一、Channel(通道)介绍
通常来说NIO中的所有IO都是从 Channel(通道) 开始的。
-
从通道进行数据读取 :创建一个缓冲区,然后请求通道读取数据。
-
从通道进行数据写入 :创建一个缓冲区,填充数据,并要求通道写入数据。
数据读取和写入操作图示:
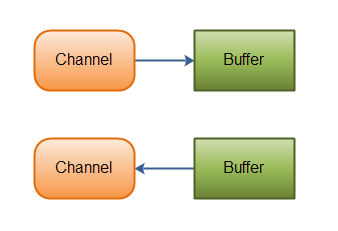
Java NIO Channel通道和流非常相似,主要有以下几点区别:
-
通道可以读也可以写,流一般来说是单向的(只能读或者写,所以之前我们用流进行IO操作的时候需要分别创建一个输入流和一个输出流)。
-
通道可以异步读写。
-
通道总是基于缓冲区Buffer来读写。
Java NIO中最重要的几个Channel的实现:
-
FileChannel: 用于文件的数据读写
-
DatagramChannel: 用于UDP的数据读写
-
SocketChannel: 用于TCP的数据读写,一般是客户端实现
-
ServerSocketChannel: 允许我们监听TCP链接请求,每个请求会创建会一个SocketChannel,一般是服务器实现
类层次结构:
下面的UML图使用Idea生成的。

二、FileChannel的使用
2.1、基本用法
示例一:使用FileChannel读取数据到Buffer(缓冲区)以及利用Buffer(缓冲区)写入数据到FileChannel:
1 /** 2 * 1、通道(Channel): 3 * 用于源节点与目标节点的连接。在Java NIO中负责缓冲区数据的传输。 4 * Channel本身不存储数据,因此需要缓冲区进行传输 5 * 6 * 2、通道的主要实现类 7 * java.nio.channels.Channel 接口 8 * |-- FIleChannel 9 * |-- SocketChannel 10 * |-- ServerSocketChannel 11 * |-- DatagramChannel 12 * 13 * 3、获取通道 14 * 1)Java 针对支持通道的类提供类 getChannel() 方法 15 * 本地IO: 16 * FileInputStream/FileOutputStream 17 * RandomAccessFile 18 * 19 * 网络IO: 20 * Socket 21 * ServerSocket 22 * DatagramSocket 23 * 24 * 2)在JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 针对各个通道提供类静态方法 open() 25 * 3)在JDK 1.7 中的 NIO.2 的Files 工具类的 newByteChannel() 26 * 27 * 4、通道之间的数据传输 28 * transferFrom() 29 * transferTo() 30 * 31 * 5、分散(Scatter)与聚集(Gather) 32 * 分散读取(Scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中 33 * 聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中 34 * 35 * 6、字符集:Charset 36 * 编码:字符串 -> 字节数组 37 * 解码:字节数组 -> 字符串 38 */ 39 public class ChannelTest { 40 41 42 // 1】利用通道完成文件的复制 43 @Test 44 public void test1(){ 45 46 FileInputStream fis = null; 47 FileOutputStream fos = null; 48 49 FileChannel inChannel = null; 50 FileChannel outChannel = null; 51 try { 52 fis = new FileInputStream("tomcat.png"); 53 fos = new FileOutputStream("tomcat2.png"); 54 55 // 1、获取通道 56 inChannel = fis.getChannel(); 57 outChannel = fos.getChannel(); 58 59 // 2、分配指定大小的缓存区 60 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 61 62 // 3、将通道中的数据存入缓冲区中 63 int len; 64 while ((len = inChannel.read(buf)) != -1) { 65 buf.flip(); // 切换成读取数据的模式 66 // 4、将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中 67 outChannel.write(buf); 68 buf.clear(); // 清空缓冲区 69 } 70 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 71 e.printStackTrace(); 72 } catch (IOException e) { 73 e.printStackTrace(); 74 } finally { 75 // 5、关闭通道 76 if(outChannel != null) { 77 try { 78 outChannel.close(); 79 } catch (IOException e) { 80 e.printStackTrace(); 81 } 82 } 83 if(inChannel != null) { 84 try { 85 inChannel.close(); 86 } catch (IOException e) { 87 e.printStackTrace(); 88 } 89 } 90 if(fos != null) { 91 try { 92 fos.close(); 93 } catch (IOException e) { 94 e.printStackTrace(); 95 } 96 } 97 if(fis != null) { 98 try { 99 fis.close(); 100 } catch (IOException e) { 101 e.printStackTrace(); 102 } 103 } 104 } 105 } 106 }
示例二:使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
1 // 2】使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件) 2 // 异常需要使用try-catch块处理 3 @Test 4 public void test2() throws IOException { 5 // READ 读文件 6 FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("tomcat.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); 7 // WRIT 写文件 CREATE_NEW 文件存在就报错,不存在就创建 CREATE 覆盖 8 FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("tomcat2.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); 9 10 // 内存映射文件,直接缓冲区内存在物理内存中 11 MappedByteBuffer inMapappedBuf = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size()); 12 MappedByteBuffer outMapappedBuf = outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size()); 13 14 // 直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作 15 byte[] dst = new byte[1024]; 16 ByteBuffer buf; 17 int len = 0; 18 while (inMapappedBuf.hasRemaining()){ 19 len = dst.length > inMapappedBuf.remaining() ? inMapappedBuf.remaining() : dst.length; 20 // System.out.println(len); 21 inMapappedBuf.get(dst, 0, len) ; 22 outMapappedBuf.put(dst, 0, len); 23 } 24 }
2.2、通道之间数据传输
在Java NIO中,如果两个通道中有一个是FileChannel,那你可以直接将数据从一个channel传输到另外一个channel。
transferFrom()
FileChannel的transferFrom()方法可以将数据从源通道传输到FileChannel中

1 // 3】通道之间数据传输(也是直接缓冲区方式) 2 // 异常需要使用try-catch块处理 3 @Test 4 public void test3() throws IOException { 5 // READ 读文件 6 FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("tomcat.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); 7 // WRIT 写文件 CREATE_NEW 文件存在就报错,不存在就创建 CREATE 存在覆盖,不存在创建 8 FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("tomcat2.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); 9 10 // inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel); 11 outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size()); 12 13 outChannel.close(); 14 inChannel.close(); 15 }
transferTo()
transferTo()方法将数据从FileChannel传输到其他的channel中
2.3、分散(scatter)与聚集(gather)
Java NIO开始支持scatter/gather,scatter/gather用于描述从Channel(译者注:Channel在中文经常翻译为通道)中读取或者写入到Channel的操作。
分散(scatter)从Channel中读取是指在读操作时将读取的数据写入多个buffer中。因此,Channel将从Channel中读取的数据“分散(scatter)”到多个Buffer中。
聚集(gather)写入Channel是指在写操作时将多个buffer的数据写入同一个Channel,因此,Channel 将多个Buffer中的数据“聚集(gather)”后发送到Channel。
scatter / gather经常用于需要将传输的数据分开处理的场合,例如传输一个由消息头和消息体组成的消息,你可能会将消息体和消息头分散到不同的buffer中,这样你可以方便的处理消息头和消息体。
Scattering Reads
Scattering Reads是指数据从一个channel读取到多个buffer中。如下图描述:
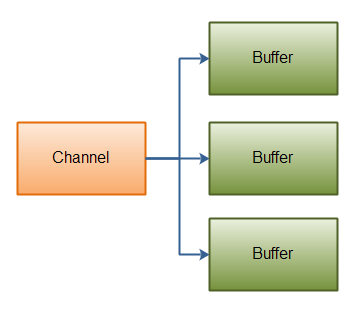
代码示例如下:
1 ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128); 2 ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 3 4 ByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body }; 5 6 channel.read(bufferArray);
注意buffer首先被插入到数组,然后再将数组作为channel.read() 的输入参数。read()方法按照buffer在数组中的顺序将从channel中读取的数据写入到buffer,当一个buffer被写满后,channel紧接着向另一个buffer中写。
Scattering Reads在移动下一个buffer前,必须填满当前的buffer,这也意味着它不适用于动态消息(译者注:消息大小不固定)。换句话说,如果存在消息头和消息体,消息头必须完成填充(例如 128byte),Scattering Reads才能正常工作。
Gathering Writes
Gathering Writes是指数据从多个buffer写入到同一个channel。如下图描述:
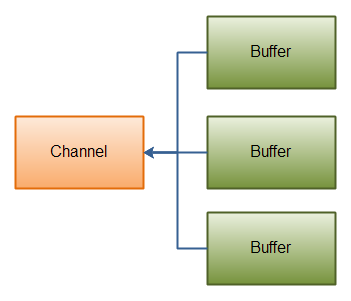
代码示例如下:
1 ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128); 2 ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 3 4 //write data into buffers 5 6 ByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body }; 7 8 channel.write(bufferArray);
buffers数组是write()方法的入参,write()方法会按照buffer在数组中的顺序,将数据写入到channel,注意只有position和limit之间的数据才会被写入。因此,如果一个buffer的容量为128byte,但是仅仅包含58byte的数据,那么这58byte的数据将被写入到channel中。因此与Scattering Reads相反,Gathering Writes能较好的处理动态消息。
完整示例演示如下:

1 // 4】分散和聚集 2 @Test 3 public void test4() { 4 FileChannel inRafChannel = null; 5 FileChannel outRafChannel = null; 6 try { 7 RandomAccessFile inRaf = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "r"); 8 RandomAccessFile outRaf = new RandomAccessFile("hello2.txt", "rw"); 9 10 // 1、获取通道 11 inRafChannel = inRaf.getChannel(); 12 outRafChannel = outRaf.getChannel(); 13 14 // 2、分配指定大小的缓冲区 15 ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5); 16 ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); 17 18 // 3、分散读取 19 ByteBuffer[] bufs = {buf1, buf2}; 20 long len; 21 while ((len = inRafChannel.read(bufs)) != -1){ 22 for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs) { 23 // 切换读模式 24 byteBuffer.flip(); 25 System.out.print(new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, byteBuffer.limit())); 26 } 27 28 // 4、聚集写入 29 outRafChannel.write(bufs); 30 31 for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs) { 32 // 清除缓存 33 byteBuffer.clear(); 34 } 35 } 36 37 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } finally { 42 if (outRafChannel != null) { 43 try { 44 outRafChannel.close(); 45 } catch (IOException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 if (inRafChannel != null) { 50 try { 51 inRafChannel.close(); 52 } catch (IOException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 }
