目录:
盒子阴影
轮廓线
清除浮动带来的影响的方法
两种标签的边距问题
变态盒模型
练习之拼接图
相对定位
绝对定位
练习之船图
盒子阴影
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> #div1{ width: 300px; height: 300px; margin: 0 auto; background-color: #878787; box-shadow: 10px 5px 0px 0px green; /*x轴偏移 y轴偏移 模糊范围 阴影扩展范围 阴影颜色*/ } </style> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> </div> </body> </html>
运行图

轮廓线
案例一
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> #div1 { width: 475px; height: 330px; border: 10px solid red; border-right: 20px solid red; padding: 10px 15px 20px 10px; outline: 2px dotted blue;/*轮廓线*/ } </style> <title>保时捷+轮廓线</title> </head> <body> <div id="div1"> <img src="../../img/baoshijie.jpg" alt="" width="450" height="300"> </div> </body> </html>
运行图
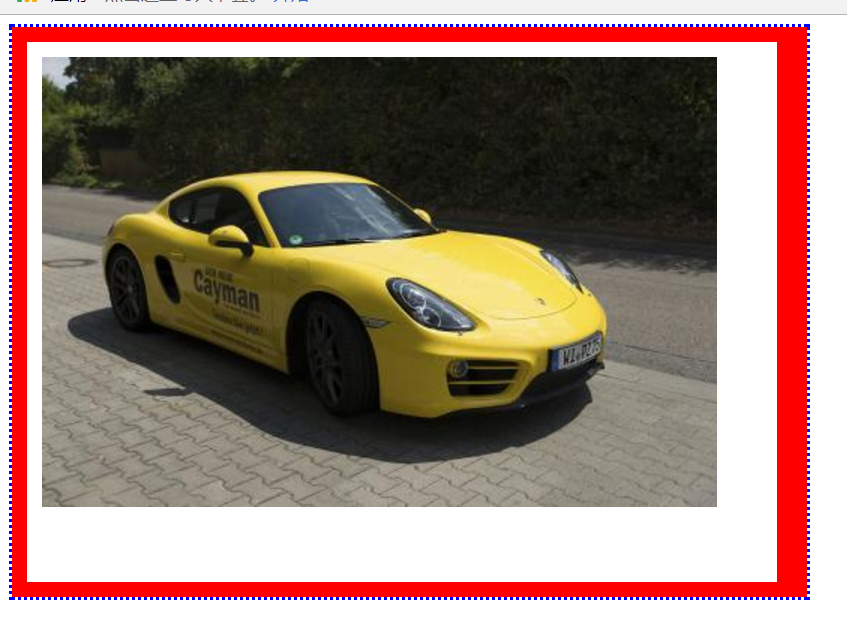

案例2
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> input:focus{ outline: none;/*指针选取时,没有轮廓线*/ } </style> <title>轮廓线</title> </head> <body> 姓名:<input type="text"> <br> 姓名:<input type="text"> </body> </html>
运行图
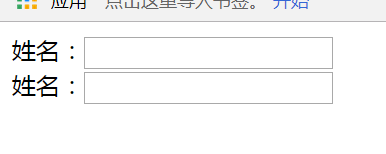
如果没有
input:focus{
outline: none;/*指针选取时,没有轮廓线*/
}
这段,鼠标指针点击输入框,输入框边框会变蓝色,有了这段,变化只是输入框里出现光标。
浮动:怎么清除浮动带来的影响
有两种方法,全在代码里标注起来了
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> #div1{ height: 100px; background-color: red; } #div2{ /*height: 400px;*/ background-color: yellow; overflow: hidden; } #div3{ height: 100px; background-color: green; clear: both; } #div21{ width: 20%; height: 750px; background-color: aqua; float: left; } #div22{ width: 60%; height: 750px; background-color: aquamarine; float: left; } #div23{ width: 10%; height: 750px; background-color: bisque; float: left; } /*#div26{!*方法一:清除浮动野路子*! clear: both; }*/ /*.clearfix{ zoom: 1;!*兼容模式:给ie低版本*! } .clearfix:after{ !*方法二:清除浮动best方法*! content: ""; display: block; clear: both; }*/ </style> <title>浮动:怎么清除浮动带来的影响</title> </head> <body> <div> <div id="div1"></div> <div id="div2" class="clearfix"> <div id="div21">左</div> <div id="div22">中</div> <div id="div23">右</div> <!--<div id="div26"></div>--> </div> <div id="div3"></div> </div> </body> </html>
行级标签和块级标签 两种盒子模型的外边距问题
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> span { height: 20px; background-color: #878787; } #s1 { margin-right: 20px; } #s2 { margin-left: 30px; } /*距离相加*/ div { height: 30px; background-color: red; } #div1 { margin-bottom: 20px; } #div2 { margin-top: 30px; } /*距离选最大的展示*/ </style> <title>Margin</title> </head> <body> <span id="s1">asdfasf</span> <span id="s2">asfdasfa</span> <div id="div1"></div> <div id="div2"></div> </body> </html>
运行图

