the Policy for preempting pods with lower priority. One 147 of Never, PreemptLowerPriority. Defaults to PreemptLowerPriority if unset. 148 This field is alpha-level and is only honored by servers that enable the 149 NonPreemptingPriority feature. 150 151 priority <integer> 152 The priority value. Various system components use this field to find the 153 priority of the pod. When Priority Admission Controller is enabled, it 154 prevents users from setting this field. The admission controller populates 155 this field from PriorityClassName. The higher the value, the higher the 156 priority. 157 158 priorityClassName <string> 159 If specified, indicates the pod's priority. "system-node-critical" and 160 "system-cluster-critical" are two special keywords which indicate the 161 highest priorities with the former being the highest priority. Any other 162 name must be defined by creating a PriorityClass object with that name. If 163 not specified, the pod priority will be default or zero if there is no 164 default. 165 166 readinessGates <[]Object> 167 If specified, all readiness gates will be evaluated for pod readiness. A 168 pod is ready when all its containers are ready AND all conditions specified 169 in the readiness gates have status equal to "True" More info: 170 https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-network/0007-pod-ready%2B%2B.md 171 172 restartPolicy <string> 173 Restart policy for all containers within the pod. One of Always, OnFailure, 174 Never. Default to Always. More info: 175 https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle/#restart-policy 176 177 runtimeClassName <string> 178 RuntimeClassName refers to a RuntimeClass object in the node.k8s.io group, 179 which should be used to run this pod. If no RuntimeClass resource matches 180 the named class, the pod will not be run. If unset or empty, the "legacy" 181 RuntimeClass will be used, which is an implicit class with an empty 182 definition that uses the default runtime handler. More info: 183 https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/runtime-class.md This is a 184 beta feature as of Kubernetes v1.14. 185 186 schedulerName <string> 187 If specified, the pod will be dispatched by specified scheduler. If not 188 specified, the pod will be dispatched by default scheduler. 189 190 securityContext <Object> 191 SecurityContext holds pod-level security attributes and common container 192 settings. Optional: Defaults to empty. See type description for default 193 values of each field. 