一、中缀表达式
我们日常的运算表达式通常是如下形式,这种成为中缀表达式,也就是运算符在运算数的中间。这种表达式人类人容易识别,并根据其进行计算,但计算机识别这种表达式非常困难。
中缀表达式:(a + b) * c - d
中缀表达式的计算机求值:参考:【数据结构】栈,中的计算器应用部分
二、前缀表达式(波兰表达式)
因此,1920年,波兰科学家扬·武卡谢维奇(Jan ukasiewicz)发明了一种不需要括号的计算表达式的表示法将操作符号写在操作数之前,也就是前缀表达式,即波兰式(Polish Notation, PN)。
中缀表达式:(a + b) * c - d
转换为波兰表达式的格式如下
前缀表达式(波兰表达式):- * + a b c d
前缀表达式的计算机求值:
从右至左扫描表达式,遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算(栈顶元素 和 次顶元素),并将结果入栈;重复上述过程直到表达式最左端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果
例如:(3+4)×5-6 对应的前缀表达式就是 - × + 3 4 5 6 ,
针对前缀表达式求值步骤如下:
-
从右至左扫描,将6、5、4、3压入堆栈
-
遇到+运算符,因此弹出3和4(3为栈顶元素,4为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈
-
接下来是×运算符,因此弹出7和5,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈
-
最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果
三、后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
前面了解了波兰表达式,那什么是逆波兰表达式呢?波兰表达式也成为前缀表达式,而逆波兰表达式则成为后缀表达式,对比可以猜出来运算符在运算数后面的表达式就是逆波兰表达式。上述表达式如果采用逆波兰表达式则如下:
中缀表达式 :(a + b) * c - d
转换为波兰表达式的格式如下
后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式):a b + c * d -
后缀表达式的计算机求值:
从左至右扫描表达式,遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算(次顶元素 和 栈顶元素),并将结果入栈;重复上述过程直到表达式最右端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果
例如:(3+4)×5-6 对应的前缀表达式就是 3 4 + 5 × 6 - ,
针对后缀表达式求值步骤如下:
-
从左至右扫描,将3和4压入堆栈;
-
遇到+运算符,因此弹出4和3(4为栈顶元素,3为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈;
-
将5入栈;
-
接下来是×运算符,因此弹出5和7,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈;
-
将6入栈;
-
最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果
逆波兰计算器
计算器说明
-
输入一个逆波兰表达式(后缀表达式), 使用栈(Stack),计算其结果
-
支持小括号和多位数整数, 因为这里我们主要讲的是数据结构, 因此计算器进行简化, 只支持对整数的计算
代码思路
-
计算后缀表达式无需考虑运算符优先级问题,所以只需要一个数栈即可
-
分为两种情况:
-
遇到数:压入数栈
-
遇到运算符:从数栈中弹出两个数,进行计算,计算结果压入数栈
-
-
何时计算完成?处理完表达式就代表计算完成
代码实现
1 public class PolandNotation { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 //先定义给逆波兰表达式 6 // 4 * 5 - 8 + 60 + 8 / 2 => 4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / + 7 //说明为了方便,逆波兰表达式 的数字和符号使用空格隔开 8 String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +"; // 76 9 //思路 10 //1. 先将逆波兰表达式 => 放到ArrayList中 11 //2. 将 ArrayList 传递给一个方法,遍历 ArrayList 配合栈 完成计算 12 13 List<String> list = getListString(suffixExpression); 14 System.out.println("list=" + list); 15 int res = calculate(list); 16 System.out.println("计算的结果是=" + res); 17 18 } 19 20 //将一个逆波兰表达式, 依次将数据和运算符 放入到 ArrayList中 21 public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) { 22 //将 suffixExpression 分割 23 String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" "); 24 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 25 for(String ele: split) { 26 list.add(ele); 27 } 28 return list; 29 30 } 31 32 //完成对逆波兰表达式的运算 33 /* 34 * 1)从左至右扫描,将3和4压入堆栈; 35 2)遇到+运算符,因此弹出4和3(4为栈顶元素,3为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈; 36 3)将5入栈; 37 4)接下来是×运算符,因此弹出5和7,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈; 38 5)将6入栈; 39 6)最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果 40 */ 41 42 public static int calculate(List<String> ls) { 43 // 创建给栈, 只需要一个栈即可 44 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); 45 // 遍历 ls 46 for (String item : ls) { 47 // 这里使用正则表达式来取出数 48 if (item.matches("\d+")) { // 匹配的是多位数 49 // 入栈 50 stack.push(item); 51 } else { 52 // pop出两个数,并运算, 再入栈 53 int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 54 int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 55 int res = 0; 56 if (item.equals("+")) { 57 res = num1 + num2; 58 } else if (item.equals("-")) { 59 res = num1 - num2; 60 } else if (item.equals("*")) { 61 res = num1 * num2; 62 } else if (item.equals("/")) { 63 res = num1 / num2; 64 } else { 65 throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误"); 66 } 67 //把res 入栈 68 stack.push("" + res); 69 } 70 71 } 72 //最后留在stack中的数据是运算结果 73 return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 74 } 75 76 }
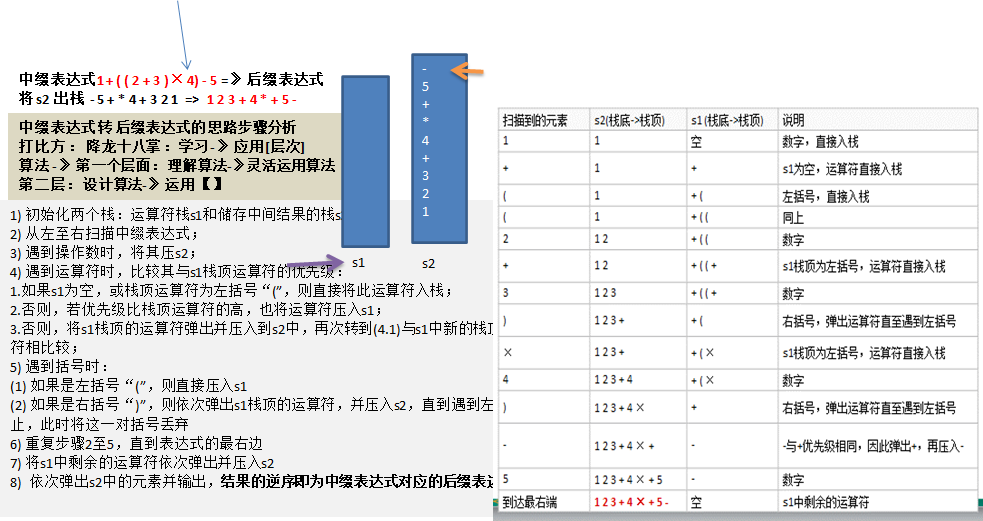
四、中缀表达式转换为逆波兰(后缀)表达式
大家看到,后缀表达式适合计算式进行运算,但是人却不太容易写出来,尤其是表达式很长的情况下,因此在开发中,我们需要将中缀表达式转成后缀表达式。
具体步骤如下:
-
初始化两个栈:运算符栈operStack和储存中间结果的栈tempStack;
-
从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
-
遇到操作数时,将其压tempStack;
-
遇到运算符时,比较其与operStack栈顶运算符的优先级:
-
如果operStack为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(”,则直接将此运算符入tempStack栈(分如下两种情况)
-
operStack 栈顶为空:之前的优先级别高的运算已经处理完成,已经得到了一个结果,将当前运算符直接压入 operStack 栈即可
-
operStack 栈顶为左括号:我都挨着左括号了,我要和它同生共死!当把我从operStack 出栈,用于运算后,这对括号中的表达式的值也就计算出来了
-
- 如果当前运算符优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入tempStack(当前运算符优先级高,先执行运算)
-
否则,当前运算符优先级 <= 栈顶运算符优先级,将operStack栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到tempStack中(operStack 栈顶运算符优先级高,先执行运算),再次转到(4.1)与operStack中新的栈顶运算符相比较(分如下两种情况);
-
一直循环,将 tempStack 栈顶元素取出,直到在 operStack 栈中找到比当前运算符优先级高的运算符,让其先执行运算
-
如果在 tempStack 栈中找不到比当前运算符优先级高的运算符,则会直接将 operStack 栈掏空,然后将当前运算符压入 tempStack 栈中(放在栈底)
-
-
-
遇到括号时:
-
如果是左括号“(”,则直接压入operStack,等待与其配对的右括号,因为括号中的表达式需要优先运算
-
如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出operStack栈顶的运算符,并压入tempStack,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃(此时括号内的运算完成,并将结果压入了tempStack)
-
-
重复步骤2至5,直到表达式的最右边
-
将operStack中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入tempStack(operStack 栈中剩下的运算都是优先级相同的运算符,按顺序执行即可)
-
依次弹出tempStack中的元素并输出,结果的逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表达式
代码实现
1 public class PolandNotation { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 // 完成将一个中缀表达式转成后缀表达式的功能 6 7 // 说明 8 // 1. 1+((2+3)×4)-5 => 转成 1 2 3 + 4 × + 5 – 9 10 // 2. 因为直接对str 进行操作,不方便,因此 先将 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" =》 中缀的表达式对应的List 11 // 即 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" => ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] 12 13 // 3. 将得到的中缀表达式对应的List => 后缀表达式对应的List 14 // 即 ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–] 15 16 String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";// 注意表达式 17 List<String> infixExpressionList = toInfixExpressionList(expression); 18 System.out.println("中缀表达式对应的List=" + infixExpressionList); // ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] 19 List<String> suffixExpreesionList = parseSuffixExpreesionList(infixExpressionList); 20 System.out.println("后缀表达式对应的List" + suffixExpreesionList); // ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–] 21 System.out.printf("expression=%d", calculate(suffixExpreesionList)); // ? 