结果:span两个盒子左右相距50px div两个盒子上下相距30px
知识点:span标签是行级,所以看她的margin左右边距,会发现 两个span盒子模型的最终距离是margin边距相加的
div标签是块级,看他的margin上下边距,会发现 两个div盒子的最终距离 展现的是其中margin边距最大的
变态盒模型
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } #left { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: #F2AD0A; float: left; border: 1px solid green; } #center { height: 100px; width: 60%; background-color: #FF0000; float: left; } #right { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: #FFFF00; float: left; } </style> <title>怪异盒子模型</title> </head> <body> <div> <div id="left"></div> <div id="center"></div> <div id="right"></div> </div> </body> </html>
运行图

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } #left { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: #F2AD0A; float: left; border: 1px solid green; /*变态盒模型*/ box-sizing: border-box; /*内容区变少了*/ } #center { height: 100px; width: 60%; background-color: #FF0000; float: left; } #right { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: #FFFF00; float: left; } </style> <title>怪异盒子模型</title> </head> <body> <div> <div id="left"></div> <div id="center"></div> <div id="right"></div> </div> </body> </html>
运行图

上边两个运行图的差别就是有无
box-sizing: border-box;这段的区别。
练习之拼接图:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> #container { height: 500px; width: 800px; margin: 0 auto; } #top { height: 100px; } #tleft { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: antiquewhite; float: left; } #tcenter { height: 100px; width: 60%; background-color: aquamarine; float: left; } #tright { height: 100px; width: 20%; background-color: bisque; float: left; } #center { height: 50px; background-color: chartreuse; } #bottom { height: 350px; } #bleft { height: 350px; width: 75%; float: left; } #bright { height: 350px; width: 25%; background-color: darkturquoise; float: left; } #btop { height: 50%; } #btleft { height: 100%; width: 50%; background-color: cornflowerblue; float: left; } #btright { height: 100%; width: 50%; background-color: bisque; float: left; } #bbottom { height: 50%; } #bbleft { height: 100%; width: 50%; background-color: coral; float: left; } #bbright { height: 100%; width: 50%; background-color: cyan; float: left; } </style> <title>色彩图拼接</title> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="top"> <div id="tleft"></div> <div id="tcenter"></div> <div id="tright"></div> </div> <div id="center"></div> <div id="bottom"> <div id="bleft"> <div id="btop"> <div id="btleft"></div> <div id="btright"></div> </div> <div id="bbottom"> <div id="bbleft"></div> <div id="bbright"></div> </div> </div> <div id="bright"></div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行图:
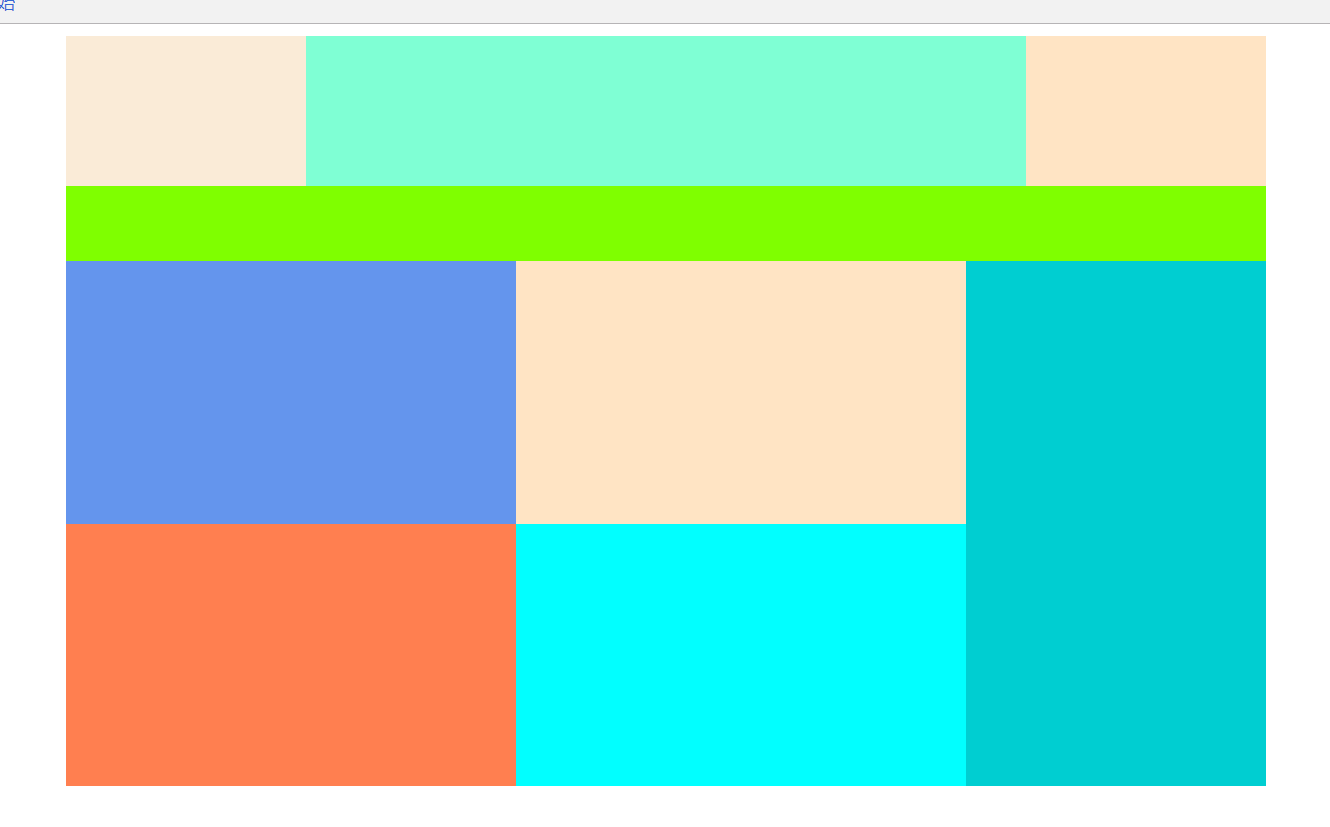
相对定位:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> /*相对定位: 1:相对与自己原来的位置进行定位 2:移动以后,自己原来的位置不会被其他元素占用*/ #left { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: aqua; float: left; } #center { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: antiquewhite; float: left; position: relative; top: 20px; left: 50px; z-index: -1; /*有这条代码就会让right盖住center*/ } #right { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: aquamarine; float: left; } </style> <title>相对定位</title> </head> <body> <div id="left"></div> <div id="center"></div> <div id="right"></div> </body> </html>
运行图

绝对定位:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> * { padding: 0px; margin: 0px; } #div1 { height: 300px; background-color: #FFFF00; margin: 20px 0 0 20px; overflow: hidden; position: relative; } #div2 { height: 250px; width: 90%; background-color: aqua; margin: 20px 0 0 20px; overflow: hidden; } #div3 { height: 200px; width: 80%; background-color: chartreuse; margin: 20px 0 0 20px; overflow: hidden; } #left { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: #433eff; float: left; } #center { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: antiquewhite; float: left; position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 10px; } #right { height: 50px; width: 200px; background-color: aquamarine; float: left; } </style> <title>绝对定位</title> </head> <body> <!--绝对定位: 1:相对于,离他最近的,bingqie使用了定位的父元素 如果没有符合的,最后以body为基准。 2:元素原来的空间会被其他元素占用。--> <div id="div1"> <div id="div2"> <div id="div3"> <div id="left"></div> <div id="center"></div> <div id="right"></div> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
运行图
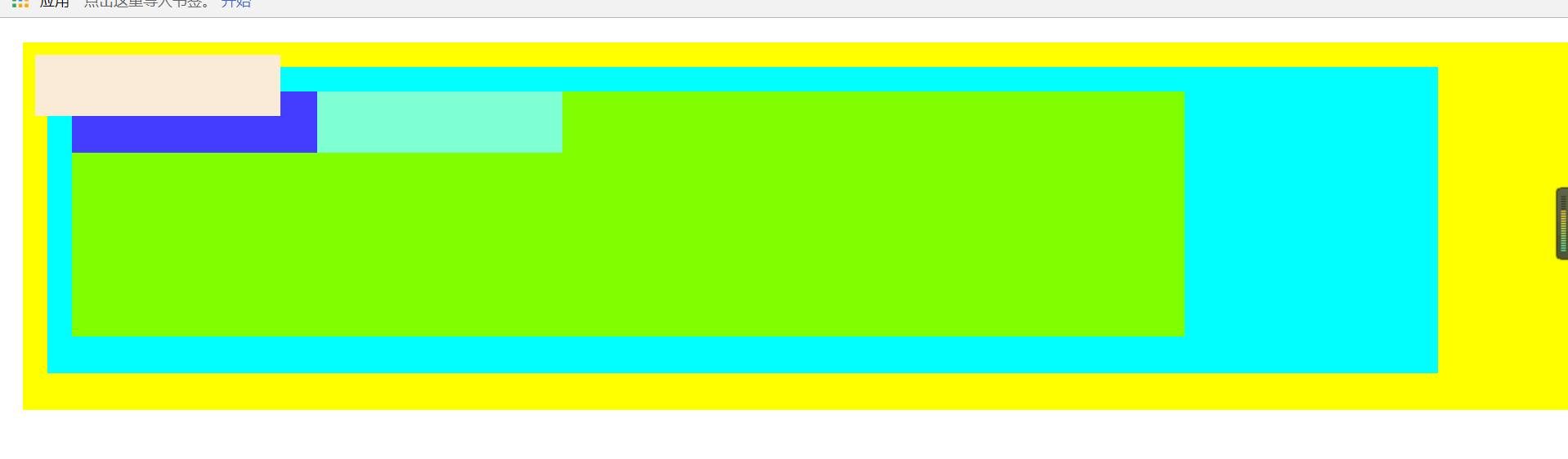

案例之船图:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style> #container { width: 306px; height: 142px; background-image: url("../../img/duo.png"); margin: 0 auto; margin-top: 50px; } #img1 { position: relative; top: 25px; left: 0px; opacity: 0; } #img1:hover { opacity: 1; } #img2 { position: relative; top: -33px; left: -64px; opacity: 0; } #img2:hover { opacity: 1; } #img3 { position: relative; top: -148px; left: 160px; opacity: 0; } #img3:hover { opacity: 1; } #img4 { position: relative; top: -90px; left: 99px; opacity: 0; } #img4:hover { opacity: 1; } </style> <title>船图</title> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <img src="../../img/duo1.png" alt="1" id="img1"> <img src="../../img/duo2.png" alt="2" id="img2"> <img src="../../img/duo3.png" alt="3" id="img3"> <img src="../../img/duo4.png" alt="4" id="img4"> </div> </body> </html>
运行图

运行效果是鼠标指针点在哪个图标上,那个图标就会展现成放大外凸