194 195 serviceAccount <string> 196 DeprecatedServiceAccount is a depreciated alias for ServiceAccountName. 197 Deprecated: Use serviceAccountName instead. 198 199 serviceAccountName <string> 200 ServiceAccountName is the name of the ServiceAccount to use to run this 201 pod. More info: 202 https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/ 203 204 shareProcessNamespace <boolean> 205 Share a single process namespace between all of the containers in a pod. 206 When this is set containers will be able to view and signal processes from 207 other containers in the same pod, and the first process in each container 208 will not be assigned PID 1. HostPID and ShareProcessNamespace cannot both 209 be set. Optional: Default to false. 210 211 subdomain <string> 212 If specified, the fully qualified Pod hostname will be 213 "<hostname>.<subdomain>.<pod namespace>.svc.<cluster domain>". If not 214 specified, the pod will not have a domainname at all. 215 216 terminationGracePeriodSeconds <integer> 217 Optional duration in seconds the pod needs to terminate gracefully. May be 218 decreased in delete request. Value must be non-negative integer. The value 219 zero indicates delete immediately. If this value is nil, the default grace 220 period will be used instead. The grace period is the duration in seconds 221 after the processes running in the pod are sent a termination signal and 222 the time when the processes are forcibly halted with a kill signal. Set 223 this value longer than the expected cleanup time for your process. Defaults 224 to 30 seconds. 225 226 tolerations <[]Object> 227 If specified, the pod's tolerations. 228 229 topologySpreadConstraints <[]Object> 230 TopologySpreadConstraints describes how a group of pods ought to spread 231 across topology domains. Scheduler will schedule pods in a way which abides 232 by the constraints. This field is only honored by clusters that enable the 233 EvenPodsSpread feature. All topologySpreadConstraints are ANDed. 234 235 volumes <[]Object> 236 List of volumes that can be mounted by containers belonging to the pod. 237 More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes
# vim rs_damo.yaml //ReplicaSet(简称rs)简单示例
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2 //创建pod资源数
selector: //是一个对象,表示rs所使用的标签来选择pod
matchLabels:
app: myapp 这两个标签是逻辑与,即必须符合这两个标签的pod才能被选中
release: canary //以上是rs的,以下是定义rs模板,即定义pod的
template: //此模板嵌套的对象有两个,一个人metadata,一个是spec
metadata: //表示pod的元数据
name: myapp-pod
labels: //这里必须创建标签,且符合rs标签选择器中的标准
app: myapp
release: canary
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp-container
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
ports: //pod暴露的端口
- name: http
containerPort: 80
# kubectl get rs
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
myapp 2 2 2 30s
# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
myapp-jl49s 1/1 Running 0 2m13s //这里pod的名称是: myapp(控制器的名称)+一段随机串
myapp-jzmsf 1/1 Running 0 2m13s
目前rs的副本数量是2,如果新加的一个其他pod的标签正好符合rs的标签选择器的选择标准,那么这个新加的pod就会被加进rs中,同时之前的rs由于副本数是2,所以会导致rs从原来的2个pod副本数中下掉一个
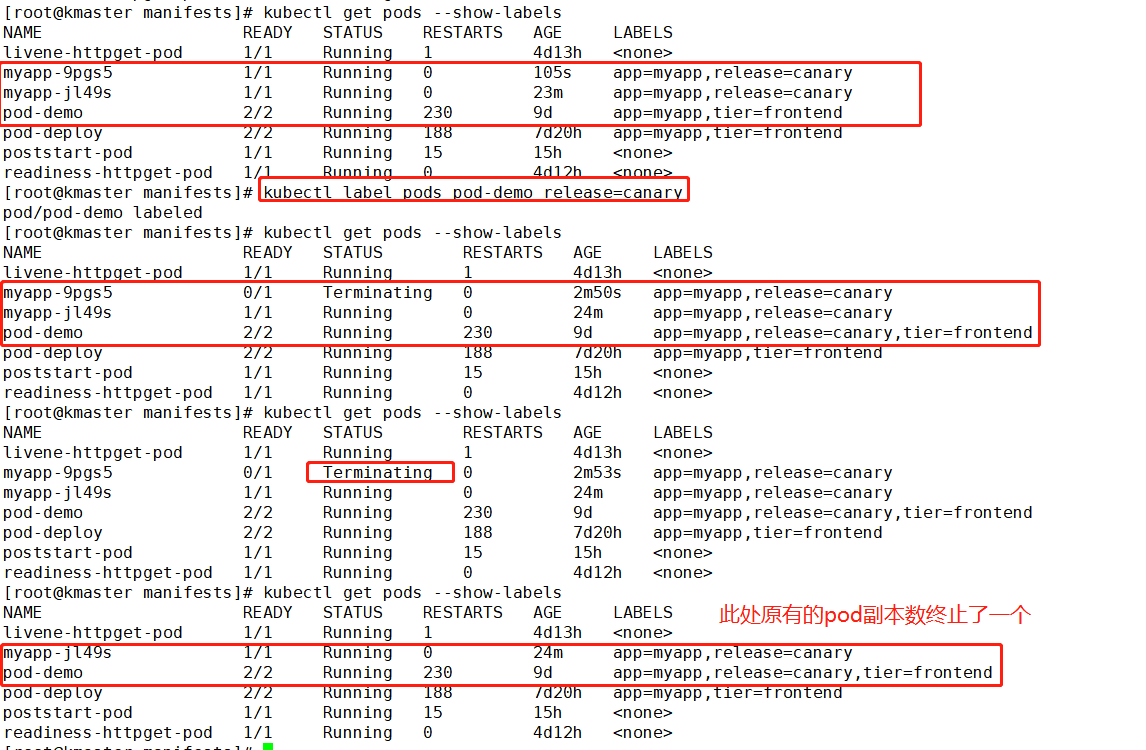
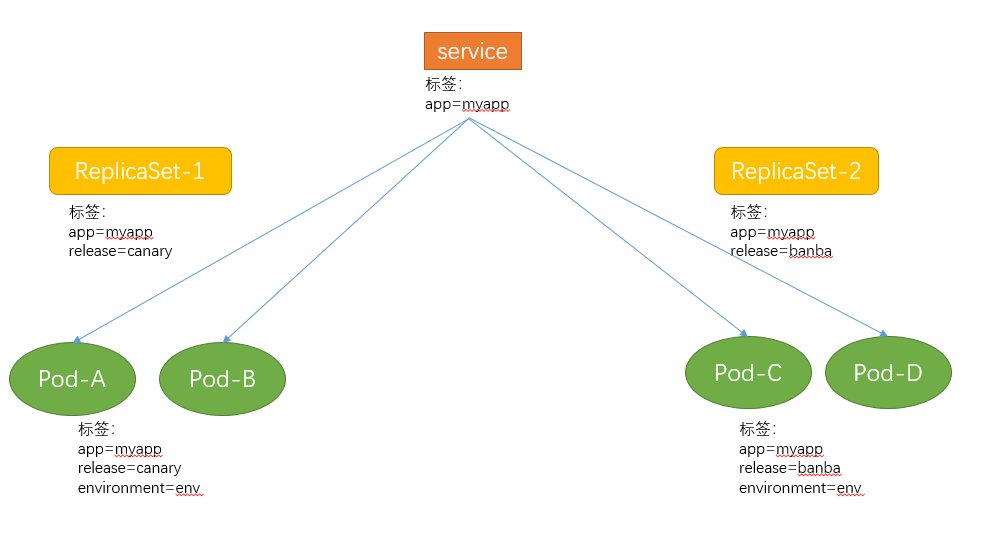
service和ReplicaSet之间的关系:
ReplicaSet创建一组pod资源后,需要被客户端访问,这时访问就需要不受pod资源生命周期的影响,即pod可能出现故障被删除,控制器就会创建另外一下pod,这时pod的名称和地址可能已经改变;所以为了让用户能有一个固定访问端点,就需要添加一个service,service也是根据标签选择器关联到pod资源,才能把客户端的资源请求端口代理至后端的pod上;
但是service和ReplicaSet之间并不是一一对应的关系,比如ReplicaSet-1有两个标签,ReplicaSet-2也有两个标签,但是两者标签不同,但是service只有一个标签,且包含在两个rs的标签中,那个rs1和rs2下的pod都可以被service选中的,即可以关联至service下;
所以service和replicaset之间没有关系,只是service可以使用replicaset创建的pod资源作为后端而已,而且service后端的pod资源可能来自多个replicaset中的pod副本,这取决于service的标签选择器;
# kubectl edit rs myapp //实时动态修改,可以动态扩缩容,也可以修改版本

# kubectl get rs -o wide
AME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR myapp 4 4 4 3h58m myapp-container ikubernetes/myapp:v2 app=myapp,release=canary
# curl 10.246.2.17 //但是此时的pod版本仍然是V1,所以改了pod控制器即replicaset,但是pod资源不会被重置的,只有pod资源被重建,版本才是新版本
Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
# kubectl delete pods myapp-jl49s //删除其中一个pod,pod控制器就会重新构建一下
# curl 10.246.1.29 //重新构建后,就是V2的版本了
Hello MyApp | Version: v2 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
以上共有四个pod,可以手动一个一个删除,然后replicaset会重新构建,这就是灰度发布
另外一种方法就是创建另外一个rs,新的rs的标签选择器跟老的标签选择器不完全相同,但是符合service的标签选择器标准,新的rs中包含的pod副本的版本是v2,这些高版本的pod通关关联至service中;
同样,可以先创建rs2,rs2上的pod资源的标签也可以不符合现有service的标签选择器的标准,等到rs2上的所有pod资源都已经ready的时候,就修改service的标签跟rs2上的pod标签一致;

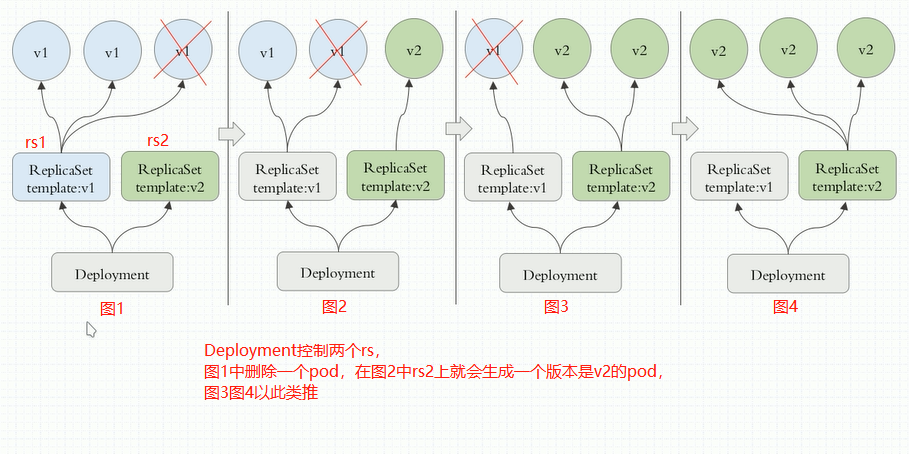
9、Kubernetes Pod控制器
# kubectl explain deploy
KIND: Deployment VERSION: apps/v1 DESCRIPTION: Deployment enables declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets. FIELDS: apiVersion <string> APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string> Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object> Standard object metadata. spec <Object> Specification of the desired behavior of the Deployment. status <Object> Most recently observed status of the Deployment.
