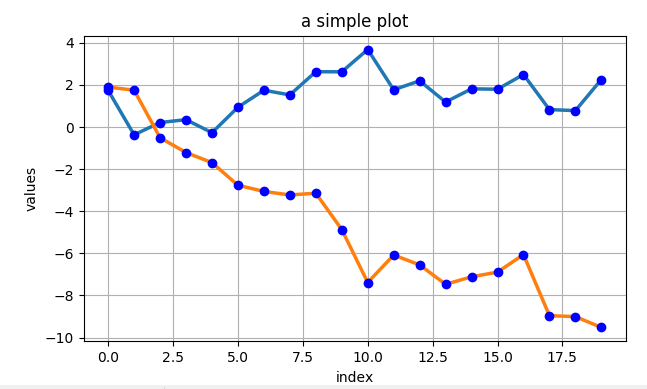
import matplotlib as mpl import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(2000) y = np.random.standard_normal((20,2)) # print(y) ''' 不同的求和 print(y.cumsum()) print(y.sum(axis=0)) print(y.cumsum(axis=0)) ''' # 绘图 plt.figure(figsize=(7,4)) plt.plot(y.cumsum(axis=0),linewidth=2.5) plt.plot(y.cumsum(axis=0),'bo') plt.grid(True) plt.axis("tight") plt.xlabel('index') plt.ylabel('values') plt.title('a simple plot')
plt.show()
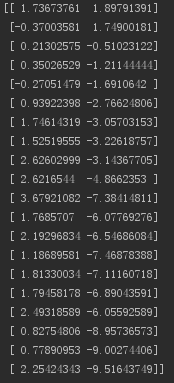
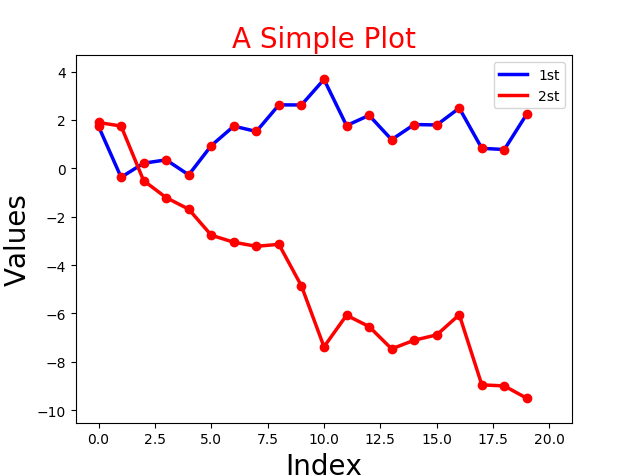
2.下面分别提取两组数据,进行绘图。
import matplotlib as mpl import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(2000) date = np.random.standard_normal((20,2)) y = date.cumsum(axis=0) print(y) # 重点下面两种情况的区别 print(y[1]) # 取得是 第1行的数据 [-0.37003581 1.74900181] print(y[:,0]) # 取得是 第1列的数据 [ 1.73673761 -0.37003581 0.21302575 0.35026529 ... # 绘图 plt.plot(y[:,0],lw=2.5,label="1st",color='blue') plt.plot(y[:,1],lw=2.5,label="2st",color='red') plt.plot(y,'ro') # 添加细节 plt.title("A Simple Plot",size=20,color='red') plt.xlabel('Index',size=20) plt.ylabel('Values',size=20) # plt.axis('tight') plt.xlim(-1,21) plt.ylim(np.min(y)-1,np.max(y)+1) # 添加图例 plt.legend(loc=0) plt.show()
3.双坐标轴。
import matplotlib as mpl import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(2000) date = np.random.standard_normal((20,2)) y = date.cumsum(axis=0) y[:,0]=y[:,0]*100 fig,ax1 = plt.subplots() plt.plot(y[:,0],'b',label="1st") plt.plot(y[:,0],'ro') plt.grid(True) plt.axis('tight') plt.xlabel("Index") plt.ylabel('Values of 1st') plt.title("This is double axis label") plt.legend(loc=0) ax2=ax1.twinx() plt.plot(y[:,1],'g',label="2st") plt.plot(y[:,1],'r*') plt.ylabel("Values of 2st") plt.legend(loc=0) plt.show()
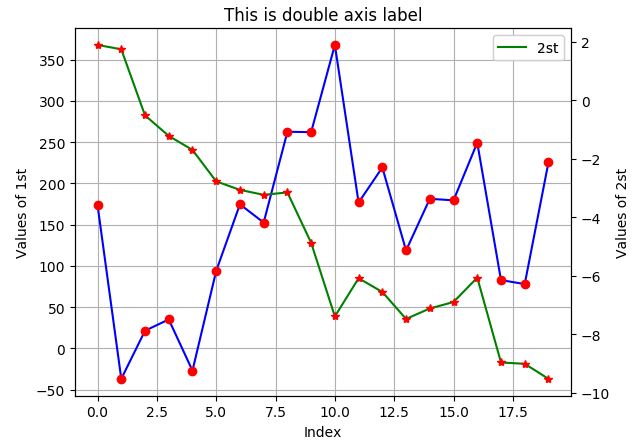
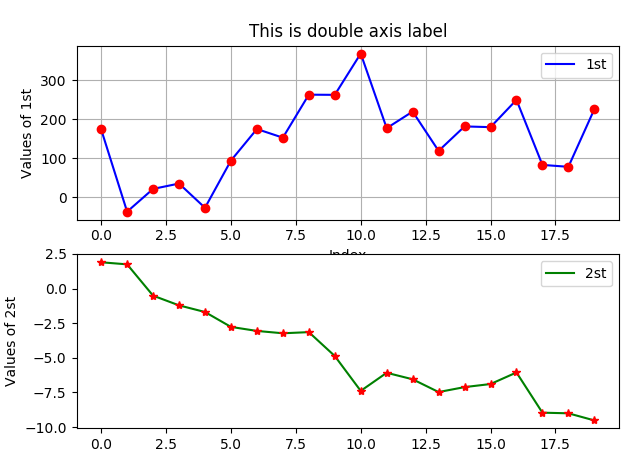
4. 分为两个图绘画。
import matplotlib as mpl import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(2000) date = np.random.standard_normal((20,2)) y = date.cumsum(axis=0) y[:,0]=y[:,0]*100 plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) # 确定图片大小 plt.subplot(211) # 确定第一个图的位置 (行,列,第几个)两行一列第一个图 plt.plot(y[:,0],'b',label="1st") plt.plot(y[:,0],'ro') plt.grid(True) plt.axis('tight') plt.xlabel("Index") plt.ylabel('Values of 1st') plt.title("This is double axis label") plt.legend(loc=0) plt.subplot(212) # 确定第一个图的位置 plt.plot(y[:,1],'g',label="2st") plt.plot(y[:,1],'r*') plt.ylabel("Values of 2st") plt.legend(loc=0) plt.show()
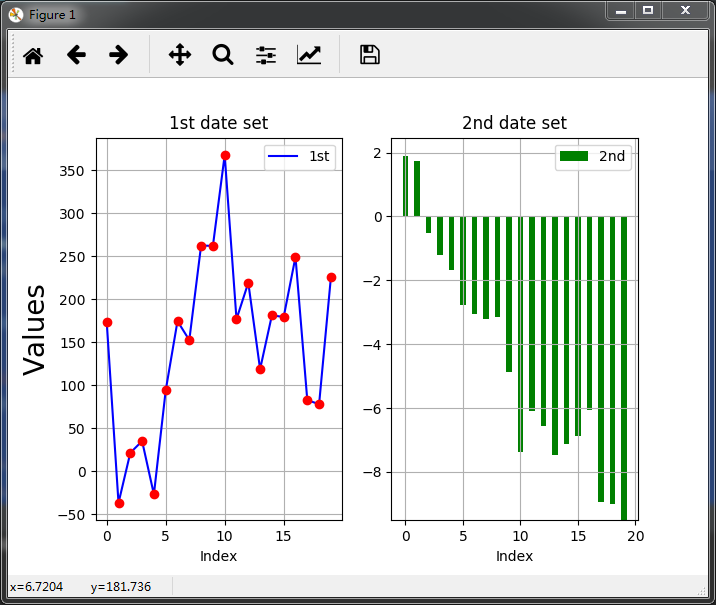
5.在两个图层中绘制两种不同的图(直线图立方图)
import matplotlib as mpl import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(2000) date = np.random.standard_normal((20,2)) y = date.cumsum(axis=0) y[:,0]=y[:,0]*100 plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) # 确定图片大小 plt.subplot(121) # 确定第一个图的位置 plt.plot(y[:,0],'b',label="1st") plt.plot(y[:,0],'ro') plt.grid(True) plt.axis('tight') plt.xlabel("Index") plt.ylabel('Values',size=20) plt.title("1st date set") plt.legend(loc=0) plt.subplot(122) # 确定第一个图的位置 plt.bar(np.arange(len(y[:,1])),y[:,1],width = 0.5,color='g',label="2nd") # 直方图的画法 plt.grid(True) plt.xlabel("Index") plt.title('2nd date set') plt.legend(loc=0) plt.show()