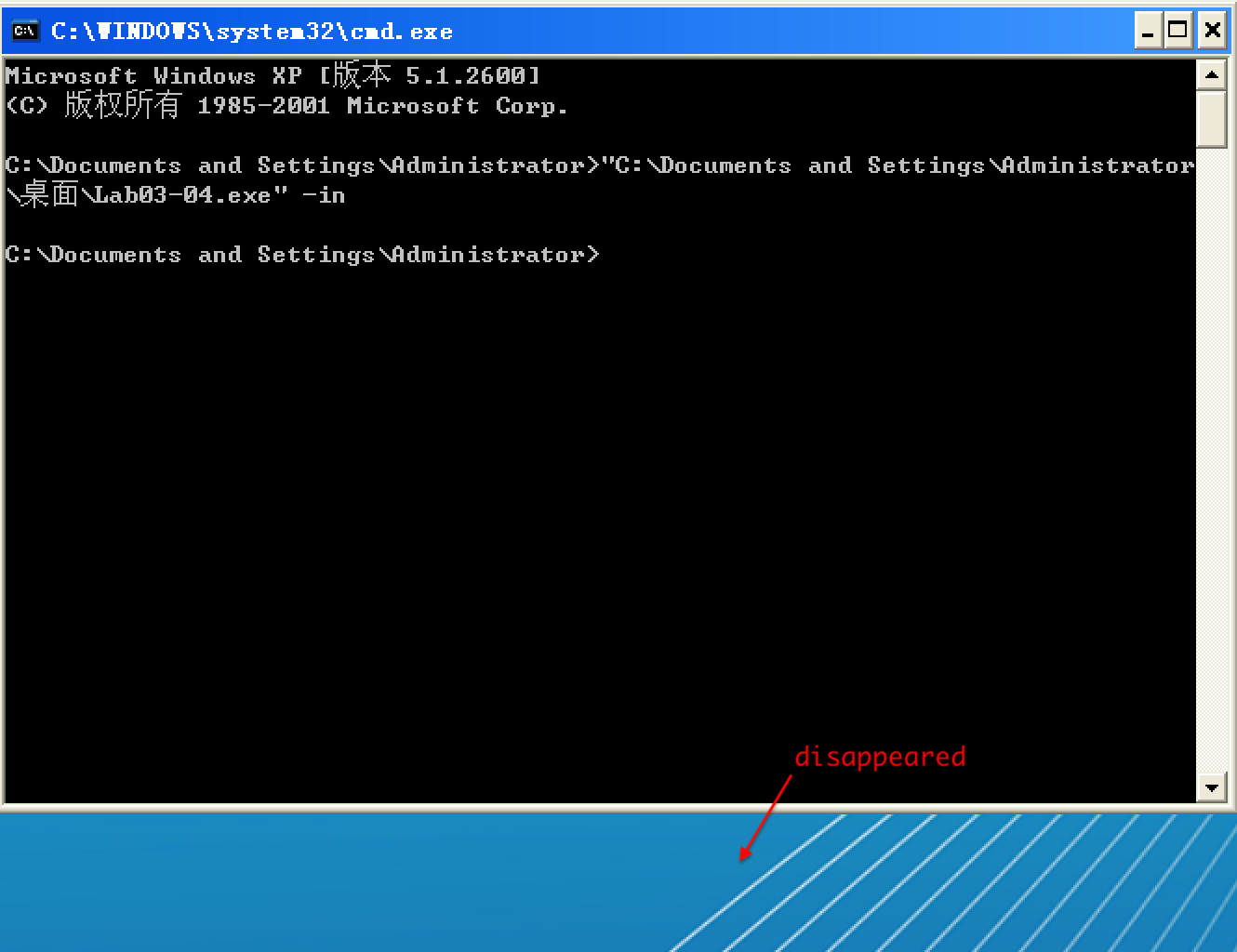
Analyze the malware found in the file Lab03-04.exe using basic dynamic analysis tools. (This program is analyzed further in the Chapter 9 labs.)
Questions and Short Answers
-
What happens when you run this file?
A: When you run this malware by double-clicking it, the program immediately deletes itself.
-
What is causing the roadblock in dynamic analysis?
A: We suspect that we may need to provide a command-line argument or a missing component to the program.
-
Are there other ways to run this program?
A: We try using the command-line parameters shown in the strings listing (like
-in), but doing so is not fruitful. More in-depth analysis is required. (We’ll analyze this malware further in the labs for Chapter 9.)
Detailed Analysis
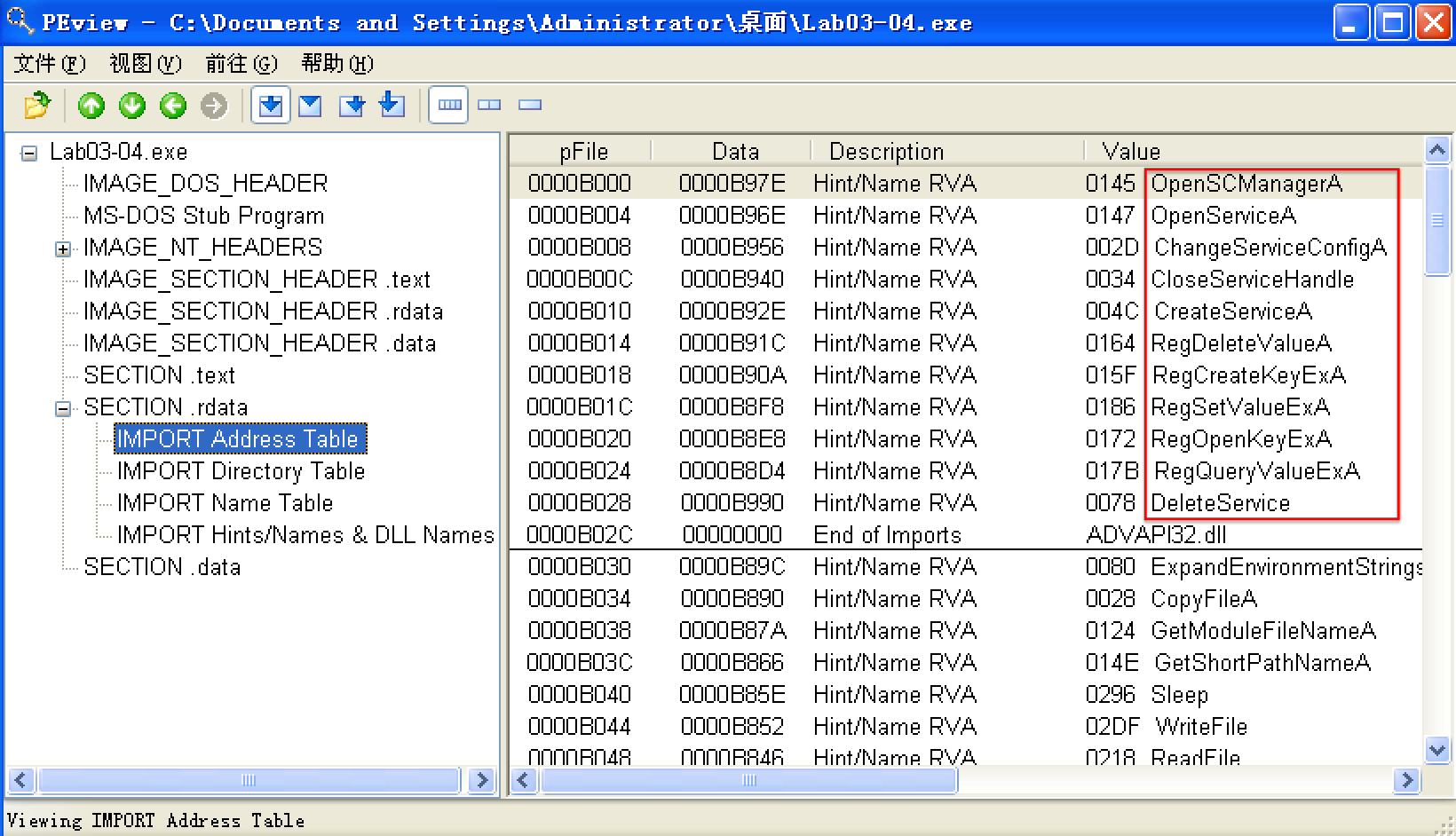
We begin with basic static analysis, examining the PE file structure and strings. We see that this malware imports networking functionality, service-manipulation functions, and registry-manipulation functions. In the following listing, we notice a number of interesting strings.
-
PEview
-
翻译版书1.3 查找字符串(英文版书,Part 1: Basic Analysis -> Finding Strings)
步骤:
-
下载Strings(英文原版书提供的链接好使,翻译版失效。)
-
cmd -> 进入下载的strings.exe可执行文件所在文件夹 -> 使用 strings 命令查看
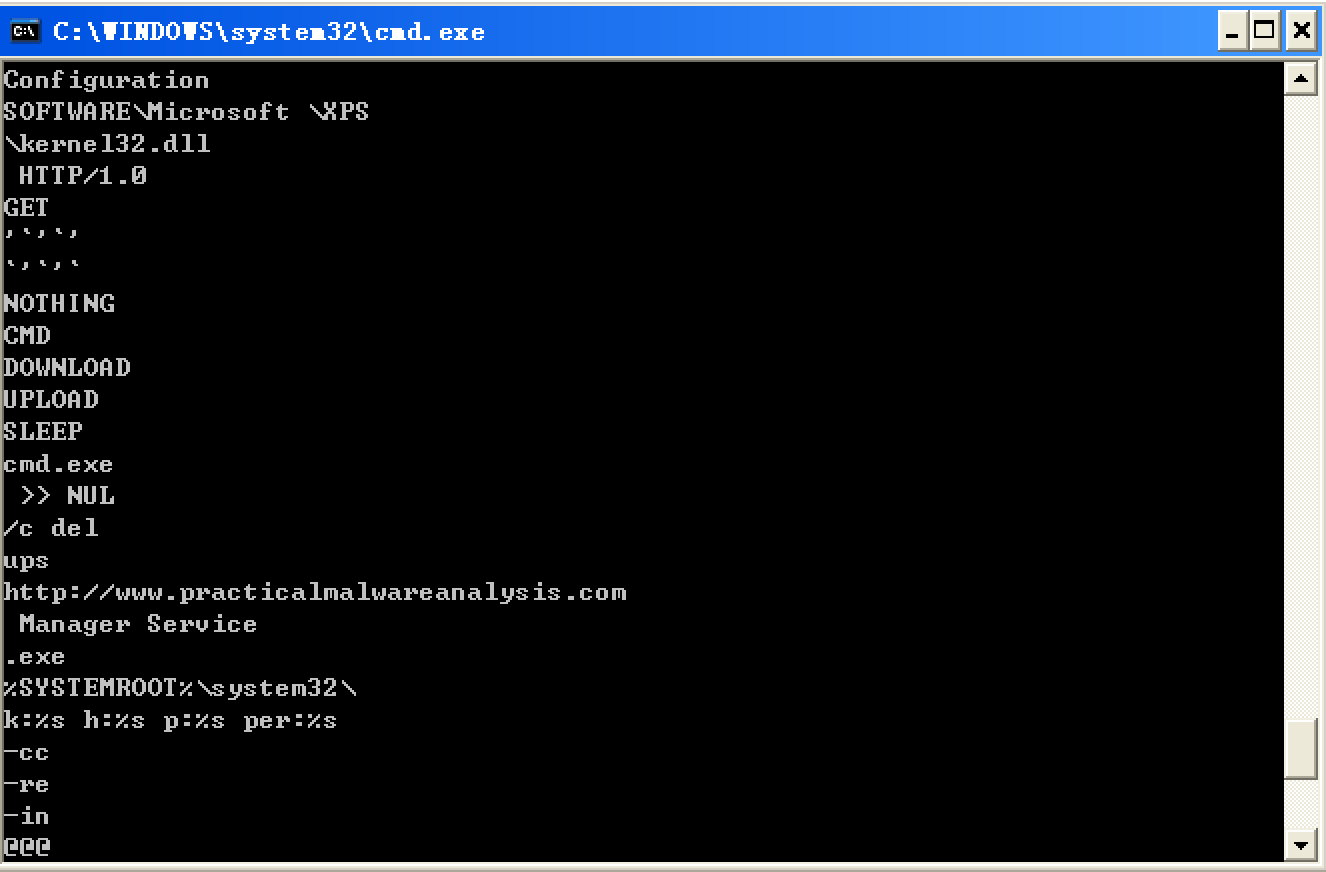
C:Documents and SettingsAdministrator桌面杂Strings>strings.exe "C:Documents and SettingsAdministrator桌面Lab03-04.exe"
-
We see strings such as a domain name and the registry location SOFTWARE Microsoft XPS. Strings like DOWNLOAD and UPLOAD, combined with the HTTP/1.0 string, suggest that this malware is an HTTP backdoor. The strings -cc, -re, and -in could be command-line parameters (for example -in may stand for install). Let’s see if basic dynamic techniques show us how these strings are used.
Before we run the malware, we run procmon and clear out all events, start Process Explorer, and set up a virtual network. When we run the malware, it appears to immediately delete itself, and we see nothing else of interest while watching with Process Explorer.
Next, we use procmon with a filter on the process name Lab03-04.exe. There aren’t any interesting WriteFile or RegSetValue entries, but upon further digging, we find an entry for Process Create. Double-clicking this entry brings up the dialog shown in Figure 3-11L, and we see that the malware is deleting itself from the system using "C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe" /c del Z: Lab03-04.exe >> NUL, as seen at ({color{red}1}).
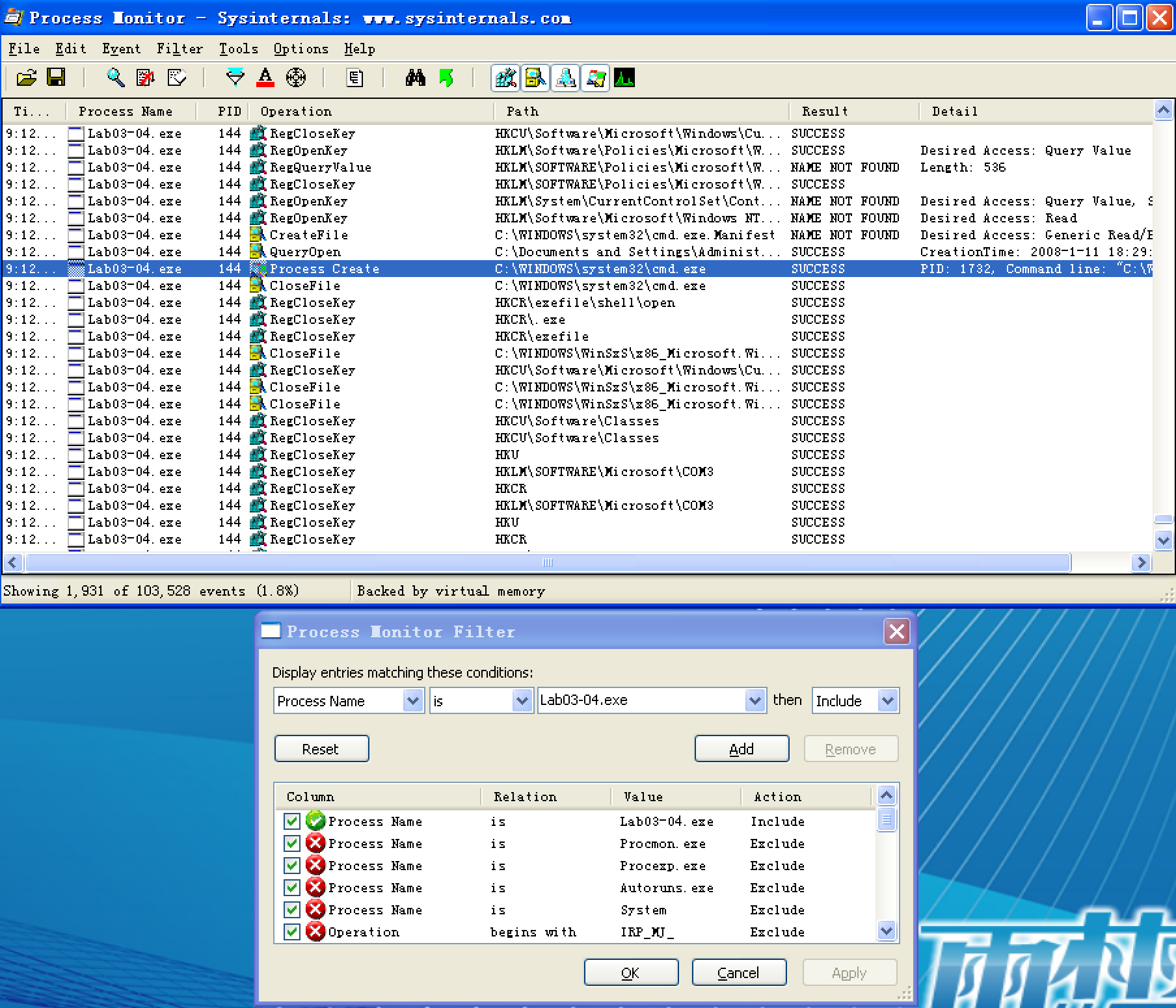
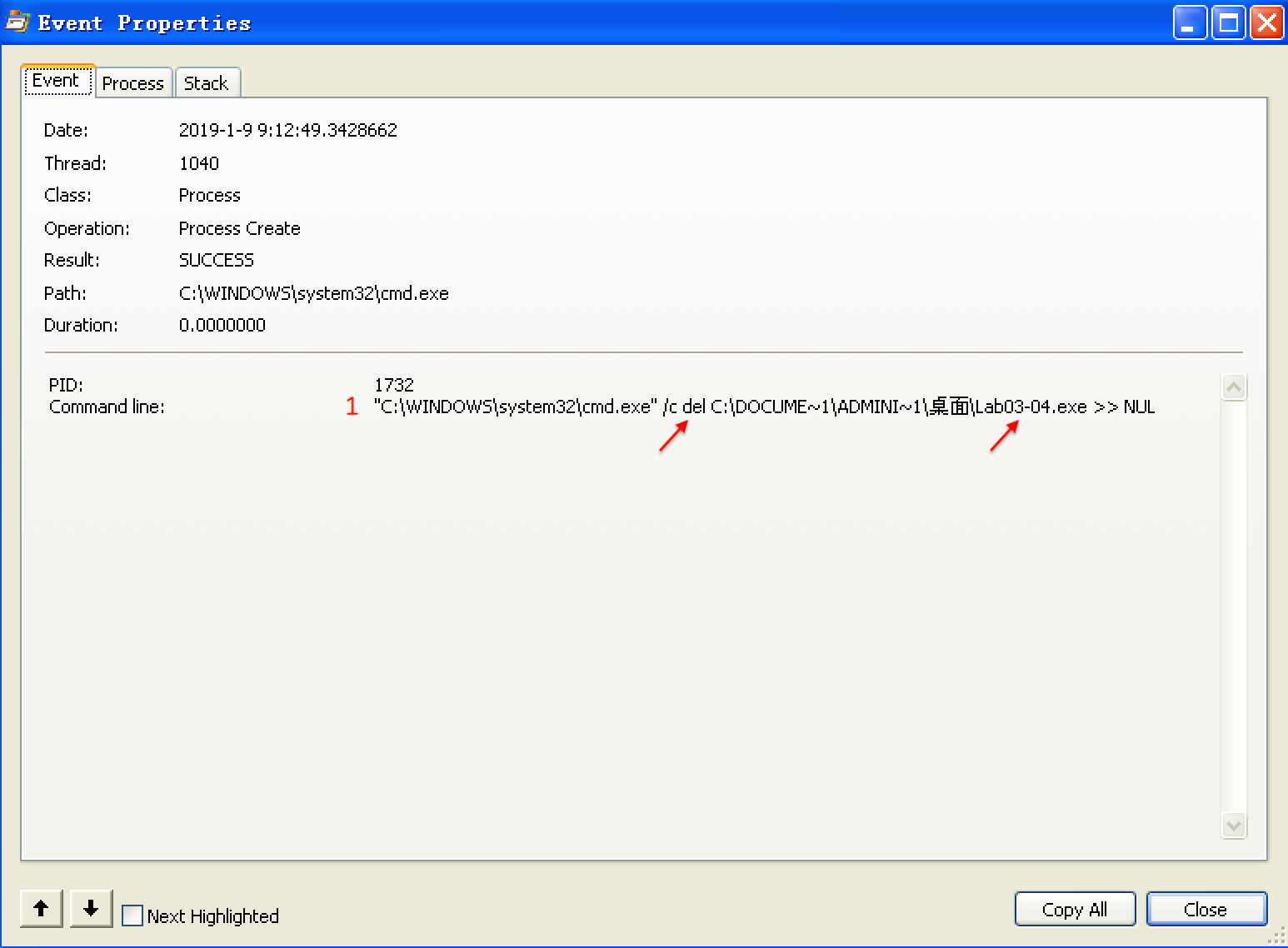
We can try to run the malware from the command line using the command-line options we saw in the strings listing (-in, -re, and –cc), but all of them fail and result in the program deleting itself. There isn’t much more we can do with basic dynamic techniques at this point, until we dig deeper into the malware. (We will revisit this malware in the Chapter 9 labs.)
以选项 -in 试验,Lab03-04.exe 执行前:
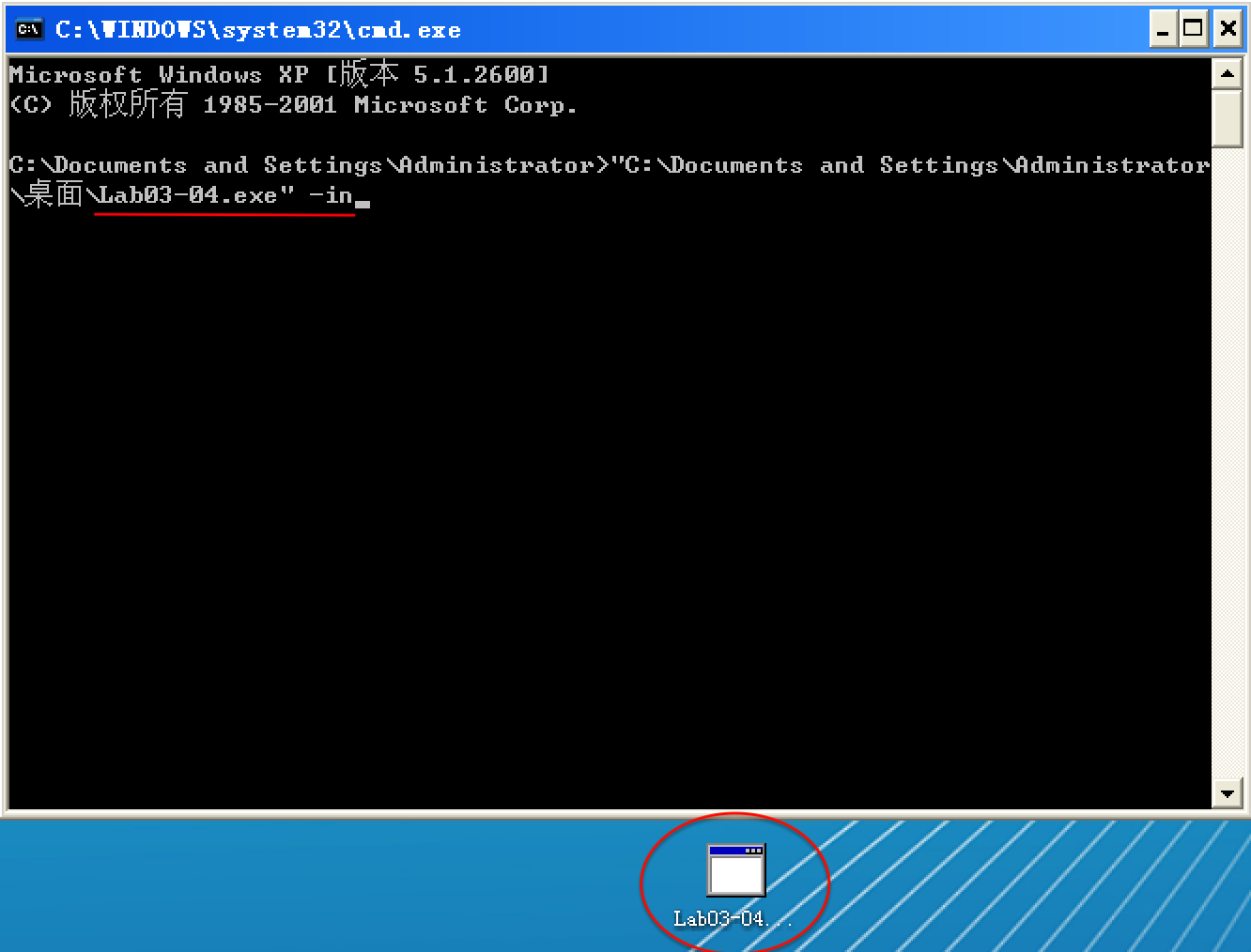
以选项 -in 试验,Lab03-04.exe 执行后: