模拟赛遇到了一道字符串匹配题,用 Hash 暴力拿了 50,赛后才知道是 KMP 板子题,发现自己 KMP 一直没学会过,于是有了这篇文章。
不适合新手入门,只适合学过的人复习。
KMP 算法学习笔记
约定记号
字符串 (S) 为主串,也就是要在 (S) 中查找其他串。
字符串 (P) 为模式串,也就是要在 (S) 中查找串 (P)。
一个字符串 (S_0) 的长度记为 (|S_0|)。
算法思想
一句话:跳过一定匹配不到的所有位置。
next 数组
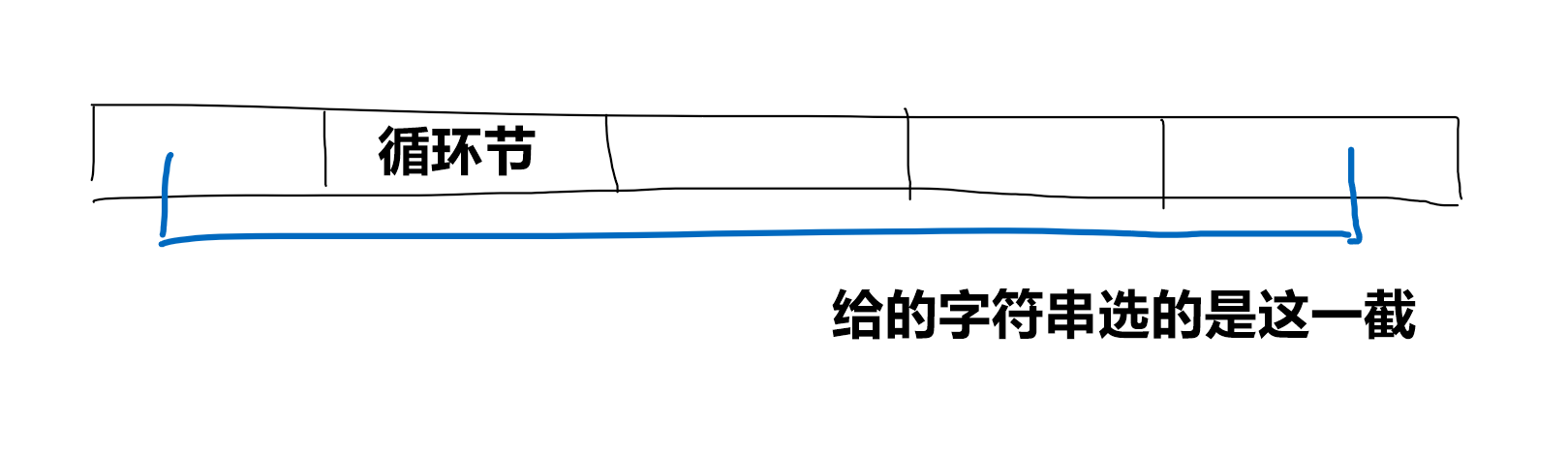
定义 next[i] 表示模式串 (P[0dots(i - 1)]) 的前缀和后缀最长匹配长度,即,前缀和后缀有几个字符是一样的。
在一次匹配成功了一部分的失配中,通过把 (P) 向右偏移到匹配的后缀那个位置,我们可以实现跳过这个串中匹配不到的所有位置,并从最靠后的位置进行继续匹配。
使用 next 数组进行匹配
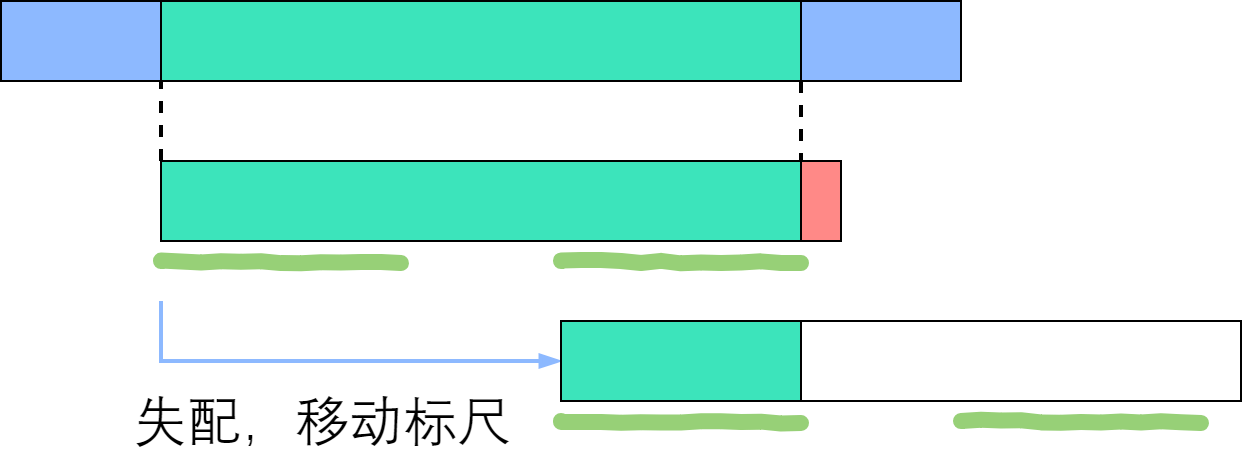
