CSS变换用于在空间中移动物体,而CSS过渡和CSS关键帧动画用于控制元素随时间推移的变化。
变换、过渡和关键帧动画的规范仍然在制定中。尽管如此,其中大多数特性已经在常用浏览器中实现了。
1.二维变换
CSS变换支持在页面中平移、旋转、变形和缩放元素。
从技术角度说,变换改变的是元素所在的坐标系统。任何落在元素渲染空间内的像素都会被畸变场捕获,然后再把它们传输到页面上的新位置,或改变大小。元素本身还在页面上原来的位置,但它们畸变之后的“影像”已经变换了。
<div class="box"></div>
.box {
/* 省略 */
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #eee;
outline: 1px solid;
transform: rotate(45deg); /* 旋转45度角 */
}
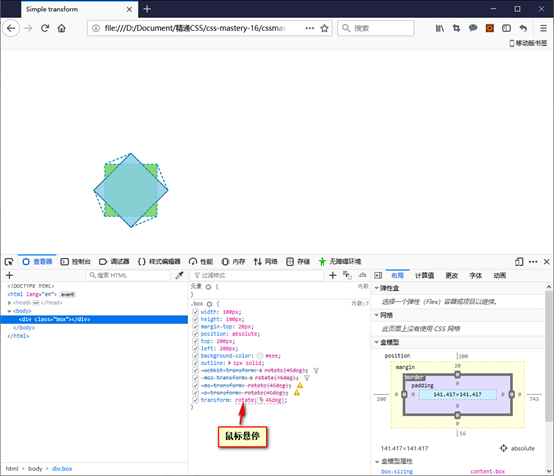
页面上元素原来的位置仍然保留了100像素×100像素的空间,但元素上所有的点都被畸变场给变换到了新位置。
旋转后的矩形不会妨碍页面其他部分的布局,就好像根本没有变换过一样。
1.1 变换原点
默认情况下,变换是以元素边框盒子的中心作为原点的。控制原点的属性叫transform-origin。
.box {
transform-origin: 10px 10px;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
1.2 平移
平移就是元素移动到新位置。可以沿一个轴平移,使用translateX()或者translateY(),也可以同时沿两个轴平移,使用translate()。
.box {
transform: translate(100%, 0);
}
使用translate()函数时,要给它传入两个坐标值,分别代表x轴和y轴平移的距离。这两个值可以是任何长度值,像素、em或百分比都可以。注意:百分比是相对于元素自身大小,而不是包含块的大小。
1.3 多重变换

<ol class="rules" start="3">
<li>If someone says ”stop”, goes limp or taps out, the fight is over.</li>
<li>Only two guys to a fight.</li>
<li>One fight at a time.</li>
<li>No shirts, no shoes.</li>
<li>Fights will go on as long as they have to.</li>
<li>If this is your first night at FIGHT CLUB, you HAVE to fight.</li>
</ol>
.rules {
/* 当前元素的计数器已经重置为rulecount的值。 */
counter-reset: rulecount 2;
list-style: none;
}
.rules li {
/* 针对列表中的每一项,都递增rulecount的值 */
counter-increment: rulecount;
}
.rules li:before {
/* 在列表中的每一项前面插入rulecount的值 */
content: '§ ' counter(rulecount);
}
.rules li {
counter-increment: rulecount;
position: relative; /* 相对定位 */
}
.rules li:before {
content: '§ ' counter(rulecount);
position: absolute; /* 绝对定位 */
transform: translate(-100%, -100%) rotate(-90deg); /* 多重变换:先平移,后旋转 */
transform-origin: 100% 100%; /* 变换原点 */
}
多重变换的值以空格分隔的列表形式提供给transform属性,按照声明的顺序依次应用。
我们给列表项左侧添加灰色边框,让编号显示在边框上方。
.rules li {
border-left: 1.5em solid #777;
padding-left: .5em;
margin-bottom: .5em;
/* 省略 */
}
.rules li:before {
/* 省略 */
top: 0;
left: 0;
padding-right: .25em;
}
1.4 缩放和变形
使用scale()函数缩放元素,这个函数有对应x轴和y轴的变体:scaleX()、scaleY()。
使用skew()函数使元素发生变形。变形是指水平或垂直方向平行的边发生相对平移,或偏移一定角度。
创造流行的“2.5D”效果(学名叫“轴侧投影构图”):
.rules li {
transform: skewX(15deg);
}
.rules li:nth-child(even) {
transform: skewX(-15deg);
}

如果给列表项交替应用深浅不同的背景和边框色,同时也交替应用不同的变形,就可以创建一种“折叠”的界面。
1.5 二维矩阵变换
CSS变换对浏览器来说,都归于一个叫变换矩阵的数学结构。
我们通过matrix()这个函数直接操纵变换矩阵的值。
matrix()函数的主要用途是通过JavaScript编程调用。
2.过渡
过渡是一种动画,可以从一种状态过渡到另一种状态。
过渡会自动双向运行,因此只要状态一反转,反向动画就会运行。
<button>Press me!</button>
button {
/* 省略 */
box-shadow: 0 .25em 0 rgba(23, 59, 109, 0.3), inset 0 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
transition: all 150ms;
}
button:active {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 rgba(23, 59, 109, 0.3), inset 0 1px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
transform: translateY(.25em);
}
在按钮被激活时,我们把它沿y轴向下平移与y轴阴影相同的距离。
按钮使用过渡来改变所有受影响的属性,而且要花150毫秒的时间。
用户界面组件的过渡多数都应该在0.3秒内完成,否则会让人觉得拖泥带水。
transition属性是一个简写形式,可以一次性设置多个属性。
button {
transition: all 150ms;
/* 相当于 */
/* transition-property: all; */
/* transition-duration: .15s; */
}
2.1 过渡计时函数
默认情况下,过渡变化的速度并不是每一帧都相同,而是开始时稍慢些,然后迅速加快,到接近最终值时再逐渐变慢。CSS通过transition-timing-function属性来控制这种速度的变化。
button {
transition: all .15s ease-in;
/* 也可以使用transition-timing-function: ease-in; */
}
transition-timing-function的默认值为ease、其他可选值包括linear、ease-in、ease-out和ease-in-out。这些值分别代表不同类型的缓动函数。
在底层,控制速度变化的数学函数基于三次贝塞尔函数(https://cubic-bezier.com)生成。每个关键字都是这些函数带特定参数的简写形式。三次贝塞尔函数需要4个参数来计算随时间的变化,在CSS变换中可以使用cubic-bezier()函数作为缓动值。换句话说,可以通过给这个函数传入自己的参数来自定义缓动函数。这4个参数是两对x和y坐标,分别代表调整曲线的两个控制点。
我们可以使用步进函数指定过渡中每一步的状态。
<div class="hello"></div>
.hello {
200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid #ccc;
background: url(images/step-animation.png) no-repeat 0 -1200px;
transition: background-position 1s steps(6, start);
}
.hello:hover {
background-position: 0 0;
}
我们希望通过改变background-position属性来实现背景动画。
这里的transition-timing-function指定为steps(6, start),意思是“把过渡过程切分为6个步骤,在每一次开始时改变属性”。总之,包括起始状态在内,就创建了7个不同的帧。
悬停状态触发动画,而悬停取消时背景立即恢复初始状态。
.hello {
transition: background-position 0s steps(6, start);
}
.hello:hover {
transition-duration: .6s;
}
通常,过渡会随状态变化立即发生,但是可以通过transition-delay属性来推迟过渡的发生。
.hello {
transition: background-position 0s 1s steps(6, start);
/* transition-delay: 1s; */
}
并非所有CSS属性都可以拿来实现过渡动画。多数情况下,涉及长度和颜色的都是可以的,比如边框、宽度、高度、背景颜色、字体大小,等等。这取决于能否计算值的中间状态。
3.CSS关键帧动画
CSS Animations规范引入了关键帧的概念来实现动画。
<h1 class="logo">
<!-- This is the box we are animating -->
<span class="box-outer"><span class="box-inner"></span></span>
<span class="logo-box">Box</span><span class="logo-model">model</span>
</h1>
/* 使用@keyframes规则来定义并命名一个关键帧序列。 */
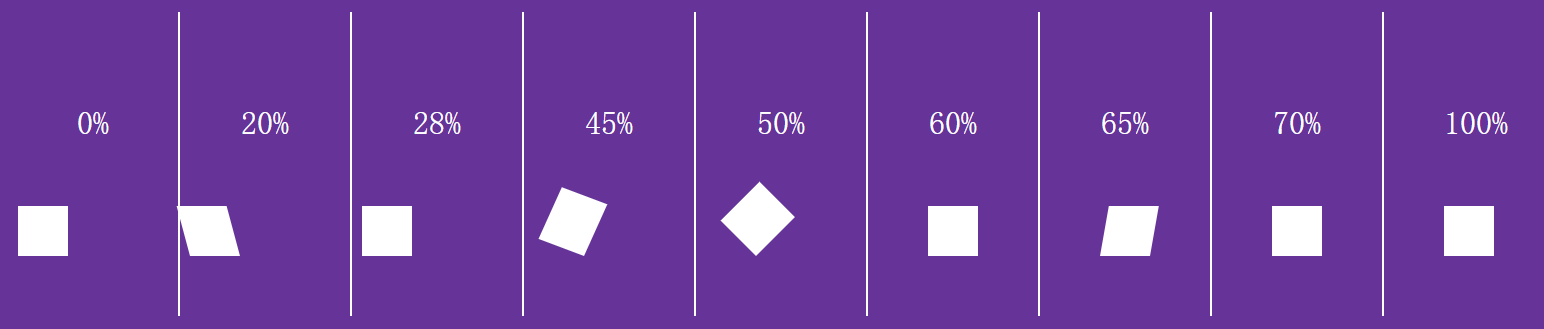
@keyframes roll {
from { /* 0% */
transform: translateX(-100%);
animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;
}
20% {
transform: translateX(-100%) skewX(15deg);
}
28% {
transform: translateX(-100%) skewX(0deg);
animation-timing-function: ease-out;
}
45% {
transform: translateX(-100%) skewX(-5deg) rotate(20deg) scaleY(1.1);
animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;
}
50% {
transform: translateX(-100%) rotate(45deg) scaleY(1.1);
animation-timing-function: ease-in;
}
60% {
transform: translateX(-100%) rotate(90deg);
}
65% {
transform: translateX(-100%) rotate(90deg) skewY(10deg);
}
70% {
transform: translateX(-100%) rotate(90deg) skewY(0deg);
}
to { /* 100% */
transform: translateX(-100%) rotate(90deg);
}
}
/* 将关键帧块连接到元素。 */
.box-inner {
display: inline-block;
.74em;
height: .74em;
background-color: #fff;
animation: roll 1.5s 1s 3 linear backwards;
/*
animation-name: roll;
animation-duration: 1.5s;
animation-delay: 1s;
animation-iteration-count: 3;
animation-timing-function: linear;
animation-fill-mode: backwards;
*/
transform-origin: bottom right;
}
animation-iteration-count: 3表示执行三次动画。
默认情况下,第一个关键帧中的属性在动画运行前不会被应用。如果我们指定了关键字backwards,那相应的属性就会反向填充,即第一个关键帧中的属性会立即应用。
/* 让方块从视口外面进入并移动到其最终位置。 */
@keyframes shift {
/* 让动画从某个值开始,到初始值结束,所以这里省略了to关键帧。 */
from {
transform: translateX(-300%);
}
}
.box-outer {
display: inline-block;
animation: shift 4.5s 1s steps(3, start) backwards;
}
3.1 曲线动画
<h1>File uploading animation</h1>
<div class="upload">
<div class="icon computer-icon"></div>
<div class="icon file-icon is-paused"></div>
<div class="icon server-icon"></div>
</div>
<button type="button" class="button-pause">Play/pause animation</button>
<button type="button" class="button-stop">Finish/restart animation</button>
@keyframes jump {
from {
transform: rotate(0deg) translateX(-170px) rotate(0deg) scale(1);
}
70%, 100% {
transform: rotate(175deg) translateX(-170px) rotate(-175deg) scale(.5);
}
}
.file-icon {
animation: jump 2s ease-in-out infinite;
/* equal to setting the following animation properties:
animation-name: jump;
animation-duration: 2s;
animation-timing-function: ease-in-out;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
*/
background-image: url(images/file.svg);
}
先旋转,接着平移,最后再向相反方向旋转相同度数,图标就会沿曲线移动。
4.三维变换
三维变换允许我们控制坐标系统,旋转、变形、缩放元素,以及向前或向后移动元素。
4.1 透视简介
z轴表示用户到屏幕的方向。屏幕表面通常被称为"z平面"(z-plane),也是z轴默认的起点位置。
这意味着离用户远的位置(z轴负方向)上的元素,在屏幕上看起来应该小一些,离用户近的位置上的元素则应该大一些。而围绕x或y轴旋转,也会导致某一部分变大,而其余部分变小。
<div class="wrapper-1">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<div class="wrapper-2">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<div class="wrapper-3">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
.box {
margin: auto;
border: 2px solid;
100px;
height: 100px;
transform: rotateY(60deg); /* 沿y轴旋转60度 */
}
单纯一个轴的变换只会导致元素变窄,体现不出任何三维效果。这是因为我们还没有定义perspective(透视)。要定义透视,先得确定用户距离这个元素有多远。离得越近变化越大,离得越远变化越小。默认的距离是无穷远,因此不会发生明显的变化。
.wrapper-2 {
perspective: 140px;
}
.wrapper-3 {
perspective: 800px;
}

透视原点:默认情况下,假定观察者的视线与应用透视的元素相交于元素的中心。
通过perspective-origin属性来修改透视原点的位置,改属性可以接受 x/y坐标值(带关键字top、right、bottom和left)、百分比或长度值。
使用perspective()函数设置个别变化元素的透视:
.box {
transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(60deg);
}
4.2 创建三维部件
<div class="flip-wrapper menu-wrapper">
<div class="flip-a menu">
<h1 class="menu-heading">Top menu choices</h1>
<ol class="menu-list">
<li>Capricciosa</li>
<!-- 省略 -->
</ol>
</div>
<div class="flip-b menu-settings">
<!-- 部件背面的表单 -->
<button type="submit" class="menu-save">Show me pizzas!</button>
</div>
</div>
.csstransforms3d.classlist body {
perspective: 1000px;
}
.csstransforms3d.classlist .flip-wrapper {
position: relative; /* 让包装元素成为其后代的定位上下文 */
transform-style: preserve-3d; /* 让子元素的变换与父元素在同一个三维空间中 */
transition: transform .25s ease-in-out; /* 过渡 */
transform: rotateY(0);
}
.csstransforms3d.classlist .flip-b {
position: absolute;
top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0;
margin: 0;
transform: rotateY(-180deg); /* 围绕y轴翻转180度 */
}
.csstransforms3d.classlist .flip-b,
.csstransforms3d.classlist .flip-a {
backface-visibility: hidden; /* 让元素从背面看不到 */
}
.csstransforms3d.classlist .flip-wrapper.is-flipped {
transform: rotateY(180deg);
}
我们使用Modernizr来检测浏览器是否支持三维变换。
.csstransforms3d.classlist是在浏览器支持三维变换时添加到html元素的一个类名。
(function (win, doc, undefined) {
defaultOpts = {
wrapperSel: '.flip-wrapper',
widgetHeadingSel: '.menu-heading',
backButtonSel: '.menu-save',
flippedClass: 'is-flipped',
// ...
};
options = options || {};
opts = extend(defaultOpts, options);
flipWrapper = doc.querySelector(opts.wrapperSel);
widgetHeading = flipWrapper.querySelector(opts.widgetHeadingSel);
backButton = flipWrapper.querySelector(opts.backButtonSel);
// ...
var trigger = doc.createElement('button'),
triggerText = doc.createTextNode('Show filters');
trigger.appendChild(triggerText);
trigger.className += ' flip-trigger';
widgetHeading.appendChild(trigger);
function toggleCard() {
flipWrapper.classList.toggle(opts.flippedClass);
}
//...
function handleDisplay(e) {
//...
rAF = win.requestAnimationFrame ||
win.webkitRequestAnimationFrame ||
win.mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
function (callback) {return setTimeout(callback, 17);};
//...
rAF(function () {
toggleCard();
// ...
});
}
backButton.addEventListener('click', handleDisplay);
})(window, document);
Tips:JS基础篇--HTML DOM classList 属性
4.3 高级三维变换
rotate3d()函数可以围绕穿越三维空间的任意一条线翻转元素。
参考:rotate3d() - CSS(层叠样式表) | MDN
matrix3d()函数可以组合多个轴向上的平移、缩放、变形和旋转。
参考:matrix3d() - CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN
参考资料: