每次修改java后,都需要重新运行main方法才能生效。这样会降低开发效率。我们可以使用
spring boot提供的开发工具来实现热部署,为项目加上一下依赖:
<!-- 开发环境增加热部署依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> </dependency>
等待maven构建后,发现project项目名字后面会增加 devtools
运行单元测试。
单元测试对于程序来说非常重要,不仅能增强程序的健壮性,而且也为程序的重构提供了依据,目前很多开源项目的测试覆盖率高达90%;
spring boot运行web应用,只需要执行main方法即可,那么如何测试web程序呢?
那就需要使用spring boot的单元测试。
1.spring boot提供了@springbootTest注解,可以让我们在单元测试中测试spring boot的程序。
需要加入依赖,使用maven构建
<!-- 增加spring-boot-starter-test依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
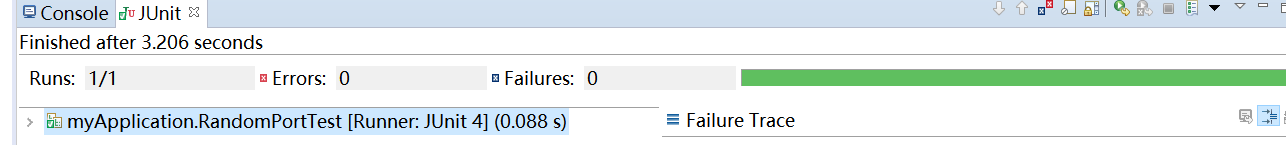
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class RandomPortTest { @Autowired private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test public void testHello() { //测试hello 方法 String result = restTemplate.getForObject("/hello", String.class); assertEquals("Hello World!", result); }
在测试类中加入了@RunWith,@SpringBootTest注解,
其中为spring boot test配置了webEnvironment属性,表示在运行测试时,会为web容器随机分配端口。
在测试方法中,使用@Test注解修饰。使用TestResultTemplate调用“/hello”服务。
这种测试会启动web容器。
只测试业务组件,不测试web容器,那么只启动spring的容器。
MyService.java @Service public class MyService { public String helloService() { return "hello"; } }
MyServiceTest.java @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.NONE) public class MyServiceTest { @Autowired private MyService myService; @Test public void testHello() { String result = myService.helloService(); System.out.println(result); } }
新建了一个MyService服务类,MyServiceTest会对该类进行测试,直接在测试类中注入MyService实例
SpringBootTest的webEnvironment属性会被设置为NONE,因此web容器不会被启动。