图源知乎。
快速求 next 数组
朴素的做法是 (O(|P|^2)) 的。考虑优化:自己和自己做匹配。
假设我们已经知道了 next[0..x - 1],现在要求出 next[x]。记 now = next[x - 1],分情况讨论一下:
-
P[(now - 1) + 1] = P[x],这种情况直接令next[x] = now + 1即可;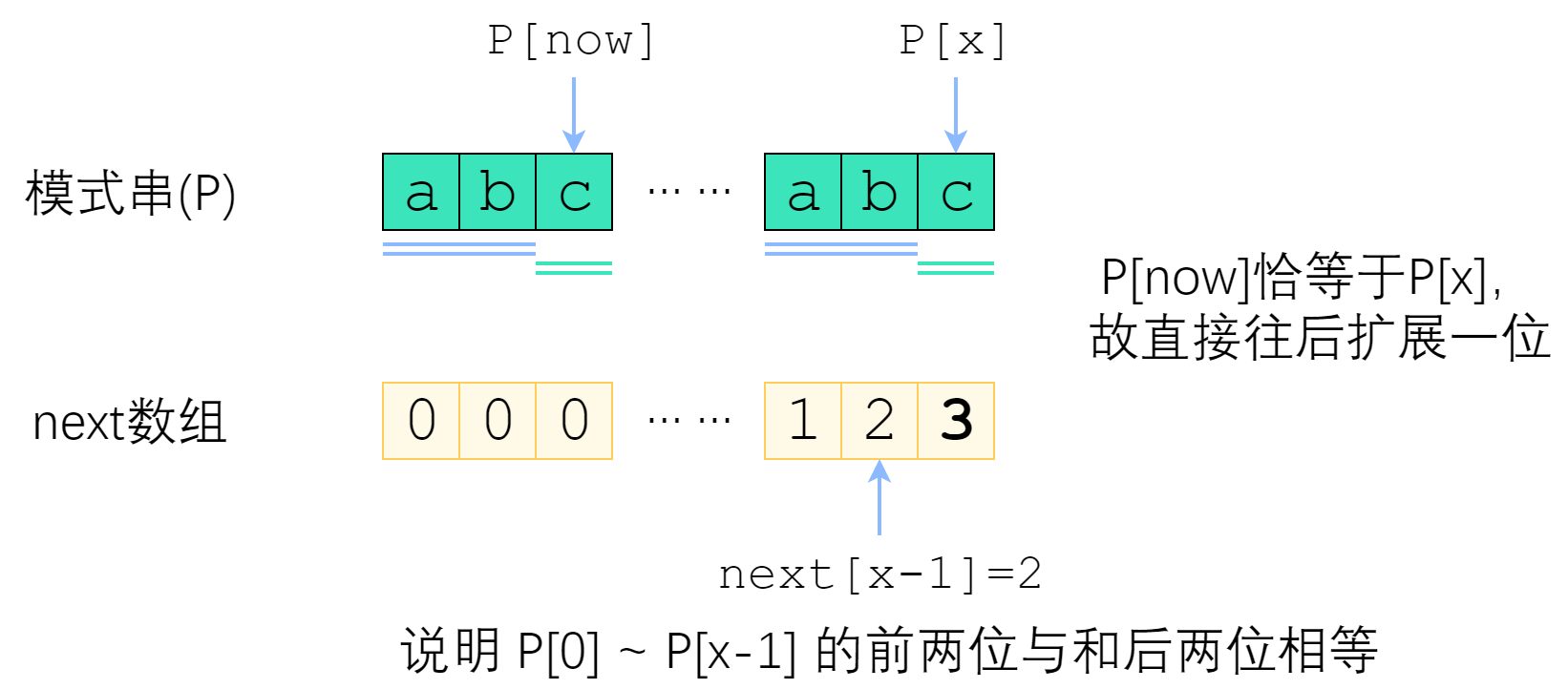
-
不相等。
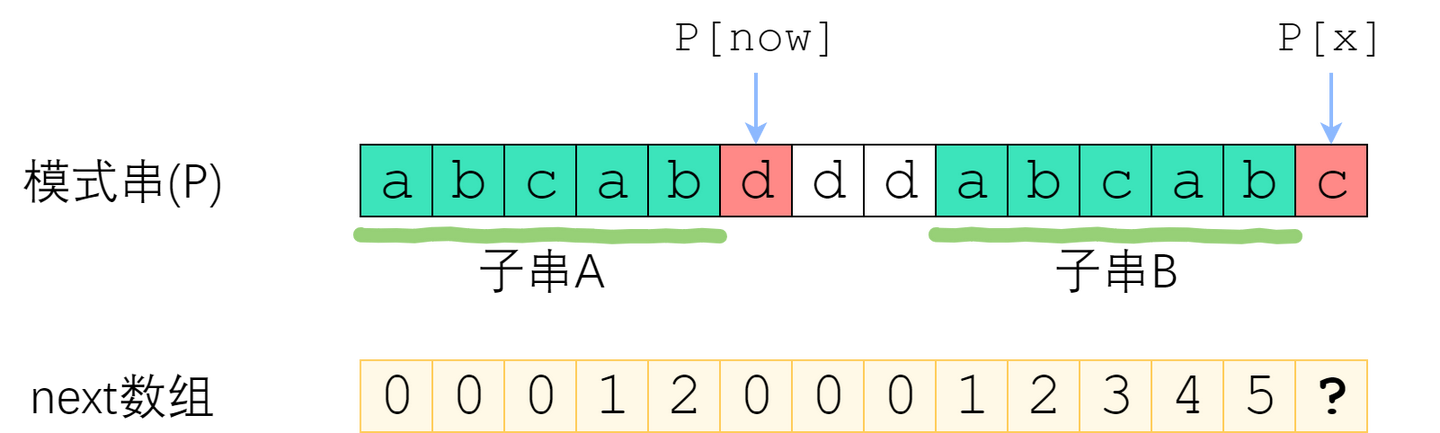
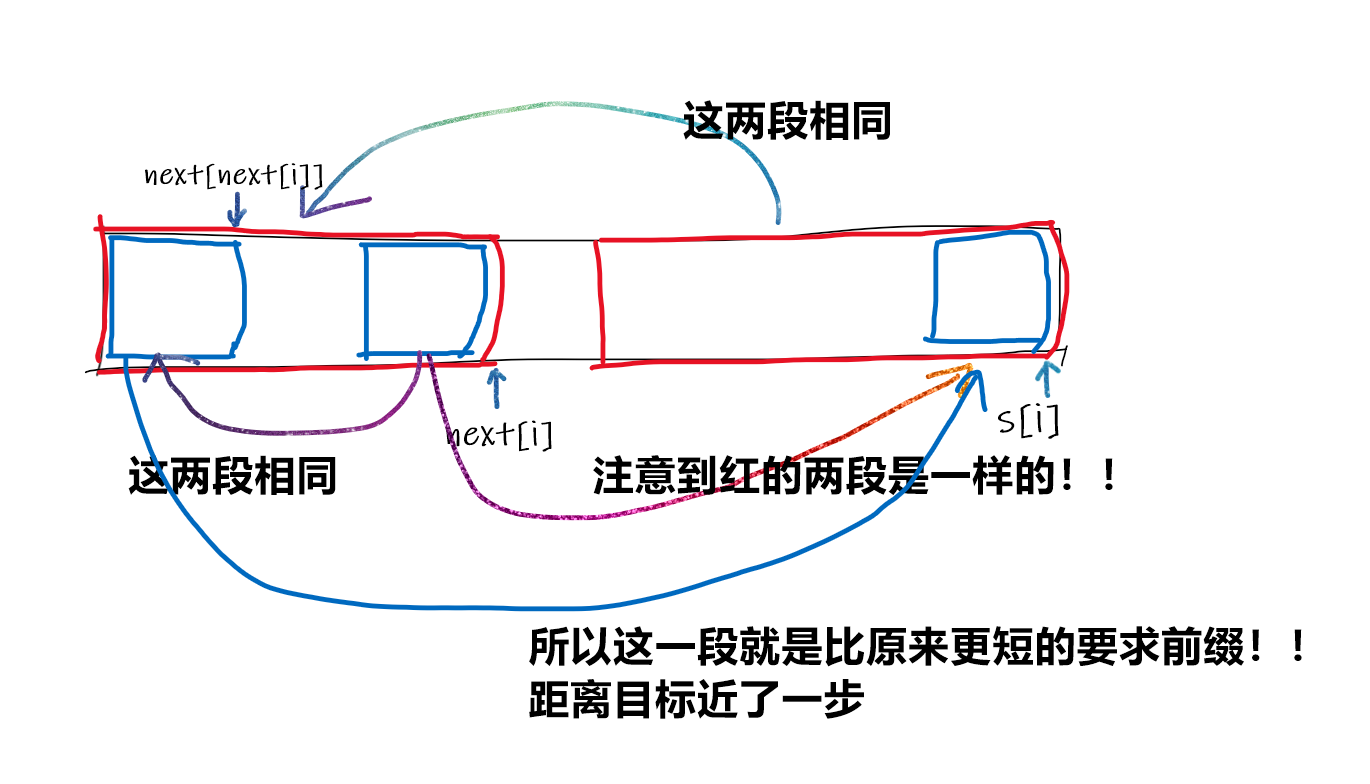
这种情况下,我们要不断地缩小
now,来找到一个新的匹配满足:子串 (A) 的前缀 (A[0dots mathrm{now}-1]) 和子串 (B) 对应的后缀是相等的,且 (A[(mathrm{now}-1) +1] = P[x])。观察到前面的条件,其实就是
next[now - 1]!所以做法已经呼之欲出了:不断地令
now = next[now - 1],直到 (P[mathrm{now}] = P[x])。
代码实现
求 next 数组
下标从 0 开始的写法
std::string P;
int next[MAXN];
void getNext() {
next[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < P.length(); ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now >= 0 && P[i] != P[now]) now = next[now - 1];
if (P[i] == P[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
else next[i] = -1;
}
}
下标从 1 开始的写法
char P[MAXN + 1];
int len, next[MAXN + 1];
void getNext() {
for (int i = 2; i <= len; ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now && P[i] != P[now + 1]) now = next[now];
if (P[i] == P[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
else next[i] = 0;
}
}
KMP 匹配
下标为 0 的写法
std::string S, P;
int next[MAXN];
void KMP() {
int i = 0, j = 0; std::vector<int> ans;
while (i < S.length()) {
if (S[i] == S[j]) {
++i; ++j;
if (j == P.length()) {
ans.push_back({i - j + 1});
j = next[j - 1] + 1;
}
} else {
if (j == 0) ++i;
else j = next[j - 1] + 1;
}
}
}
杂题选讲
P4391 [BOI2009]Radio Transmission 无线传输
解题报告
先说结论:答案是 (n - ext{next}[n])。
考虑这样一个字符串:
代码实现
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
char ss[MAXN];
int next[MAXN];
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
cin >> (ss + 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now && ss[i] != ss[now + 1]) now = next[now];
if (ss[i] == ss[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
} cout << n - next[n] << endl;
return 0;
}
P3435 [POI2006]OKR-Periods of Words
解题报告
先考虑对一个字符串该怎么搞。
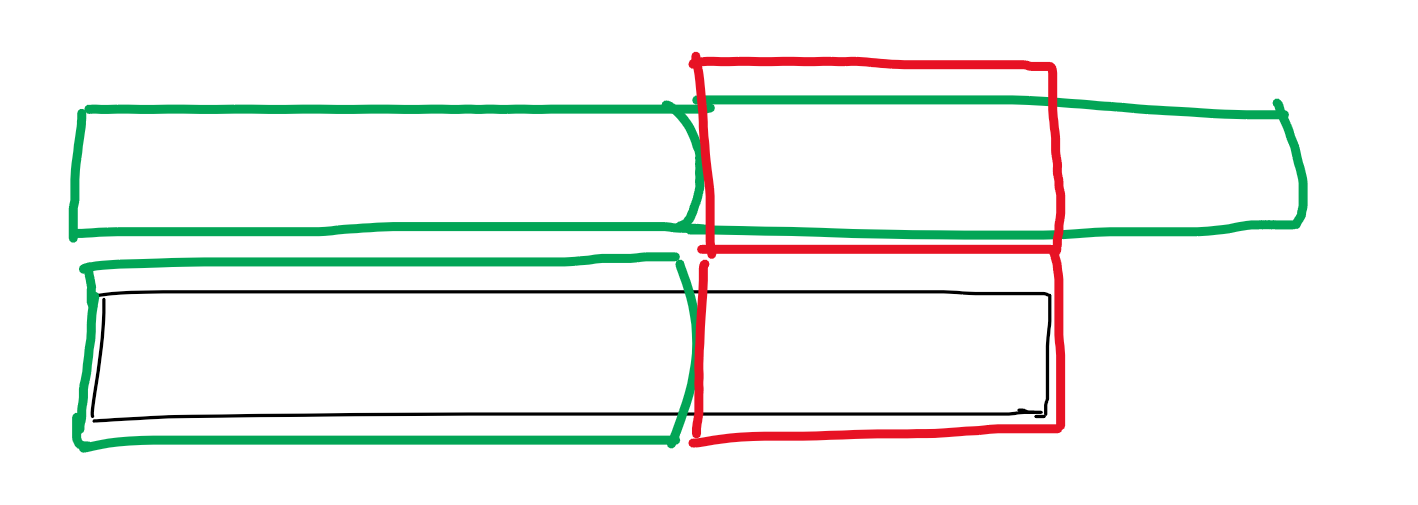
题目翻译过来就是求字符串的最长前缀(非原串),满足把这个前缀复制一遍后,这个字符串是两个前缀拼起来的前缀。
类似于这样:
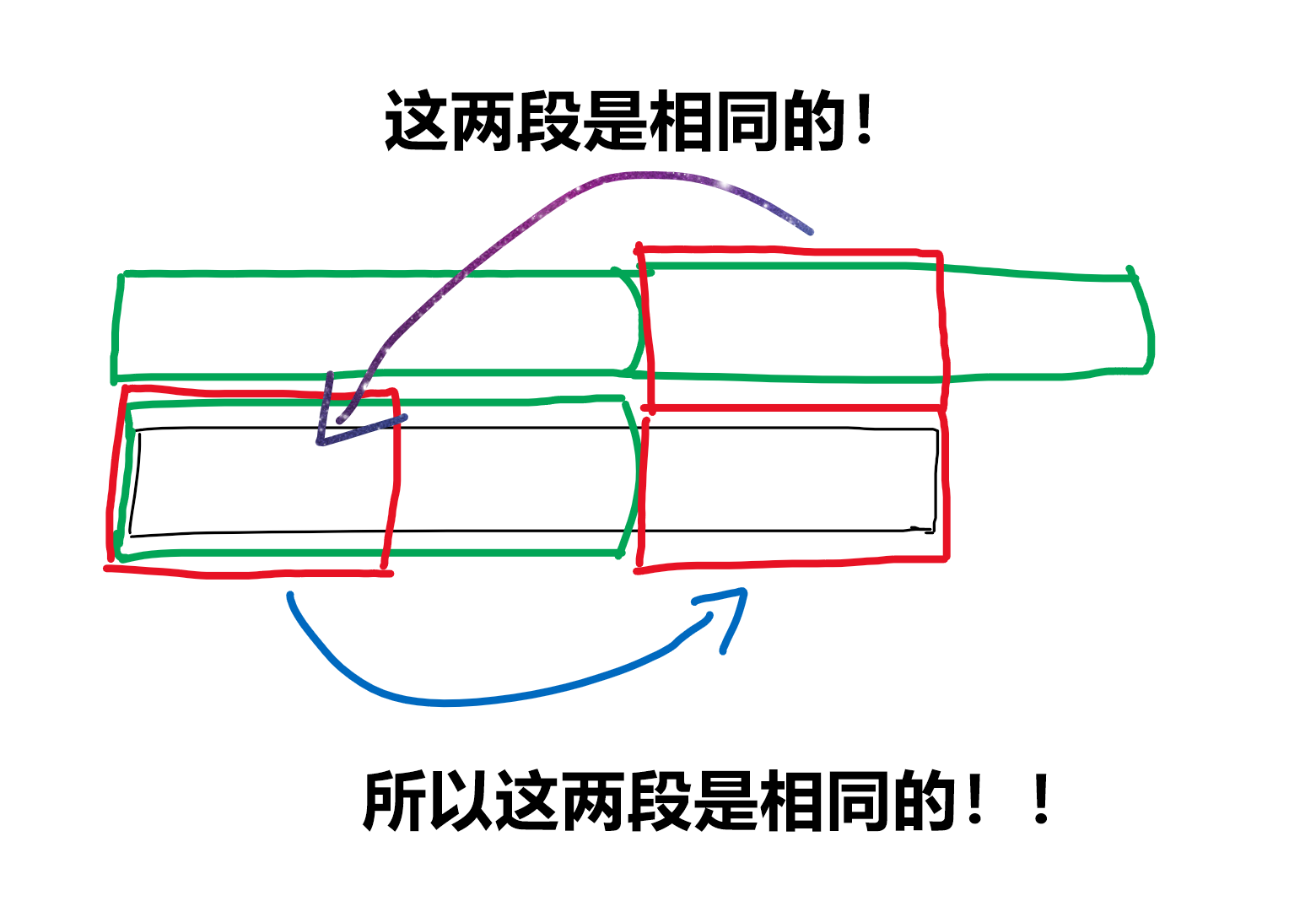
仔细观察,发现这里有一个重要的性质:
字符串的后缀等于字符串的前缀。是不是有点 next 数组的味道?
题目要求绿色段尽可能长,所以红色段要尽量短。问题转化成了求字符串的最短前缀,满足它既是前缀又是后缀。
可是 next 数组求的是最大值,这和要求的正好相反。
想一想跳 next 的过程。
所以只要我们不断跳 next,前缀就会不断变短,所以啊,不要停下来啊!
问题在于这个复杂度还是最坏 (O(n^2)) 的,不过我们只需要加一个记忆化即可,类似于路径压缩,把当前点的 next 直接指向最短前缀那里。
代码实现
const int MAXN = 1000000 + 10;
int n;
char ss[MAXN];
int next[MAXN];
void getNext() {
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now && ss[i] != ss[now + 1]) now = next[now];
if (ss[i] == ss[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
cin >> (ss + 1);
getNext();
lli ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int now = i;
while (next[now]) now = next[now];
if (next[i]) next[i] = now; // 路径压缩(bushi
ans += i - now;
} cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
P4824 [USACO15FEB]Censoring S
解题报告
上面的题都是从 next 数组下手,本题就来到了 KMP 算法的内部。
KMP 算法是从左往右扫字符串,观察新加入的字符能不能匹配来移动匹配指针,于是我们也要顺着这条思维路径,考虑加入一个字符之后会发生什么。
S: ifeelsohhighighlalala
T: high
为了简化篇幅,我们从 sohhigh 的 g 开始考虑。
S: ifeelsoh
T: high
S: ifeelsohhig
T: high
S: ifeelsohhigh
T: high
加入这个 h 之后,high 匹配成功,这时候就要把最后一段字符删掉。
S: ifeelsoh
T: high
然后后面又会有一个 igh 跟上来,我们要一块把它删干净;但如果是普通的 KMP,失配指针应该跳到 next 那里,这样会导致前面的 h 甚至更早的字符串失配(这个例子是看不出来的,可以自己手玩其他的试试)。所以为了把前面残留没匹配完的一块删干净,我们应该让匹配指针回到之前的状态。
S: ifeelsoh
T: high
然后继续加入字符继续删。
S: ifeelsohigh
T: high
这个过程就是每次加一个字符,或者删除末尾的一连串字符,删完后让匹配指针跳到之前匹配好的位置。前两个可以用栈维护,后一个直接对每个字符记一下,到这匹配指针指哪,就行了。
代码实现
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
char ss[MAXN], tt[MAXN], stk[MAXN];
int next[MAXN], pos[MAXN], top, n, m;
void getNext() {
for (int i = 2; i <= m; ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now && tt[i] != tt[now + 1]) now = next[now];
if (tt[i] == tt[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
}
}
void KMP() {
int j = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
stk[++top] = ss[i];
while (j && ss[i] != tt[j + 1]) j = next[j];
if (ss[i] == tt[j + 1]) ++j;
pos[top] = j;
if (j == m) {
top -= m; j = pos[top];
// 在栈中删除匹配成功的串
// 从删除的串之前那里继续往后匹配
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= top; ++i) cout << stk[i];
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> (ss + 1); cin >> (tt + 1);
n = (int) strlen(ss + 1); m = (int) strlen(tt + 1);
getNext();
KMP();
return 0;
}
NOI2014 动物园
解题报告
和那个 Periods of Words 类似的想法。
难点在于如何优化这个最坏情况下 (O(Tn^2)) 的算法,记忆化的做法已经不适用了,但是可以倍增。(上面那题同样也可以倍增)
时间有点紧,还需要一个玄学优化——把倍增数组两维交换,第一维是跳 (2^j) 次。
代码实现
const int MAXN = 1000000 + 10;
const int HA = 1e9 + 7;
char ss[MAXN]; int n;
int next[MAXN];
int fail[20][MAXN];
void getNext() {
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int now = next[i - 1];
while (now && ss[i] != ss[now + 1]) now = next[now];
if (ss[i] == ss[now + 1]) next[i] = now + 1;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
fail[0][i] = next[i];
for (int k = 1; k <= 19; ++k) {
fail[k][i] = fail[k - 1][fail[k - 1][i]];
}
}
}
void cleanup() {
memset(next, 0, sizeof next);
memset(fail, 0, sizeof fail);
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
cin >> (ss + 1); n = (int) strlen(ss + 1);
getNext(); int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int now = i;
for (int k = 19; k >= 0; --k) {
if (fail[k][now] * 2 > i) now = fail[k][now];
} int fx = 0;
for (int k = 19; k >= 0; --k) {
if (fail[k][now]) { fx += (1 << k); now = fail[k][now]; }
} now = fx;
ans = 1ll * ans * (now + 1) % HA;
} cout << ans << endl; cleanup();
}
return 0;
}