1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.abel533</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4</version>
</dependency>
2、配置plugins(Mapper拦截器)
Mybatis-config.xml的plugins下新增plugin配置,配置通用Mapper的接口。
<plugins>
<!-- 分页插件 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
</plugin>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.abel533.mapperhelper.MapperInterceptor">
<!--通用Mapper接口 -->
<property name="mappers" value="com.github.abel533.mapper.Mapper" />
</plugin>
</plugins>
注意:通用Mapper的插件必须配置在分页插件下
3、自定义接口继承通用mapper的接口
public interface NewMapper extends Mapper<User>{ }
注意:继承通用Mapper<T>的接口,必须指定泛型<T>
4、泛型实体类<T>的属性的注解
实体类按照如下规则和数据库表进行转换,注解全部是JPA中的注解:
表名默认使用类名,驼峰转下划线,如UserInfo默认对应的表名为user_info.
表名可以使用@Table(name = "tableName")进行指定,对不符合第一条默认规则的可以通过这种方式指定表名.
字段默认和@Column一样,都会作为表字段,表字段默认为Java对象的Field名字驼峰转下划线形式.
可以使用@Column(name = "fieldName")指定不符合第3条规则的字段名
使用@Transient注解可以忽略字段,添加该注解的字段不会作为表字段使用.
建议一定是有一个@Id注解作为主键的字段,可以有多个@Id注解的字段作为联合主键.
默认情况下,实体类中如果不存在包含@Id注解的字段,所有的字段都会作为主键字段进行使用(这种效率极低).
实体类可以继承使用,可以参考测试代码中的com.github.abel533.model.UserLogin2类.
由于基本类型,如int作为实体类字段时会有默认值0,而且无法消除,所以实体类中建议不要使用基本类型.
除了上面提到的这些,Mapper还提供了序列(支持Oracle)、UUID(任意数据库,字段长度32)、主键自增(类似Mysql,Hsqldb)三种方式,其中序列和UUID可以配置多个,主键自增只能配置一个。
这三种方式不能同时使用,同时存在时按照 序列>UUID>主键自增的优先级进行选择.下面是具体配置方法:
使用序列可以添加如下的注解:
//可以用于数字类型,字符串类型(需数据库支持自动转型)的字段 @SequenceGenerator(name="Any",sequenceName="seq_userid") @Id private Integer id;
使用UUID时:
//可以用于任意字符串类型长度超过32位的字段 @GeneratedValue(generator = "UUID") private String countryname;
使用主键自增:
//不限于@Id注解的字段,但是一个实体类中只能存在一个(继承关系中也只能存在一个) @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id;
为了可以回写主键的值,使用注解:@GeneratedValue(generator ="JDBC")
为了可以使用通用mapper中通过主键查询的方法:一定要配置主键@Id
5、通用方法的使用
1、selectOne():查询单个对象,返回值为实体类对象
public void testSelectOne() { User user = new User(); // 设置一个唯一的属性用来查询 user.setId(2L); User selectOne = newMapper.selectOne(user); System.out.println(selectOne); }
注意:
a、初始化的user对象中封装的查询条件必须是唯一的,否则查询会报ToManyResultsException异常。
b、若实体类中的属性与表对应不了,也会报错,可以使用注解@Transient忽略字段
2、select():查询多个对象,返回值为List<T>
/** * 条件为null或者是未初始化的实体类对象,会查询所有数据 * user中设置了数据:就按user中封装的数据进行条件查询 * 条件只能按照=来查询,不能按照>或者<等方式来查询 */ public void testSelect() { User user = new User(); List<User> select = newMapper.select(user); for (User user2 : select) { System.out.println(user2); } }
3、selectCount():统计查询,返回值为int类型
/** * 统计查询: * 1、赋值为null或未初始化的实体类对象:统计所有记录数 * 2、若设置属性,则按照属性查询符合的记录数 */ public void testSelectCount() { User user = new User(); user.setAge(20); int selectCount = newMapper.selectCount(user); System.out.println(selectCount); }
4、selectByPrimaryKey():按照主键查询单个,返回返回值为实体类对象
/** * 通过主键进行查询: * 1、参数类型一定要主键一致 * 2、必须在对象中通过@Id指定主键 * 如果满足前两点,但没有查询到,返回null,若不满足前两点,报ClassCastException */ public void testSelectByPrimaryKey() { User user = newMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(2l); System.out.println(user); }
5、insert():返回值为int类型
/** * 新增方法:按全属性插入数据,如果不设置属性,自动设置为null */ public void testInsert() { }
6、insertSelective()(推荐使用):返回值为int类型
/** * 按属性插入数据:如果不设置属性,自动设置为null */ public void testInsertSelective() { User user = new User(); user.setUserName("huahu"); user.setPassword("123456"); user.setName("花花"); newMapper.insertSelective(user); }
注意:虽然从结果来说,insert()与insertSelective()执行效果都是一样的,但是从效率上来说insertSelective()更高。前者按照全属性插入,后者按照给定属性插入, 不设置属性,则自动设置为null。
7、delete():返回值为int类型
// 条件删除:如果条件为null或未初始化的实体类对象,删除全部数据 public void testDelete() { User user = new User(); user.setUserName("admin1"); newMapper.delete(user); }
注意:如果有外键约束,并且主键被某个外键所引用,无法删除。
8、deleteByPrimaryKey():返回值为int类型
// 按主键删除 public void testDeleteByPrimaryKey() { newMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(18L); }
9、updateByPrimaryKey()(不推荐):返回值为int类型
/** * 通过主键更新: * 将设置的属性进行更新,如果不设置属性,自动更新为null。 * 必须设置主键 */ public void testUpdateByPrimaryKey() { }
10、updateByPrimaryKeySelective():返回值为int类型
/** * 通过主键按属性进行选择更新: * 必须设置主键 * 将设置的属性进行更新,没有设置的属性不更新 */ public void testUpdateByPrimaryKeySelective() { User user = new User(); user.setId(1L); user.setUserName("admin"); user.setPassword("123"); newMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(user); }
11、selectCountByExample():返回值为int类型
/** * 通过条件统计记录数 * 1、需要初始化Example对象 * 2、通过example获取criteria来设置条件 */ public void testSelectCountByExample() { Example example = new Example(User.class); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andBetween("age", 15, 30); int count = newMapper.selectCountByExample(example); System.out.println(count); }
12、selectByExample():返回值类型为List<T>
通过Example对象设置查询条件的步骤:
- 初始化Example对象
- 通过Example对象获取多个Criteria对象来设置查询条件
- 通过example设置并集查询or
- 通过example设置排序查询
/** * 通过条件进行查询: * 查询年龄在15-30之间的并且用户名中有zhang的用户,或者密码是123456的用户。 * 显示的时候通过age倒序排序,如果age一样那么根据id正序执行。 */ public void testSelectByExample() { Example example = new Example(User.class); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andBetween("age", 15, 30); criteria.andLike("userName", "%zhang%"); //添加or的条件 Criteria criteria2 = example.createCriteria(); criteria2.andEqualTo("password", "123456"); example.or(criteria2); //按年龄倒序排序,如果年龄相同,按id正序排序 example.setOrderByClause("age desc,id asc"); List<User> list = newMapper.selectByExample(example); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user); } }
13、deleteByExample():返回值为int类型
// 条件查询 @Test public void testDeleteByExample() { Example example = new Example(User.class); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andLike("userName", "admin"); newUserMapper.deleteByExample(example); }
14、updateByExampleSelective():返回值为int类型
/** * 按条件选择更新:没设置的属性就不做修改 * 将年龄>22的用户的密码修改成123 */ public void testUpdateByExampleSelective() { Example example = new Example(User.class); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andGreaterThan("age", 22); User user = new User(); user.setPassword("123"); newMapper.updateByExampleSelective(user, example); }
15、updateByExample():返回值为int类型
/** * 将年龄大于22的用的密码修改为321 * 条件更新:没有设置属性的都更新为null. */ public void testUpdateByExample() { Example example = new Example(User.class); Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andGreaterThan("age", 22); User user = new User(); user.setPassword("321"); newMapper.updateByExample(user, example); }
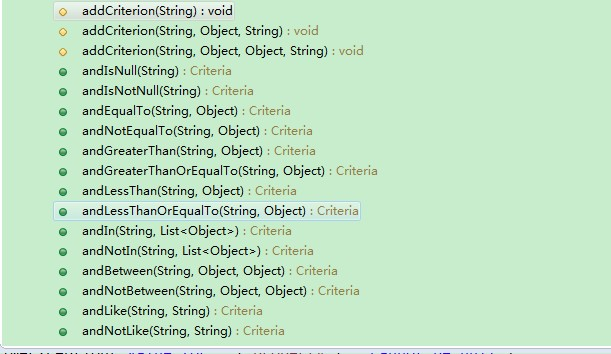
附上Criteria类中设置条件的方法
最后注意
如果使用的
TK包下的通用mapper
使用TKMapper主键的坑
selectByPrimaryKey
deleteByPrimaryKey
updateByPrimaryKey
updateByPrimaryKeySelective
出现错误,无法正确查询出结果;观察日志中自动生成的 SQL 语句如下
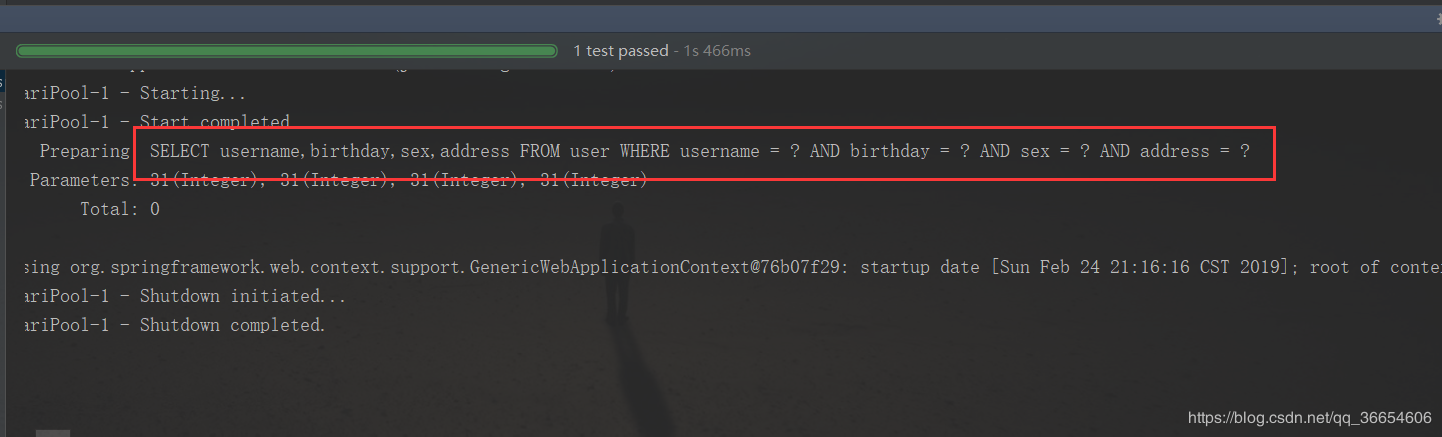
错误原因
- 通用 Mapper 的 selectByPrimaryKey 方法无法识别 int 类型,需要在 POJO 类中将 int 改为包装类型 Integer
- 其他类型如 Long 则无这种情况
- 主键加注解@Id(一定要导入import javax.persistence.Id;不要导成import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;)
问题解决

今天使用这个方法updateByPrimaryKeySelective遇到连接数据库异常额问题

改用updateByExampleSelective方法就没错,之后想到id需要加注解@Id,尝试在普通属性加上@Column
再次使用updateByPrimaryKeySelective方法后没有报错,应该是tk的mapper有识别的问题,因为其他几个接口也是用了这个方法就没有问题,所以尽量还是不用根据主键查询新增修改删除(ByPrimaryKey)