# kubectl explain deploy.spec.strategy //启动策略
# vim deploy-damo.yaml
kind: Deployment metadata: name: myapp-deploy namespace: default spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: myapp release: canary template: metadata: labels: app: myapp release: canary spec: containers: - name: myapp image: ikubernets/myapp:v1 ports: - name: http containerPort: 80
# kubectl apply -f deploy-damo.yaml
# kubectl get deploy NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE myapp-deploy 2/2 2 2 89s # kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459 2 2 2 92s //这是deployment(myapp)自动创建的,65fb6c8459是deploy-damo.yaml中所使用的pod的template中hash,是固定的,所以可以根据pod # kubectl get pods //名字,追踪到关联的模板 NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459-5f5k4 1/1 Running 0 96s myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459-zlch8 1/1 Running 0 96s
myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459-zlch8 //myapp-deploy是deployment的名称,myapp-deploy-65fbc8459是rs的名称,myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459-zlch8是pod的名称,注意: z1ch8是随机的
# kubectl get pods -l app=myapp
修改deploy-damo.yaml中的myapp的版本为v2,然后使用apply滚动更新
此时是有两个rs,老版本的rs依然保留着,随时可以回滚

# kubectl rollout --help
Manage the rollout of a resource. Valid resource types include: * deployments * daemonsets * statefulsets Examples: # Rollback to the previous deployment kubectl rollout undo deployment/abc # Check the rollout status of a daemonset kubectl rollout status daemonset/foo Available Commands: history View rollout history pause Mark the provided resource as paused restart Restart a resource resume Resume a paused resource status Show the status of the rollout undo Undo a previous rollout Usage: kubectl rollout SUBCOMMAND [options] Use "kubectl <command> --help" for more information about a given command. Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
# kubectl rollout history -h //查看滚动历史
View previous rollout revisions and configurations. Examples: # View the rollout history of a deployment kubectl rollout history deployment/abc # View the details of daemonset revision 3 kubectl rollout history daemonset/abc --revision=3 Options: --allow-missing-template-keys=true: If true, ignore any errors in templates when a field or map key is missing in the template. Only applies to golang and jsonpath output formats. -f, --filename=[]: Filename, directory, or URL to files identifying the resource to get from a server. -k, --kustomize='': Process the kustomization directory. This flag can't be used together with -f or -R. -o, --output='': Output format. One of: json|yaml|name|go-template|go-template-file|template|templatefile|jsonpath|jsonpath-file. -R, --recursive=false: Process the directory used in -f, --filename recursively. Useful when you want to manage related manifests organized within the same directory. --revision=0: See the details, including podTemplate of the revision specified --template='': Template string or path to template file to use when -o=go-template, -o=go-template-file. The template format is golang templates [http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview]. Usage: kubectl rollout history (TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [flags] [options] Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
# kubectl explain deploy.spec.strategy.rollingUpdate
KIND: Deployment VERSION: apps/v1 RESOURCE: rollingUpdate <Object> DESCRIPTION: Rolling update config params. Present only if DeploymentStrategyType = RollingUpdate. Spec to control the desired behavior of rolling update. FIELDS: maxSurge <string> The maximum number of pods that can be scheduled above the desired number of pods. Value can be an absolute number (ex: 5) or a percentage of desired pods (ex: 10%). This can not be 0 if MaxUnavailable is 0. Absolute number is calculated from percentage by rounding up. Defaults to 25%. Example: when this is set to 30%, the new ReplicaSet can be scaled up immediately when the rolling update starts, such that the total number of old and new pods do not exceed 130% of desired pods. Once old pods have been killed, new ReplicaSet can be scaled up further, ensuring that total number of pods running at any time during the update is at most 130% of desired pods. maxUnavailable <string> The maximum number of pods that can be unavailable during the update. Value can be an absolute number (ex: 5) or a percentage of desired pods (ex: 10%). Absolute number is calculated from percentage by rounding down. This can not be 0 if MaxSurge is 0. Defaults to 25%. Example: when this is set to 30%, the old ReplicaSet can be scaled down to 70% of desired pods immediately when the rolling update starts. Once new pods are ready, old ReplicaSet can be scaled down further, followed by scaling up the new ReplicaSet, ensuring that the total number of pods available at all times during the update is at least 70% of desired pods.
# kubectl rollout history deployment myapp-deployment //应该是可以记录deployment的滚动操作的
deployment.apps/myapp-deploy REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 <none> 2 <none>
# kubectl patch --help
Update field(s) of a resource using strategic merge patch, a JSON merge patch, or a JSON patch. JSON and YAML formats are accepted. Examples: # Partially update a node using a strategic merge patch. Specify the patch as JSON. kubectl patch node k8s-node-1 -p '{"spec":{"unschedulable":true}}' # Partially update a node using a strategic merge patch. Specify the patch as YAML. kubectl patch node k8s-node-1 -p $'spec: unschedulable: true' # Partially update a node identified by the type and name specified in "node.json" using strategic merge patch. kubectl patch -f node.json -p '{"spec":{"unschedulable":true}}' # Update a container's image; spec.containers[*].name is required because it's a merge key. kubectl patch pod valid-pod -p '{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"kubernetes-serve-hostname","image":"new image"}]}}' # Update a container's image using a json patch with positional arrays. kubectl patch pod valid-pod --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/containers/0/image", "value":"new image"}]' Options: --allow-missing-template-keys=true: If true, ignore any errors in templates when a field or map key is missing in the template. Only applies to golang and jsonpath output formats. --dry-run='none': Must be "none", "server", or "client". If client strategy, only print the object that would be sent, without sending it. If server strategy, submit server-side request without persisting the resource. -f, --filename=[]: Filename, directory, or URL to files identifying the resource to update -k, --kustomize='': Process the kustomization directory. This flag can't be used together with -f or -R. --local=false: If true, patch will operate on the content of the file, not the server-side resource. -o, --output='': Output format. One of: json|yaml|name|go-template|go-template-file|template|templatefile|jsonpath|jsonpath-file. -p, --patch='': The patch to be applied to the resource JSON file. --record=false: Record current kubectl command in the resource annotation. If set to false, do not record the command. If set to true, record the command. If not set, default to updating the existing annotation value only if one already exists. -R, --recursive=false: Process the directory used in -f, --filename recursively. Useful when you want to manage related manifests organized within the same directory. --template='': Template string or path to template file to use when -o=go-template, -o=go-template-file. The template format is golang templates [http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview]. --type='strategic': The type of patch being provided; one of [json merge strategic] Usage: kubectl patch (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME) -p PATCH [options] Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
# kubectl explain deploy.spec.strategy.rollingUpdate
# kubectl patch deployment myapp-deploy -p '{"spec":{"replicas":5}}' //打补丁,扩容pod
# kubectl patch deployment myapp-deploy -p '{"spec":{"strategy":{"rollingUpdate":{"maxSurge":1,"maxUnavailable":0}}}}' //打补丁,字段嵌套
deployment.apps/myapp-deploy patched
# kubectl describe deployment myapp-deploy
Name: myapp-deploy Namespace: default CreationTimestamp: Tue, 02 Jun 2020 22:20:42 +0800 Labels: <none> Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 2 Selector: app=myapp,release=canary Replicas: 2 desired | 2 updated | 2 total | 2 available | 0 unavailable StrategyType: RollingUpdate MinReadySeconds: 0 RollingUpdateStrategy: 0 max unavailable, 1 max surge // Pod Template: Labels: app=myapp release=canary Containers: myapp: Image: ikubernetes/myapp:v2 Port: 80/TCP Host Port: 0/TCP Environment: <none> Mounts: <none> Volumes: <none> Conditions: Type Status Reason ---- ------ ------ Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable OldReplicaSets: <none> NewReplicaSet: myapp-deploy-559ff5c66 (2/2 replicas created) Events: <none>
# kubectl set image --help
Usage: kubectl set image (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME) CONTAINER_NAME_1=CONTAINER_IMAGE_1 ... CONTAINER_NAME_N=CONTAINER_IMAGE_N
# kubectl set image deployment myapp-deploy myapp=ikubernetes/myapp:v3 && kubectl rollout pause deployment myapp-deploy
# kubectl rollout status deployment myapp-deploy
Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 3 out of 5 new replicas have been updated...
# kubectl rollout resume deployment myapp-deploy //恢复暂停模式
# kubectl get pods -l app=myapp -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-6sxhg 1/1 Running 0 34m myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-j48kz 1/1 Running 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-s55vh 1/1 Running 0 22h myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-59mkh 1/1 Running 0 10m myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-92lpr 1/1 Running 0 10m myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-nffbc 1/1 Running 0 10m myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-s55vh 1/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-b9d8p 0/1 Pending 0 0s myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-b9d8p 0/1 Pending 0 0s myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-b9d8p 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-s55vh 0/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-b9d8p 1/1 Running 0 1s myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-6sxhg 1/1 Terminating 0 35m myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-gf74b 0/1 Pending 0 0s myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-gf74b 0/1 Pending 0 0s myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-gf74b 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-s55vh 0/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-s55vh 0/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-6sxhg 0/1 Terminating 0 35m myapp-deploy-6b9865d969-gf74b 1/1 Running 0 3s myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-j48kz 1/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-j48kz 0/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-6sxhg 0/1 Terminating 0 35m myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-6sxhg 0/1 Terminating 0 35m myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-j48kz 0/1 Terminating 0 22h myapp-deploy-559ff5c66-j48kz 0/1 Terminating 0 22h
# kubectl rollout status deployment myapp-deploy //全部更新完成
Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 3 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment spec update to be observed... Waiting for deployment spec update to be observed... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 3 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 3 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 4 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 4 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 4 out of 5 new replicas have been updated... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 1 old replicas are pending termination... Waiting for deployment "myapp-deploy" rollout to finish: 1 old replicas are pending termination... deployment "myapp-deploy" successfully rolled out
# kubectl get rs -o wide //现在已经有三个版本了
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR myapp-deploy-559ff5c66 0 0 0 22h myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v2 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=559ff5c66,release=canary myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459 0 0 0 22h myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v1 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=65fb6c8459,release=canary myapp-deploy-6b9865d969 5 5 5 14m myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v3 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=6b9865d969,release=canary //当前工作是V3
