引子:
android SDK中会提供一些基础的控件以供开发。但是大多数情况下,这些基础的控件无法满足业务需求。本文主要说明自定义控件的分类,以及提供示例代码。
本文只做入门级选手阅读,或者 加深印象 或 温故而知新,大佬大神敬请绕道。
android控件的3种方式:
1)派生控件 :
从SDK已有的控件为基础,改变其部分特征,形成符合需求的自定义控件。
具体做法举例:
public class MyTextView extends EditText(){...}
或者
public class MyListView extends ListView {...}
能够这样做,是因为SDK已有的控件其实已经提供了某些接口让开发者可以进行改造。
示例代码:这是一个继承了EditText,重写了某些函数,调用了EditText自己的API,形成了这种特殊效果,请看示例图。
1 package com.example.administrator.hankstest0415.custom;
2
3 import android.content.Context;
4 import android.graphics.Rect;
5 import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;
6 import android.text.Editable;
7 import android.text.TextWatcher;
8 import android.util.AttributeSet;
9 import android.util.Log;
10 import android.view.MotionEvent;
11 import android.widget.EditText;
12
13 import com.example.administrator.hankstest0415.R;
14
15 /**17 * 这是一个带删除按钮的EditText,它能够在输入框中有内容时,显示最右边的删除按钮,点击该按钮可以直接清空内容
18 */
19 public class DelEditText extends EditText {
20
21 private Drawable imgClear;
22 private Context mContext;
23
24 public DelEditText(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
25 super(context, attrs);
26 this.mContext = context;
27 setDrawable();
28 init();
29 }
30
31 private void init() {
32 imgClear = mContext.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.delete);
33 //添加watcher监听器,监听 文本被改变之后的事件
34 addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
35 //内容变化前
36 @Override
37 public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
38
39 }
40
41 //内容正在改变
42 @Override
43 public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
44 }
45
46 //在内容改变完之后
47 @Override
48 public void afterTextChanged(Editable editable) {
49 Log.d("mytagX", "" + editable.toString());
50 setDrawable();
51 }
52 });
53 }
54
55 //绘制删除图片
56 //这里的setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds方法解释一下:
57 //按照原注释的意思,这个方法会在组件的上下左右,如果只需要在右侧显示,那就把其他3个参数设置为null,显示一个Drawable
58 private void setDrawable() {
59 if (length() < 1)//
60 setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(null, null, null, null);
61 else
62 setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(null, null, imgClear, null);
63 }
64
65
66 //当触摸范围在右侧时,触发删除方法,隐藏叉叉
67
68 /**
69 * 继承父组件的触摸事件
70 *
71 * @param event
72 * @return
73 */
74 @Override
75 public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
76 if (imgClear != null && event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {//如果触发的是 按下并释放的动作,也就是平时的点一下
77 int eventX = (int) event.getRawX();//就拿到当前点击的位置X,Y坐标
78 int eventY = (int) event.getRawY();
79 Log.d("mytagX", "" + eventX + " - " + eventY);
80 Rect rect = new Rect();//新建一个矩形
81 getGlobalVisibleRect(rect);//将当前View的绘制范围大小,设置到这个属性中. 比如说,这个View的绘制范围是 从 (0,0)到(100,200), 那么Rect的4个属性值就是0,0,100,200sa
82
83 Log.d("onTouchEvent", "" + rect.left + " - " + rect.top + " - " + rect.right + " - " + rect.bottom);
84
85 rect.left = rect.right - 100;//将rect的左 ,设置为它 右的值-100. 这是在控制触发事件的范围大小
86 if (rect.contains(eventX, eventY))//如果点击的位置,在Rect范围之内,那就触发清空事件
87 {
88 setText("");
89 Log.d("onTouchEvent", "点击了EditText并且触发了清空事件");
90 } else
91 Log.d("onTouchEvent", "点击了EditText但是并没有点击到删除按钮的范围之内");
92
93 }
94 return super.onTouchEvent(event);
95 }
96
97 }
示例效果:

(注:右边的这个图片,是调用EditText的api生成的)
2)自绘控件:
当SDK已有控件完全不能满足需求时,就需要我们直接继承所有控件的父类android.view.View来进行完全的自定义。
能够这么做的基础,就是 继承了View之后,可以重写其中的onDraw方法,使用参数提供的Canvas对象以及 自己创建的paint对象,进行绘图,并且可以调用postInvalidate产生动画效果。
示例代码:
1 package com.example.administrator.hankstest0415.custom;
2
3 import android.content.Context;
4 import android.graphics.Canvas;
5 import android.graphics.Paint;
6 import android.graphics.RectF;
7 import android.util.AttributeSet;
8 import android.util.Log;
9 import android.view.View;
10 import android.widget.EditText;
11
12 import com.example.administrator.hankstest0415.R;
13 import com.example.administrator.hankstest0415.util.DensityUtils;
14
15 import org.jetbrains.annotations.Nullable;
16
17 public class PColumn extends View {
18 int MAX = 100;//最大
19 int corner = 40;
20 int data = 0;//显示的数
21 int tempData = 0;
22 int textPadding = 20;
23 Paint mPaint;
24 int mColor;
25
26 Context mContext;
27
28 //首先,构造函数和 编译器自动生成的方式有所不同
29 public PColumn(Context context) {
30 super(context);
31 mContext = context;
32 }
33
34 public PColumn(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
35 super(context, attrs);
36 mContext = context;
37 initPaint();
38 }
39
40 public PColumn(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
41 super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
42 mContext = context;
43 initPaint();
44 }
45
46 private void initPaint() {
47 mPaint = new Paint();
48 mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
49 mColor = mContext.getResources().getColor(R.color.colorPrimary);
50 mPaint.setColor(mColor);
51 setData(80, 100);
52 }
53
54
55 private int defaultHeight = 400;
56 private int defaultWidth = 180;
57
58 /**
59 * 重写onMeasure,设定控件最小宽高值。
60 *
61 * 因为当布局xml中对这个控件设置wrap_content,而 onMeasure方法并没有指定最小宽高值的话,该控件就会默认match_parent.
62 *
63 * @param widthMeasureSpec
64 * @param heightMeasureSpec
65 */
66 @Override
67 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
68 int width = measureDimension(defaultWidth, widthMeasureSpec);
69 int height = measureDimension(defaultHeight, heightMeasureSpec);
70 setMeasuredDimension(width, height);//重写onMeasure一定要调用setMeasuredDimension()。
71 }
72
73
74 public int measureDimension(int defaultSize, int measureSpec) {
75 int result;
76
77 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
78 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
79
80 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {//如果直接指定了宽度,比如100dp
81 result = specSize;
82 } else {
83 result = defaultSize; //UNSPECIFIED 设定一个默认值
84 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果设定宽度match_parent
85 result = Math.min(result, specSize);
86 }
87 }
88 //如果既没有指定宽度,也没有设定match_parent,那么,就用之前设定好的默认值
89 return result;
90 }
91
92 @Override
93 protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
94 super.onDraw(canvas);
95 if (data == 0) {
96 mPaint.setTextSize(getWidth() / 2);
97 RectF oval3 = new RectF(0, getHeight() - DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, 20), getWidth(), getHeight());// 设置个新的长方形
98 //圆角长方形,醉了,drawRoundRect
99 canvas.drawRoundRect(oval3, DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, corner), DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, corner), mPaint);
100
101 canvas.drawText("0",
102 getWidth() * 0.5f - mPaint.measureText("0") * 0.5f,
103 getHeight() - DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, 20) - 2 * DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, textPadding),
104 mPaint);
105 return;
106 }
107
108 //防止数值很大的的时候,动画时间过长
109 int step = data / 100 + 1;
110
111 if (tempData < data - step) {
112 tempData = tempData + step;
113 } else {
114 tempData = data;
115 }
116 //画圆角矩形
117 String S = tempData + "";
118 //一个字和两,三个字的字号相同
119 if (S.length() < 4) {
120 mPaint.setTextSize(getWidth() / 2);
121 } else {
122 mPaint.setTextSize(getWidth() / (S.length() - 1));
123 }
124
125 float textH = mPaint.ascent() + mPaint.descent();
126 float MaxH = getHeight() - textH - 2 * DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, textPadding);
127 //圆角矩形的实际高度
128 float realH = MaxH / MAX * tempData;
129 RectF oval3 = new RectF(0, getHeight() - realH, getWidth(), getHeight());// 设置个新的长方形
130 canvas.drawRoundRect(oval3, DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, corner), DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, corner), mPaint);
131 //写数字
132 canvas.drawText(S,
133 getWidth() * 0.5f - mPaint.measureText(S) * 0.5f,
134 getHeight() - realH - 2 * DensityUtils.pxTodip(mContext, textPadding),
135 mPaint);
136 if (tempData != data) {
137 postInvalidate();
138 }
139 }
140
141 /**
142 * 如果只是自定义View,则onLayout方法不需要实现
143 * @param changed
144 * @param left
145 * @param top
146 * @param right
147 * @param bottom
148 */
149 @Override
150 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
151 super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
152 }
153
154 @Override
155 public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
156 super.draw(canvas);
157 }
158
159 public void setData(int data, int MAX) {
160 this.data = data;
161 tempData = 0;
162 this.MAX = MAX;
163 postInvalidate();//进行画面刷新
164 }
165
166
167 }
示例效果:

另外,除了继承View之外,还可以继承SurfaceView. 两者的区别如下:
SurfaceView和View画图的区别:
1、SurfaceView更新图像不依赖主线程,直接用工作线程就行。View则是必须依赖主线程, 还有可能卡住主线程;
2、SurfaceView可以控制帧数,刷新频率。View的帧率则是系统默认的,无法控制。
3、SurfaceView消耗大,View消耗较小。
示例代码:
2
3 import android.content.Context;
4 import android.graphics.Canvas;
5 import android.graphics.Color;
6 import android.graphics.Paint;
7 import android.util.AttributeSet;
8 import android.util.Log;
9 import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
10 import android.view.SurfaceView;
11
12 import java.util.Date;
13
14 public class CircleClock extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback, Runnable {
15
16 private Paint mPaint, mPaint_face, mPaint_second, mPaint_minute, mPaint_hour;
17 private static final String cloclColor = "#000000";
18 // 子线程标志位
19 private boolean mIsDrawing;//控制绘制过程的停和走
20 private Canvas mCanvas;// 保存画布对象为全局变量
21
22 private void initPaint() {
23 mPaint = new Paint();
24 mPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(cloclColor));
25 mPaint.setStrokeWidth(2);
26 mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
27 mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
28
29 mPaint_face = new Paint();
30 mPaint_face.setColor(Color.parseColor(cloclColor));
31 mPaint_face.setStrokeWidth(4);
32 mPaint_face.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
33 mPaint_face.setAntiAlias(true);
34
35 mPaint_second = new Paint();
36 mPaint_second.setColor(Color.parseColor(cloclColor));
37 mPaint_second.setStrokeWidth(4);
38 mPaint_second.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
39 mPaint_second.setAntiAlias(true);
40
41 mPaint_minute = new Paint();
42 mPaint_minute.setColor(Color.parseColor(cloclColor));
43 mPaint_minute.setStrokeWidth(5);
44 mPaint_minute.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
45 mPaint_minute.setAntiAlias(true);
46
47 mPaint_hour = new Paint();
48 mPaint_hour.setColor(Color.parseColor(cloclColor));
49 mPaint_hour.setStrokeWidth(6);
50 mPaint_hour.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
51 mPaint_hour.setAntiAlias(true);
52 }
53
54 public CircleClock(Context context) {
55 super(context);
56 initPaint();
57 initView();
58 }
59
60 public CircleClock(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
61 super(context, attrs);
62 initPaint();
63 initView();
64 }
65
66 public CircleClock(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
67 super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
68 initPaint();
69 initView();
70 }
71
72
73 @Override
74 public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
75 // 一旦被创建成功,就启动动画
76 reset();
77 }
78
79 @Override
80 public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) {
81
82 }
83
84 @Override
85 public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
86 mIsDrawing = false;
87 }
88
89 @Override
90 public void run() {
91 while (mIsDrawing) {
92 drawClock();//无限循环绘制指针
93 try {
94 Thread.sleep(500);//每隔1000MS绘制一次
95 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
96 e.printStackTrace();
97 }
98 }
99 }
100
101 private SurfaceHolder holder;
102
103 private void initView() {
104 holder = getHolder();//获得holder对象
105 holder.addCallback(this);//添加callback
106 setFocusable(true);
107 setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
108 setKeepScreenOn(true);
109 }
110
111
112 private int radiusTarget = 80;
113 private int currentRadius = 0;
114
115 //详细的绘制过程
116
117 /**
118 * 这个myDraw方法会无限循环调用
119 */
120 private void drawClock() {
121 try {
122 mCanvas = holder.lockCanvas();//
123 mCanvas.drawColor(Color.parseColor("#FFFFFF"));//绘制背景
124 drawClockFace();
125 drawPointer();
126
127 } catch (Exception e) {
128
129 } finally {
130 if (mCanvas != null) {
131 holder.unlockCanvasAndPost(mCanvas);//释放,并且刷新surface
132 }
133 }
134 }
135
136 private void drawPointer() {
137
138 //这里逻辑会发生变化,因为我打算将当前系统时间的时分秒提取出来,然后计算出各自的角度,再将3个指针绘制出来
139 Date date = new Date();
140 int hour = date.getHours();
141 int minute = date.getMinutes();
142 int second = date.getSeconds();
143
144 //先把秒钟指针画出来
145 // 如何把秒钟转化成角度
146 mCanvas.rotate(second * 6);// 表盘一共360度。 一共60秒,所以每走一秒,度数就走6度
147 mCanvas.drawLine(0, 0, radiusTarget * 7 / 10, 0, mPaint_second);//刻度的长度,设定为半径的1/10
148
149 //再把分钟指针画出来
150
151 //其实分钟数是一个小数,而不是int
152 //算出真正的分钟数
153 float realMinute = minute + second / 60.0f;
154 Log.d("drawPointer", "" + realMinute);
155 mCanvas.rotate(-second * 6);// 还得先把原来的角度转回去
156 mCanvas.rotate((realMinute * 6));//再旋转分钟的角度,表盘一共360度。 一共60分,所以每走一分,度数就走6度
157 mCanvas.drawLine(0, 0, radiusTarget * 6 / 10, 0, mPaint_minute);//
158
159 hour = hour % 12;
160
161 float realHour = hour + minute / 60.0f;
162 mCanvas.rotate(-realMinute * 6);// 还得先把原来的角度转回去
163 mCanvas.rotate((realHour * 30));//再旋转时钟的角度,表盘上一共12个小时,一共360度,所以每一个小时代表的是30度
164 mCanvas.drawLine(0, 0, radiusTarget * 5 / 10, 0, mPaint_hour);//
165 }
166
167 /**
168 * 画出表盘
169 */
170 private void drawClockFace() {
171 //这些东西都是只需要绘制一次的
172 int w = getWidth();
173 int h = getHeight();
174 int cx = w / 2;
175 int cy = h / 2;
176 mCanvas.drawCircle(cx, cy, currentRadius, mPaint);
177 mCanvas.drawPoint(cx, cy, mPaint);
178
179 mCanvas.translate(cx, cy);// 转移坐标轴中心,到原点处
180 mCanvas.rotate(-90);//让指针从12点位置开始走,因为原始的是从3点位置。中间差了90度,所以需要逆时针旋转坐标90度
181 for (int i = 1; i <= 60; i++) {//120次循环,绘制表盘
182 mCanvas.rotate(6);//每一次旋转3度,
183 if (i % 5 == 0) {//如果遇到整点,,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12
184 mCanvas.drawLine(radiusTarget * 8 / 10, 0, radiusTarget, 0, mPaint_face);//就用较粗的画笔画出较长的线条
185 } else
186 mCanvas.drawLine(radiusTarget * 9 / 10, 0, radiusTarget, 0, mPaint);//否则,就用较细的画笔画出较短的线条
187 }
188 }
189
190 public void reset() {
191 radiusTarget = getWidth() / 3;
192 currentRadius = radiusTarget;
193 mIsDrawing = true;
194 new Thread(this).start();
195 }
196 }
效果如下:
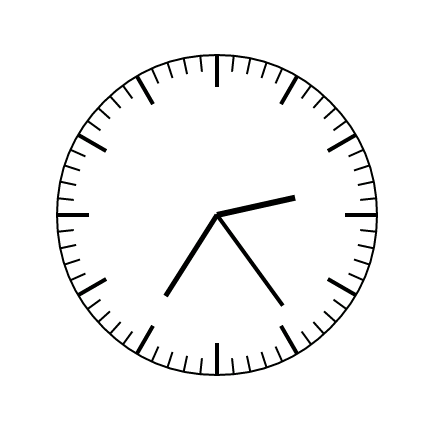
组合控件:
其实这里有两层境界:
1- 继承SDK已有的Layout(比如,public class MyLayout extends FrameLayout)
2-继承所有Layout的父类:ViewGroup;
一般情况下,由于第二种境界需要完全重写onLayout方法,比较复杂。通常情况下,还是会采用 方案1:继承某种已有的Layout类。
案例如下:比如我们需要做一个 app中常用的 可复用的TitleBar,包含左边按钮,中间文本,以及右边按钮。
首先看:
attr.xml 自定义的属性预设
(熟悉自定义控件的自定义属性的同学应该知道这个,不多做解释了)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyTitleBar">
<attr name="left_text" format="string" />
<attr name="left_drawable" format="reference" />
<attr name="mid_text" format="string" />
<attr name="right_text" format="string" />
<attr name="right_drawable" format="reference" />
<attr name="title_bg_color" format="color" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
title_merge.xml 组合控件预设
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_left"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:gravity="center" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_mid"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_right"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:gravity="center" />
</LinearLayout>
</merge>
MyTitleBar.java java 代码中的自定义控件编写
1 package com.example.custom_layout.custom;
2
3 import android.content.Context;
4 import android.content.res.TypedArray;
5 import android.graphics.Color;
6 import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
7 import android.util.AttributeSet;
8 import android.view.LayoutInflater;
9 import android.view.View;
10 import android.widget.Button;
11 import android.widget.LinearLayout;
12 import android.widget.TextView;
13
14 import com.example.custom_layout.R;
15
16 public class MyTitleBar extends LinearLayout {
17
18 public MyTitleBar(Context context) {
19 this(context, null);
20 }
21
22 public MyTitleBar(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
23 this(context, attrs, 0);
24 }
25
26 public MyTitleBar(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
27 super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
28 initView(context, attrs);
29 }
30
31 private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
32 //关键代码:看以下3个参数
33 //第一个,是 将要实例化的布局
34 //第二个,是 设置rootView(注:布局被实例化之后,可以单独作为一块, 也可以跟随在某一个View下面,作为子view)
35 //第三个,设置是否放置在rootView下面,作为子view
36 // 在这里,我们后面两个参数都必须加上。一个是this,本Layout,一个是true,确定添加到LinearLayout下面去作为子view
37 View titleView = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.title_merge, this, true);
38
39 Button btn_left = titleView.findViewById(R.id.btn_left);
40 TextView tv_mid = titleView.findViewById(R.id.tv_mid);
41 Button btn_right = titleView.findViewById(R.id.btn_right);
42 LinearLayout ll_title = titleView.findViewById(R.id.ll_title);
43
44 //1,集合转换,将attrs转换成TypedArray,两个参数,第一个是 attrs,第二个,则是在attrs.xml里面定义的styleable,
45 // 两个参数结合,就是要将布局xml里面获得的参数,与之前定义好的参数对照起来
46 TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyTitleBar);
47 //下面来解析attrs(来自xml的可选参数)
48 if (typedArray != null) {
49
50 String text_mid = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_mid_text);
51 tv_mid.setText(text_mid);
52
53
54 int right_drawable = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_right_drawable, -1);
55 if (right_drawable != -1) {
56 btn_right.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0, 0, right_drawable, 0);
57 } else {
58 String text_right = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_right_text);
59 btn_right.setText(text_right);
60 }
61
62 int leftDrawable = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_left_drawable, -1);
63 if (leftDrawable != -1) {
64 btn_left.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(leftDrawable, 0, 0, 0);//优先图片显示
65 } else {
66 String text_left = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_left_text);
67 btn_left.setText(text_left);
68 }
69
70 int bg_color = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.MyTitleBar_title_bg_color, Color.CYAN);//获得颜色,默认蓝绿色
71 ll_title.setBackgroundColor(bg_color);
72
73 typedArray.recycle();
74 }
75
76 }
77 }
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:MyTitleBar="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.example.custom_layout.custom.MyTitleBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:text="Hello World!"
MyTitleBar:left_drawable="@drawable/back"
MyTitleBar:left_text="left1"
MyTitleBar:mid_text="mid1"
MyTitleBar:right_drawable="@drawable/next"
MyTitleBar:right_text="right1"
MyTitleBar:title_bg_color="@android:color/holo_blue_bright" />
<com.example.custom_layout.custom.MyTitleBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:text="Hello World!"
MyTitleBar:left_text="left2"
MyTitleBar:mid_text="mid2"
MyTitleBar:right_text="right2"
MyTitleBar:title_bg_color="@color/colorPrimary" />
<com.example.custom_layout.custom.MyTitleBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:text="Hello World!"
MyTitleBar:left_text="left3"
MyTitleBar:mid_text="mid3"
MyTitleBar:right_text="right3"
MyTitleBar:title_bg_color="@color/colorPrimaryDark" />
</LinearLayout>
最后是 MainActivity.java (可以看见activity内基本是空白,自定义layout使用起来很简单,只需要在activity_main.xml里面写 控件标签即可)
1 package com.example.custom_layout;
2
3 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
4 import android.os.Bundle;
5
6 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
7
8 @Override
9 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
10 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
11 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
12 }
13 }
最后的效果:

OK,这就是经常用到的自定义layout。 至于更多更高境界的骚操作,以后研究到了,就更新博客。