22 23 } 24 25 // 方法:将 中缀表达式转成对应的List 26 // s="1+((2+3)×4)-5"; 27 public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s) { 28 // 定义一个List,存放中缀表达式 对应的内容 29 List<String> ls = new ArrayList<String>(); 30 int i = 0; // 这时是一个指针,用于遍历 中缀表达式字符串 31 String str; // 对多位数的拼接 32 char c; // 每遍历到一个字符,就放入到c 33 do { 34 // 如果c是一个非数字,我需要加入到ls 35 if ((c = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = s.charAt(i)) > 57) { 36 ls.add("" + c); 37 i++; // i需要后移 38 } else { // 如果是一个数,需要考虑多位数 39 str = ""; // 先将str 置成"" '0'[48]->'9'[57] 40 while (i < s.length() && (c = s.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c = s.charAt(i)) <= 57) { 41 str += c;// 拼接 42 i++; 43 } 44 ls.add(str); 45 } 46 } while (i < s.length()); 47 return ls;// 返回 48 } 49 50 // 即 ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–] 51 // 方法:将得到的中缀表达式对应的List => 后缀表达式对应的List 52 public static List<String> parseSuffixExpreesionList(List<String> ls) { 53 // 定义两个栈 54 Stack<String> operStack = new Stack<String>(); // 符号栈 55 // 说明:因为tempList 这个栈,在整个转换过程中,没有pop操作,而且后面我们还需要逆序输出 56 // 因此比较麻烦,这里我们就不用 Stack<String> 直接使用 List<String> tempList 57 // Stack<String> tempStack = new Stack<String>(); // 储存中间结果的栈tempStack 58 List<String> tempList = new ArrayList<String>(); // 储存中间结果的tempList 59 60 // 遍历ls 61 for (String item : ls) { 62 if (item.matches("\d+")) { // 如果是一个数,加入tempList 63 tempList.add(item); 64 } else if (item.equals("(")) { // 如果是 ( ,则直接入operStack 65 operStack.push(item); 66 } else if (item.equals(")")) { // 如果是 ) ,则将括号内的值算出,并压入 tempList) 67 // 如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出operStack栈顶的运算符,并压入tempList,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这一对括号丢弃 68 while (!operStack.peek().equals("(")) { 69 tempList.add(operStack.pop()); 70 } 71 operStack.pop();// !!! 将 ( 弹出 s1栈, 消除小括号 72 } else { // 否则比较当前运算符和栈顶运算符优先级 73 // 当item的优先级小于等于operStack栈顶运算符, 74 // 将operStack栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到tempList中,再次转到(4.1)与operStack中新的栈顶运算符相比较 75 // 问题:我们缺少一个比较优先级高低的方法 76 while (operStack.size() != 0 && Operation.getValue(operStack.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item)) { 77 tempList.add(operStack.pop()); 78 } 79 // 还需要将item压入栈 80 operStack.push(item); 81 } 82 } 83 84 // 将operStack中剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入tempList 85 while (operStack.size() != 0) { 86 tempList.add(operStack.pop()); 87 } 88 89 return tempList; // 注意因为是存放到List, 因此按顺序输出就是对应的后缀表达式对应的List 90 91 } 92 93 // 完成对逆波兰表达式的运算 94 /* 95 * 1)从左至右扫描,将3和4压入堆栈; 2)遇到+运算符,因此弹出4和3(4为栈顶元素,3为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈; 3)将5入栈; 96 * 4)接下来是×运算符,因此弹出5和7,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈; 5)将6入栈; 6)最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果 97 */ 98 99 public static int calculate(List<String> ls) { 100 // 创建给栈, 只需要一个栈即可 101 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); 102 // 遍历 ls 103 for (String item : ls) { 104 // 这里使用正则表达式来取出数 105 if (item.matches("\d+")) { // 匹配的是多位数 106 // 入栈 107 stack.push(item); 108 } else { 109 // pop出两个数,并运算, 再入栈 110 int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 111 int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 112 int res = 0; 113 if (item.equals("+")) { 114 res = num1 + num2; 115 } else if (item.equals("-")) { 116 res = num1 - num2; 117 } else if (item.equals("*")) { 118 res = num1 * num2; 119 } else if (item.equals("/")) { 120 res = num1 / num2; 121 } else { 122 throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误"); 123 } 124 // 把res 入栈 125 stack.push("" + res); 126 } 127 128 } 129 // 最后留在stack中的数据是运算结果 130 return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); 131 } 132 133 } 134 135 //编写一个类 Operation 可以返回一个运算符 对应的优先级 136 class Operation { 137 private static int LEFT_BRACKET = 0; 138 private static int ADD = 1; 139 private static int SUB = 1; 140 private static int MUL = 2; 141 private static int DIV = 2; 142 143 // 写一个方法,返回对应的优先级数字 144 public static int getValue(String operation) { 145 int result = 0; 146 switch (operation) { 147 case "(": 148 result = LEFT_BRACKET; 149 break; 150 case "+": 151 result = ADD; 152 break; 153 case "-": 154 result = SUB; 155 break; 156 case "*": 157 result = MUL; 158 break; 159 case "/": 160 result = DIV; 161 break; 162 default: 163 System.out.println("不存在该运算符" + operation); 164 break; 165 } 166 return result; 167 } 168 169 }
完整版逆波兰计算器
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collections; 3 import java.util.List; 4 import java.util.Stack; 5 import java.util.regex.Pattern; 6 7 public class ReversePolishMultiCalc { 8 9 /** 10 * 匹配 + - * / ( ) 运算符 11 */ 12 static final String SYMBOL = "\+|-|\*|/|\(|\)"; 13 14 static final String LEFT = "("; 15 static final String RIGHT = ")"; 16 static final String ADD = "+"; 17 static final String MINUS= "-"; 18 static final String TIMES = "*"; 19 static final String DIVISION = "/"; 20 21 /** 22 * 加減 + - 23 */ 24 static final int LEVEL_01 = 1; 25 /** 26 * 乘除 * / 27 */ 28 static final int LEVEL_02 = 2; 29 30 /** 31 * 括号 32 */ 33 static final int LEVEL_HIGH = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 34 35 36 static Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); 37 // 线程安全集合 38 static List<String> data = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<String>()); 39 40 /** 41 * 去除所有空白符 42 * @param s 43 * @return 44 */ 45 public static String replaceAllBlank(String s ){ 46 // \s+ 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等, 等价于[ f v] 47 return s.replaceAll("\s+",""); 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * 判断是不是数字 int double long float 52 * @param s 53 * @return 54 */ 55 public static boolean isNumber(String s){ 56 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\+]?[.\d]*$"); 57 return pattern.matcher(s).matches(); 58 } 59 60 /** 61 * 判断是不是运算符 62 * @param s 63 * @return 64 */ 65 public static boolean isSymbol(String s){ 66 return s.matches(SYMBOL); 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * 匹配运算等级 71 * @param s 72 * @return 73 */ 74 public static int calcLevel(String s){ 75 if("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s)){ 76 return LEVEL_01; 77 } else if("*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)){ 78 return LEVEL_02; 79 } 80 return LEVEL_HIGH; 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * 匹配 85 * @param s 86 * @throws Exception 87 */ 88 public static List<String> doMatch (String s) throws Exception{ 89 if(s == null || "".equals(s.trim())) throw new RuntimeException("data is empty"); 90 if(!isNumber(s.charAt(0)+"")) throw new RuntimeException("data illeagle,start not with a number"); 91 92 s = replaceAllBlank(s); 93 94 String each; 95 int start = 0; 96 97 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { 98 if(isSymbol(s.charAt(i)+"")){ 99 each = s.charAt(i)+""; 100 //栈为空,(操作符,或者 操作符优先级大于栈顶优先级 && 操作符优先级不是( )的优先级 及是 ) 不能直接入栈 101 if(stack.isEmpty() || LEFT.equals(each) 102 || ((calcLevel(each) > calcLevel(stack.peek())) && calcLevel(each) < LEVEL_HIGH)){ 103 stack.push(each); 104 }else if( !stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek())){ 105 //栈非空,操作符优先级小于等于栈顶优先级时出栈入列,直到栈为空,或者遇到了(,最后操作符入栈 106 while (!stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek()) ){ 107 if(calcLevel(stack.peek()) == LEVEL_HIGH){ 108 break; 109 } 110 data.add(stack.pop()); 111 } 112 stack.push(each); 113 }else if(RIGHT.equals(each)){ 114 // ) 操作符,依次出栈入列直到空栈或者遇到了第一个)操作符,此时)出栈 115 while (!stack.isEmpty() && LEVEL_HIGH >= calcLevel(stack.peek())){ 116 if(LEVEL_HIGH == calcLevel(stack.peek())){ 117 stack.pop(); 118 break; 119 } 120 data.add(stack.pop()); 121 } 122 } 123 start = i ; //前一个运算符的位置 124 }else if( i == s.length()-1 || isSymbol(s.charAt(i+1)+"") ){ 125 each = start == 0 ? s.substring(start,i+1) : s.substring(start+1,i+1); 126 if(isNumber(each)) { 127 data.add(each); 128 continue; 129 } 130 throw new RuntimeException("data not match number"); 131 } 132 } 133 //如果栈里还有元素,此时元素需要依次出栈入列,可以想象栈里剩下栈顶为/,栈底为+,应该依次出栈入列,可以直接翻转整个stack 添加到队列 134 Collections.reverse(stack); 135 data.addAll(new ArrayList<>(stack)); 136 137 System.out.println(data); 138 return data; 139 } 140 141 /** 142 * 算出结果 143 * @param list 144 * @return 145 */ 146 public static Double doCalc(List<String> list){ 147 Double d = 0d; 148 if(list == null || list.isEmpty()){ 149 return null; 150 } 151 if (list.size() == 1){ 152 System.out.println(list); 153 d = Double.valueOf(list.get(0)); 154 return d; 155 } 156 ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); 157 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 158 list1.add(list.get(i)); 159 if(isSymbol(list.get(i))){ 160 Double d1 = doTheMath(list.get(i - 2), list.get(i - 1), list.get(i)); 161 list1.remove(i); 162 list1.remove(i-1); 163 list1.set(i-2,d1+""); 164 list1.addAll(list.subList(i+1,list.size())); 165 break; 166 } 167 } 168 doCalc(list1); 169 return d; 170 } 171 172 /** 173 * 运算 174 * @param s1 175 * @param s2 176 * @param symbol 177 * @return 178 */ 179 public static Double doTheMath(String s1,String s2,String symbol){ 180 Double result ; 181 switch (symbol){ 182 case ADD : result = Double.valueOf(s1) + Double.valueOf(s2); break; 183 case MINUS : result = Double.valueOf(s1) - Double.valueOf(s2); break; 184 case TIMES : result = Double.valueOf(s1) * Double.valueOf(s2); break; 185 case DIVISION : result = Double.valueOf(s1) / Double.valueOf(s2); break; 186 default : result = null; 187 } 188 return result; 189 190 } 191 192 public static void main(String[] args) { 193 //String math = "9+(3-1)*3+10/2"; 194 String math = "12.8 + (2 - 3.55)*4+10/5.0"; 195 try { 196 doCalc(doMatch(math)); 197 } catch (Exception e) { 198 e.printStackTrace(); 199 } 200 } 201 202 }
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/oneby1314/article/details/107843972