现在从V3版本回滚到v2版本,undo默认是回滚到当前版本的前一个版本,如果想从V3版本直接回滚到v1版本,使用 --to-revision=3
# kubectl rollout undo --help
Rollback to a previous rollout. Examples: # Rollback to the previous deployment kubectl rollout undo deployment/abc # Rollback to daemonset revision 3 kubectl rollout undo daemonset/abc --to-revision=3 # Rollback to the previous deployment with dry-run kubectl rollout undo --dry-run=server deployment/abc Options: --allow-missing-template-keys=true: If true, ignore any errors in templates when a field or map key is missing in the template. Only applies to golang and jsonpath output formats. --dry-run='none': Must be "none", "server", or "client". If client strategy, only print the object that would be sent, without sending it. If server strategy, submit server-side request without persisting the resource. -f, --filename=[]: Filename, directory, or URL to files identifying the resource to get from a server. -k, --kustomize='': Process the kustomization directory. This flag can't be used together with -f or -R. -o, --output='': Output format. One of: json|yaml|name|go-template|go-template-file|template|templatefile|jsonpath|jsonpath-file. -R, --recursive=false: Process the directory used in -f, --filename recursively. Useful when you want to manage related manifests organized within the same directory. --template='': Template string or path to template file to use when -o=go-template, -o=go-template-file. The template format is golang templates [http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview]. --to-revision=0: The revision to rollback to. Default to 0 (last revision). Usage: kubectl rollout undo (TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [flags] [options] Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
# kubectl rollout history deployment myapp-deploy //查看版本
deployment.apps/myapp-deploy REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 <none> 2 <none> 3 <none> //当前第三版本,默认回滚第二版
# kubectl rollout undo deployment myapp-deploy --to-revision=1 //回滚到版本1
# kubectl rollout history deployment myapp-deploy
deployment.apps/myapp-deploy REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 2 <none> 3 <none> 4 <none>
# kubectl get rs -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR myapp-deploy-559ff5c66 0 0 0 22h myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v2 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=559ff5c66,release=canary myapp-deploy-65fb6c8459 5 5 5 23h myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v1 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=65fb6c8459,release=canary //当前正在工作的是V1版本 myapp-deploy-6b9865d969 0 0 0 28m myapp ikubernetes/myapp:v3 app=myapp,pod-template-hash=6b9865d969,release=canary
daemon set
演示使用daemon set控制资源
在整个集群的每一个节点上只运行某个指定pod的一个资源副本,用于实现系统级别的管理功能,可以把节点上的某个目录作为存储卷,关联至pod中,让pod实现某些管理功能;
在集群中运行redis并启动一个filebeat服务,自动把收集到的日志直接发给指定的reids,
daemon set不用指定副本数量,因为副本数是随即群变动而自动创建的,
# kubectl explain ds //五个字段
KIND: DaemonSet VERSION: apps/v1 DESCRIPTION: DaemonSet represents the configuration of a daemon set. FIELDS: apiVersion <string> APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string> Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object> Standard object's metadata. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object> The desired behavior of this daemon set. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status status <Object> The current status of this daemon set. This data may be out of date by some window of time. Populated by the system. Read-only. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
# kubectl explain ds.spec //查看spec字段
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers //查看pod的spec字段中的containers字段
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.env //可以向容器传环境变量
# cat ds-damo.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: redis role: logstor template: metadata: labels: app: redis role: logstor spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:4.0-alpine ports: - name: redis containerPort: 6379 --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: filebeat namespace: default spec: selector: matchLabels: app: filebeat release: stable template: metadata: labels: app: filebeat release: stable spec: containers: - name: filebeat image: ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.5-alpine env: - name: REDIS_HOST value: redis.default.svc.cluster.local - name: REDIS_LOG_LEVEL value: info
# kubectl apply -f ds-damo.yaml
# kubectl get pods -o wide //总共有两个节点,所以有两个pod,不会调度上master上的,因为master有污点
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES myapp-ds-f9zgc 1/1 Running 0 2m 10.246.2.36 knode3 <none> <none> myapp-ds-rts6p 1/1 Running 0 2m 10.246.1.43 knode2 <none> <none>
以上是准备好了filebeat了,但是需要在集群中启动redis服务,filebeat才能收集日志,需要先起redis pod,然后定义一个service,这时filebeat采集的日志就会自动往redis发送日志
# kubectl delete -f ds-damo.yaml //删除之前运行的资源
# kubectl apply -f ds-damo.yaml //
deployment.apps/redis created
daemonset.apps/filebeat created
# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE filebeat-4lskj 1/1 Running 0 2m2s filebeat-z7zdk 1/1 Running 0 2m1s redis-588694bf8c-4mrwl 1/1 Running 0 2m2s
# kubectl expose deployment redis --port=6379 //为redis创建一个service,暴漏端口是6379
service/redis exposed
# kubectl get svc //查看服务
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE redis ClusterIP 10.108.117.98 <none> 6379/TCP 2m7s
各pod之间是通过service调用的并且指定的是service的主机名,
在调用时传递给调用者的方法是环境变量
spec: containers: - name: filebeat image: ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.5-alpine env: - name: REDIS_HOST //变量名 value: redis.default.svc.cluster.local //变量值,主机名又是服务名,它背后是有pod资源在运行并提供服务的,这里就是redis服务 - name: REDIS_LOG_LEVEL value: info
daemon set支持滚动更新
# kubectl explain ds.spec.updateStrategy
KIND: DaemonSet VERSION: apps/v1 RESOURCE: updateStrategy <Object> DESCRIPTION: An update strategy to replace existing DaemonSet pods with new pods. DaemonSetUpdateStrategy is a struct used to control the update strategy for a DaemonSet. FIELDS: rollingUpdate <Object> Rolling update config params. Present only if type = "RollingUpdate". type <string> Type of daemon set update. Can be "RollingUpdate" or "OnDelete". Default is RollingUpdate.
更新版本也可以用set images
# kubectl set image --help
Update existing container image(s) of resources. Possible resources include (case insensitive): pod (po), replicationcontroller (rc), deployment (deploy), daemonset (ds), replicaset (rs) Usage: kubectl set image (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME) CONTAINER_NAME_1=CONTAINER_IMAGE_1 ... CONTAINER_NAME_N=CONTAINER_IMAGE_N [options]
# kubectl get ds -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR filebeat 2 2 2 2 2 <none> 12h filebeat ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.5-alpine app=filebeat,release=stable
# kubectl set image daemonsets filebeat filebeat=ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.6-apline
daemonset.apps/filebeat image updated
# kubectl get pods -w //先终止一个ds,启动起来后,再终止下一个,再启动
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES filebeat-6fpds 1/1 Running 0 34s 10.246.2.43 knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-rjbl8 1/1 Running 0 34s 10.246.1.50 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-rjbl8 1/1 Terminating 0 6m21s 10.246.1.50 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-rjbl8 0/1 Terminating 0 6m22s 10.246.1.50 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-rjbl8 0/1 Terminating 0 6m26s 10.246.1.50 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-rjbl8 0/1 Terminating 0 6m26s 10.246.1.50 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-7xdk6 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> <none> <none> <none> filebeat-7xdk6 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-7xdk6 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-7xdk6 1/1 Running 0 2s 10.246.1.51 knode2 <none> <none> filebeat-6fpds 1/1 Terminating 0 6m28s 10.246.2.43 knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-6fpds 0/1 Terminating 0 6m29s 10.246.2.43 knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-6fpds 0/1 Terminating 0 6m37s 10.246.2.43 knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-6fpds 0/1 Terminating 0 6m37s 10.246.2.43 knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-ptdp7 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> <none> <none> <none> filebeat-ptdp7 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-ptdp7 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> knode3 <none> <none> filebeat-ptdp7 1/1 Running 0 1s 10.246.2.44 knode3 <none> <none>
# kubectl get ds -o wide
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR filebeat 2 2 2 2 2 <none> 8m54s filebeat ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.6-alpine app=filebeat,release=stable
# kubectl explain pods.spec
KIND: Pod VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: spec <Object> DESCRIPTION: Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status PodSpec is a description of a pod. FIELDS: activeDeadlineSeconds <integer> Optional duration in seconds the pod may be active on the node relative to StartTime before the system will actively try to mark it failed and kill associated containers. Value must be a positive integer. affinity <Object> If specified, the pod's scheduling constraints automountServiceAccountToken <boolean> AutomountServiceAccountToken indicates whether a service account token should be automatically mounted. containers <[]Object> -required- List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be updated. dnsConfig <Object> Specifies the DNS parameters of a pod. Parameters specified here will be merged to the generated DNS configuration based on DNSPolicy. dnsPolicy <string> Set DNS policy for the pod. Defaults to "ClusterFirst". Valid values are 'ClusterFirstWithHostNet', 'ClusterFirst', 'Default' or 'None'. DNS parameters given in DNSConfig will be merged with the policy selected with DNSPolicy. To have DNS options set along with hostNetwork, you have to specify DNS policy explicitly to 'ClusterFirstWithHostNet'. enableServiceLinks <boolean> EnableServiceLinks indicates whether information about services should be injected into pod's environment variables, matching the syntax of Docker links. Optional: Defaults to true. ephemeralContainers <[]Object> List of ephemeral containers run in this pod. Ephemeral containers may be run in an existing pod to perform user-initiated actions such as debugging. This list cannot be specified when creating a pod, and it cannot be modified by updating the pod spec. In order to add an ephemeral container to an existing pod, use the pod's ephemeralcontainers subresource. This field is alpha-level and is only honored by servers that enable the EphemeralContainers feature. hostAliases <[]Object> HostAliases is an optional list of hosts and IPs that will be injected into the pod's hosts file if specified. This is only valid for non-hostNetwork pods. hostIPC <boolean> Use the host's ipc namespace. Optional: Default to false. hostNetwork <boolean> //pod直接使用宿主机的网络 Host networking requested for this pod. Use the host's network namespace. If this option is set, the ports that will be used must be specified. Default to false. hostPID <boolean> Use the host's pid namespace. Optional: Default to false. hostname <string> Specifies the hostname of the Pod If not specified, the pod's hostname will be set to a system-defined value. imagePullSecrets <[]Object> ImagePullSecrets is an optional list of references to secrets in the same namespace to use for pulling any of the images used by this PodSpec. If specified, these secrets will be passed to individual puller implementations for them to use. For example, in the case of docker, only DockerConfig type secrets are honored. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod initContainers <[]Object> List of initialization containers belonging to the pod. Init containers are executed in order prior to containers being started. If any init container fails, the pod is considered to have failed and is handled according to its restartPolicy. The name for an init container or normal container must be unique among all containers. Init containers may not have Lifecycle actions, Readiness probes, Liveness probes, or Startup probes. The resourceRequirements of an init container are taken into account during scheduling by finding the highest request/limit for each resource type, and then using the max of of that value or the sum of the normal containers. Limits are applied to init containers in a similar fashion. Init containers cannot currently be added or removed. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/init-containers/ nodeName <string> NodeName is a request to schedule this pod onto a specific node. If it is non-empty, the scheduler simply schedules this pod onto that node, assuming that it fits resource requirements. nodeSelector <map[string]string> NodeSelector is a selector which must be true for the pod to fit on a node. Selector which must match a node's labels for the pod to be scheduled on that node. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/ overhead <map[string]string> Overhead represents the resource overhead associated with running a pod for a given RuntimeClass. This field will be autopopulated at admission time by the RuntimeClass admission controller. If the RuntimeClass admission controller is enabled, overhead must not be set in Pod create requests. The RuntimeClass admission controller will reject Pod create requests which have the overhead already set. If RuntimeClass is configured and selected in the PodSpec, Overhead will be set to the value defined in the corresponding RuntimeClass, otherwise it will remain unset and treated as zero. More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/20190226-pod-overhead.md This field is alpha-level as of Kubernetes v1.16, and is only honored by servers that enable the PodOverhead feature. preemptionPolicy <string> PreemptionPolicy is the Policy for preempting pods with lower priority. One of Never, PreemptLowerPriority. Defaults to PreemptLowerPriority if unset. This field is alpha-level and is only honored by servers that enable the NonPreemptingPriority feature. priority <integer> The priority value. Various system components use this field to find the priority of the pod. When Priority Admission Controller is enabled, it prevents users from setting this field. The admission controller populates this field from PriorityClassName. The higher the value, the higher the priority. priorityClassName <string> If specified, indicates the pod's priority. "system-node-critical" and "system-cluster-critical" are two special keywords which indicate the highest priorities with the former being the highest priority. Any other name must be defined by creating a PriorityClass object with that name. If not specified, the pod priority will be default or zero if there is no default. readinessGates <[]Object> If specified, all readiness gates will be evaluated for pod readiness. A pod is ready when all its containers are ready AND all conditions specified in the readiness gates have status equal to "True" More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-network/0007-pod-ready%2B%2B.md restartPolicy <string> Restart policy for all containers within the pod. One of Always, OnFailure, Never. Default to Always. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle/#restart-policy runtimeClassName <string> RuntimeClassName refers to a RuntimeClass object in the node.k8s.io group, which should be used to run this pod. If no RuntimeClass resource matches the named class, the pod will not be run. If unset or empty, the "legacy" RuntimeClass will be used, which is an implicit class with an empty definition that uses the default runtime handler. More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/runtime-class.md This is a beta feature as of Kubernetes v1.14. schedulerName <string> If specified, the pod will be dispatched by specified scheduler. If not specified, the pod will be dispatched by default scheduler. securityContext <Object> SecurityContext holds pod-level security attributes and common container settings. Optional: Defaults to empty. See type description for default values of each field. serviceAccount <string> DeprecatedServiceAccount is a depreciated alias for ServiceAccountName. Deprecated: Use serviceAccountName instead. serviceAccountName <string> ServiceAccountName is the name of the ServiceAccount to use to run this pod. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/ shareProcessNamespace <boolean> Share a single process namespace between all of the containers in a pod. When this is set containers will be able to view and signal processes from other containers in the same pod, and the first process in each container will not be assigned PID 1. HostPID and ShareProcessNamespace cannot both be set. Optional: Default to false. subdomain <string> If specified, the fully qualified Pod hostname will be "<hostname>.<subdomain>.<pod namespace>.svc.<cluster domain>". If not specified, the pod will not have a domainname at all. terminationGracePeriodSeconds <integer> Optional duration in seconds the pod needs to terminate gracefully. May be decreased in delete request. Value must be non-negative integer. The value zero indicates delete immediately. If this value is nil, the default grace period will be used instead. The grace period is the duration in seconds after the processes running in the pod are sent a termination signal and the time when the processes are forcibly halted with a kill signal. Set this value longer than the expected cleanup time for your process. Defaults to 30 seconds. tolerations <[]Object> If specified, the pod's tolerations. topologySpreadConstraints <[]Object> TopologySpreadConstraints describes how a group of pods ought to spread across topology domains. Scheduler will schedule pods in a way which abides by the constraints. This field is only honored by clusters that enable the EvenPodsSpread feature. All topologySpreadConstraints are ANDed. volumes <[]Object> List of volumes that can be mounted by containers belonging to the pod. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes
