1. 题目描述
给定不同面额的硬币coins和一个总金额amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回-1。
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
示例 1:
输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
输出:3
解释:11 = 5 + 5 + 1
示例 2:
输入:coins = [2], amount = 3
输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:coins = [1], amount = 0
输出:0
示例 4:
输入:coins = [1], amount = 1
输出:1
示例 5:
输入:coins = [1], amount = 2
输出:2
2. 题解
2.1 搜索回溯。
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
return coinChange(0, coins, amount);
}
private int coinChange(int idxCoin, int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (idxCoin < coins.length && amount > 0) {
int maxVal = amount / coins[idxCoin];
int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int x = 0; x <= maxVal; x++) {
if (amount >= x * coins[idxCoin]) {
int res = coinChange(idxCoin + 1, coins, amount - x * coins[idxCoin]);
if (res != -1) {
minCost = Math.min(minCost, res + x);
}
}
}
return (minCost == Integer.MAX_VALUE)? -1: minCost;
}
return -1;
}
对于给定的输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11。
数组coins的每个元素值表示硬币的不同面额,amount表示总金额。
maxVal表示某种面额的硬币的最大数量。比如总金额为11,对于面额为1的硬币,那么maxVal就是11,遍历0到11,表示当面额为1的硬币数分别为0到11的各种情况。
当面额为1的硬币数为1时,总金额变为10=11-1*1(amount - x * coins[idxCoin]),接着看其他面额的硬币的情况(在递归调用时将idxCoin + 1传给idxCoin)。
// ...
int maxVal = amount / coins[idxCoin];
int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int x = 0; x <= maxVal; x++) {
if (amount >= x * coins[idxCoin]) {
int res = coinChange(idxCoin + 1, coins, amount - x * coins[idxCoin]);
if (res != -1) {
minCost = Math.min(minCost, res + x);
}
}
}
return (minCost == Integer.MAX_VALUE)? -1: minCost;
// ...
注意到minCost是在for循环外定义的,在第一次递归调用前的for循环表示遍历面额为1的硬币数分别为0到11的各种情况,所以当这个for循环结束后就能求得全局最少硬币数minCost。
2.2 动态规划-自上而下。
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount < 1) {
return 0;
}
return coinChange(coins, amount, new int[amount]);
}
private int coinChange(int[] coins, int rem, int[] count) {
if (rem < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (rem == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (count[rem - 1] != 0) {
return count[rem - 1];
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins) {
int res = coinChange(coins, rem - coin, count);
if (res >= 0 && res < min) {
min = 1 + res;
}
}
count[rem - 1] = (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? -1 : min;
return count[rem - 1];
}
}
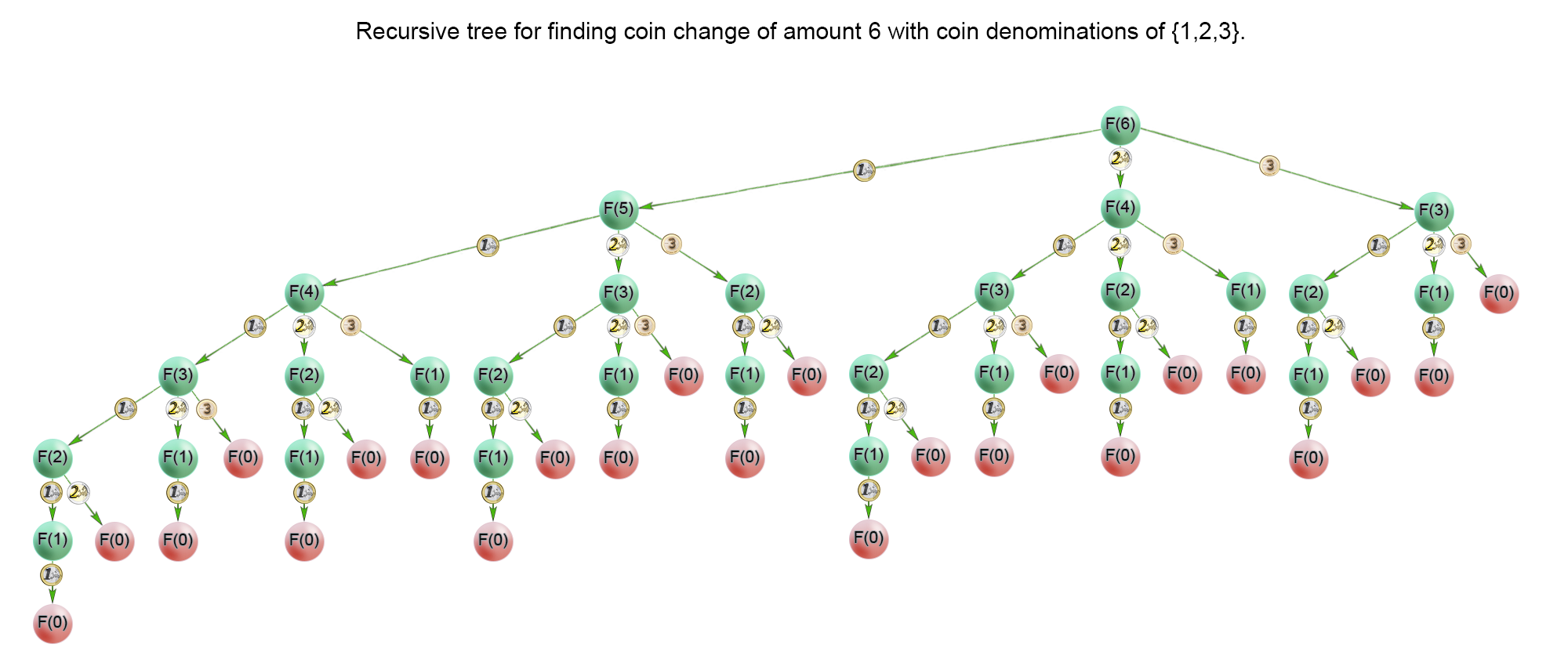
对于给定的输入:coins = [1, 2, 3], amount = 6。
在遍历不同面额的硬币时,递归调用coinChange。每次递归调用总金额都会减少,总金额为1时只需要一个面额为1的硬币,此时count[0]为1。
当总金额为2时,同样遍历面额为1、2和3的硬币:遍历面额为1的硬币时,硬币数为2(min = 1 + res);遍历面额为2的硬币时,因为res < min(0 < 2),所以min为1(min = 1 + res)。
注意到count数组为[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2],count[i]表示总金额为i+1时的最少硬币数(实际上还要看数组coins有哪些面额的硬币)。
2.3 动态规划-自下而上。
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if (coins[j] <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
还可以通过状态转移方程来做。

参考: