简介
spring框架体系包含:
- Spring framework 实现依赖注入(DI)和AOP(面向切面编程)的框架,是所有其他框架的核心
- Spring MVC 实现基于java原生Servlet开发的MVC web框架
- Spring Boot 包含 Spring + SpringMVC + 开箱即用的组件,Spring boot 的出现主要是为了解决Spring MVC 开发需要进行大量繁琐的配置,采用注解简化开发流程
- Spring cloud 实现分布式微服务
为何需要IOC容器
IOC指的是控制反转,对资源的控制权由用户转移到容器中.而DI指的是依赖注入,它是IOC的具体实现.在传统的代码中当一个类需要依赖其他类的方法或属性时,通常的做法是在当前类中new OtherClass(),这样是一种强耦合,不利于代码的维护和扩展性.
所以IOC容器解决的问题主要有2点:
- 解决类自动实例化,不需要要手动new
- 解决类之间的依赖关系
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext 容器
1.BeanFactory是Spring中最基础的容器,它由org.springframework.beans.facytory.BeanFactory 接口定义,并提供了完整的 IoC 服务支持。BeanFactory 就是一个管理 Bean 的工厂,它主要负责初始化各种 Bean,并调用它们的生命周期方法。最常用的实现类有:
- org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory 它是根据xml中定义的bean信息加载bean
使用方式如:
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("F://applicationContext.xml"));
2.ApplicationContext容器,它是 BeanFactory 的子接口,也被称为应用上下文。该接口的全路径为 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext,它不仅提供了 BeanFactory 的所有功能,还添加了对 i18n(国际化)、资源访问、事件传播等方面的良好支持。
实现类有:
- org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 该类从ClassPath路径中查找xml文件,找到后实例化bean
- org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 该类从指定的系统路径查找xml文件,找到后实例化bean
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext使用方式如:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //注意xml文件需要放置在ClassPath所在的目录,一般为src
Foo foo = (Foo)applicationContext.getBean("foo"); //foo为xml中bean的id
foo.hello();
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext使用方式:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("F://applicationContext.xml");
Foo foo = (Foo)applicationContext.getBean("foo");//foo为xml中bean的id
foo.hello();
两者区别:
如果 Bean 的某一个属性没有注入,使用 BeanFacotry 加载后,在第一次调用 getBean() 方法时会抛出异常,而 ApplicationContext 则在初始化时自检,这样有利于检查所依赖的属性是否注入。
强烈建议使用ApplicationContext实现类 ClassPathXmApplicationContext 来加载bean,而只有在系统资源较少时,才考虑使用 BeanFactory
完整的例子说明如何利用Spring容器获取bean实例
1.利用maven创建好spring项目(maven创建spring项目参考这个教程)
2.在src/mian/java/com/mike/ioc 新建PersonDao接口
package com.mike.ioc;
public interface PersonDao {
public void add();
}
3.在src/mian/java/com/mike/ioc 新建PersonDaoImpl实现类
package com.mike.ioc;
public class PersonDaoImpl implements PersonDao {
@Override
public void add() {
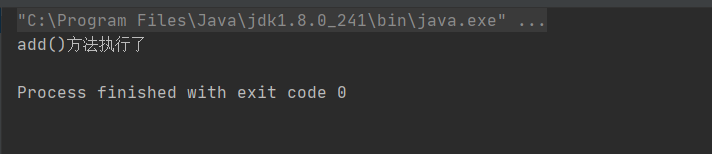
System.out.println("add()方法执行了");
}
}
4.在src/test/java/com.mike/ioc 新建TestPersonDao测试类
package com.mike.ioc;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestPersonDao {
@Test
public void test() {
String xmlPath = "applicationContext.xml";
//加载xml中bean配置
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
//通过容器获取bean实例
PersonDao personDao = (PersonDao) applicationContext.getBean("personDao"); //这里personDao就是xml中bean的 id
//调用实例方法
personDao.add();
}
}
5.在src/main/resources下新建applicationContext.xml,并配置bean信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans>
<bean id="personDao" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
</beans>
运行观察打印结果
Spring容器注入方式,主要有3种
- setter方法注入
- 构造方法注入
- 接口注入(不推荐)
1.setter方法注入
只需要在当前对象中定义需要注入的类setter方法,容器可以自动帮我们将实例化该类
在src/main/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建接口PersonService接口
package com.mike.ioc;
public interface PersonService {
public void addPerson();
}
在src/main/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建实现类PersonServiceImpl,并注入PersonDao接口的实现类PersonDaoImpl
package com.mike.ioc;
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService{
private PersonDao personDao;
//使用set方法注入容器
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void addPerson() {
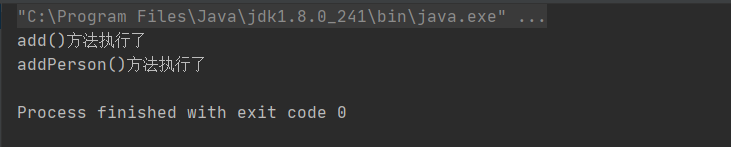
personDao.add();
System.out.println("addPerson()方法执行了");
}
}
在src/test/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建测试类TestPersonService
package com.mike.ioc;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestPersonService {
@Test
public void test() {
String xmlPath = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
PersonService personService = (PersonService)applicationContext.getBean("personService");
personService.addPerson();
}
}
配置xml中的bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans>
<bean id="personDao" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property> <!-- setter方式注入-->
</bean>
</beans>
</beans>
运行代码
2.构造方法注入
只要在当前类的构造方法中将需要注入的类传入即可,容器 会自动实例化
在src/main/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建接口PersonDaoImpl1实现类
package com.mike.ioc;
public class PersonDaoImpl1 implements PersonDao {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("personDaoImpl1 add方法被执行");
}
}
在src/main/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建接口PersonServiceImpl1实现类
package com.mike.ioc;
public class PersonServiceImpl1 implements PersonService {
private PersonDaoImpl1 personDaoImpl1;
//使用构造函数注入
PersonServiceImpl1(PersonDaoImpl1 personDaoImpl1) {
this.personDaoImpl1 = personDaoImpl1;
}
public void addPerson() {
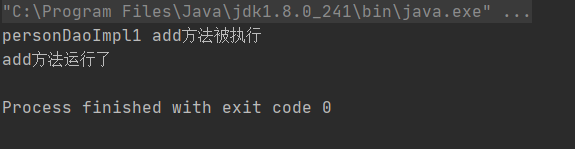
personDaoImpl1.add();
System.out.println("add方法运行了");
}
}
配置xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans>
<bean id="personDao" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property> <!-- setter方式注入-->
</bean>
<bean id="personDao1" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonDaoImpl1"></bean>
<bean id="personService1" class="com.mike.ioc.PersonServiceImpl1">
<constructor-arg ref="personDao1"></constructor-arg> <!-- 构造方法注入-->
</bean>
</beans>
</beans>
在src/test/java/com.mike/ioc目录中新建TestPersonService1
package com.mike.ioc;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestPersonService1 {
@Test
public void test() {
String xmlPath = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
PersonServiceImpl1 personService1 = (PersonServiceImpl1)applicationContext.getBean("personService1");
personService1.addPerson();
}
}
运行代码
xml中bean配置标签和属性
- id属性 bean的唯一id,例如注入将当前实例注入到其他类中,需要使用此id,利用ClassPathXmlApplicationConetxt 获取bean也使用id来检索
- name属性 bean的名称,通常配合property标签表示将此其他类注入到当前bean
- ref属性 注入时引用其他bean的id
- scope属性,bean的作用于,默认时singleton即单例,还有prototype表示每次都返回一个新实例
- class属性,bean实际引用的全限定类名
- factory-method 指定实例化调用的方法,在静态工厂和实力工厂实例化时用到
- factory-bean 指定实例工厂名称,在实例工厂实例化用到
- property标签 表示setter方法注入
- contructor-arg 表示构造方法注入