原文:
https://blog.csdn.net/samanthamao/article/details/110683533
一、前言
1、环境
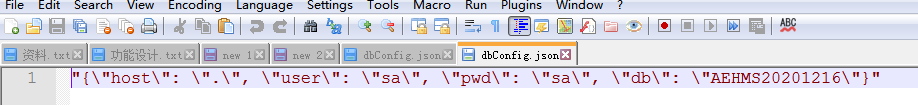
dbConfig.json:数据库配置文件
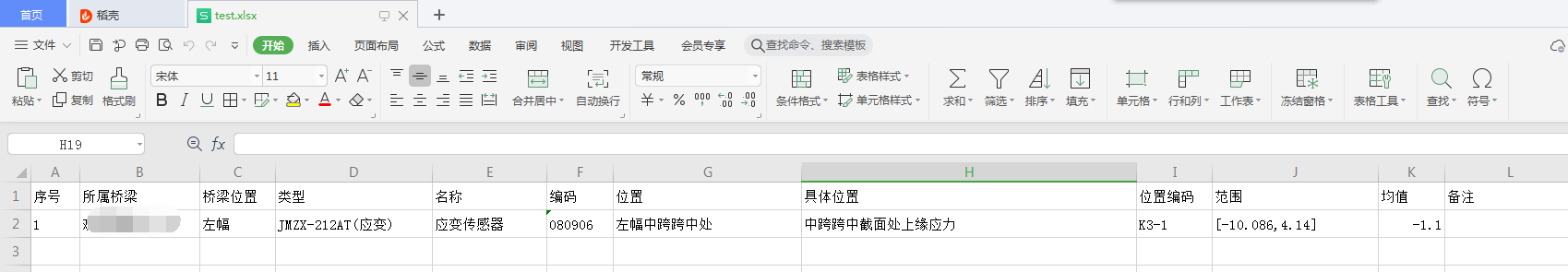
test.xlsx:传感器数据

2、主要修改
随机一下波峰,波峰之间的距离等
3、 大致逻辑
- 读取excel
- 查询应变传感器
- 根据应变传感器记录的数据 生成 相应的修正后的数据
- 根据索引一个一个的update
- 生成update sql语句
每次达到6000的时候,写入到数据库,清空sql语句
一个传感器遍历完后,如果sql语句不为空,就写入到数据库
二、代码
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import pymssql
from random import choice
import json
import time
import os
class MSSQL:
# 类的构造函数,初始化数据库连接ip或者域名,以及用户名,密码,要连接的数据库名称
def __init__(self,host,user,pwd,db):
self.host=host
self.user=user
self.pwd=pwd
self.db=db
# 得到数据库连接信息函数,返回: conn.cursor()
def __GetConnect(self):
self.conn=pymssql.connect(host=self.host,
user=self.user,
password=self.pwd,
database=self.db,
charset='utf8')
cur=self.conn.cursor() #将数据库连接信息,赋值给cur。
if not cur:
raise(NameError,"连接数据库失败")
else:
return cur
#执行查询语句,返回的是一个包含tuple的list,list的元素是记录行,tuple的元素是每行记录的字段
def ExecQuery(self,sql):
cur = self.__GetConnect() #获得数据库连接信息
cur.execute(sql) #执行Sql语句
resList = cur.fetchall() #获得所有的查询结果
self.conn.close() #查询完毕后必须关闭连接
return resList #返回查询结果
#执行Sql语句函数,无返回结果的,方向修改的
def ExecNonQuery(self,sql):
cur = self.__GetConnect()
cur.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
self.conn.close()
# new一个对象
# mssql = MSSQL('192.168.2.51', 'sa', 'Sql123456', 'AEHMS20201216')
# mssql = MSSQL('.', 'sa', 'sa', 'AEHMS20201216')
mssql = None
def randomSplit(total):# 随机分组数据
foo = [60,80,150,200,300,600]
count = 0
arr= []
bl = True
while (bl):
num = choice(foo)# 随机取值
if count + num >= total:# 最后随机取的那个数 超出当前范围 break
break
arr.append(num)
count+=num
if total != count:# 追加最后一个元素
arr.append(total-count)
print(count)
print(arr)
seg = []# 值如:[(0,50),(50,200)]
print('--------------')
curCount=0
for num in arr:
start = curCount
end = curCount + num
seg.append((start, end))
print(start, end)
curCount=end
print(seg)
return seg
def createData(pointNum, avgValue): # 生成周期性数据
long=pointNum # 400个步长,x轴的总长度
base=avgValue # 均值
ybase = np.zeros((1,long))[0] + base # 所有数据
period_multiply = 0.1 # 越大,幅值越大,调整波峰
period_frequency = 500 # 越大,周期越大
all_period_multiply = [0.1, 0,2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]# 预设多个幅值
all_period_frequency = [50, 150, 200, 300, 400, 600]# 预设多个周期值
seg = randomSplit(pointNum)# 原始: seg = [(0, pointNum)]
for (i,j) in seg: # 一组一组数据的遍历
print(i, j)
period_multiply = choice(all_period_multiply)# 随机取值
period_frequency = choice(all_period_frequency)# 随机取值
n = j-i # n=40,40 50
x = np.arange(n)
season1 = 1 * np.array([math.sin(i/period_frequency*math.pi) for i in x])
season2 = 0.5 * np.array([math.sin(i*0.5/period_frequency*math.pi) for i in x])
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.2, len(x))
y = season1 + season2 + noise # 可以叠加多尺度周期和噪声
# y = season1+season2
for idx in range(i, j): # 遍历具体的点
# print(idx, period_multiply)
value1 = ybase[idx] + y[idx-i] * period_multiply
value2 = round(value1, 3) # 保留三位小数
ybase[idx] = value2
# plt.figure(figsize=(15, 3.5))
# plt.plot(ybase)
# plt.tight_layout(pad=0.4, w_pad=0.5, h_pad=2.0)
# plt.show()
return ybase
# # 测试
# points = createData(200, 1.2)
# print(points)
def getIdsByCode(code): # 获取 ids by code
sql = "SELECT ID FROM tb_SensorRecord WHERE Code='{}' AND GetTime>='2020-08-01' AND GetTime<='2020-12-30' ORDER BY ID ASC".format(code)
results = mssql.ExecQuery(sql)
arr_ids = []
for row in results:
arr_ids.append(row[0])
return arr_ids
# # 测试
# ids = getIdsByCode('080906')
# print(len(ids))
# # 测试 执行sql语句
# mssql.ExecNonQuery("UPDATE tb_SensorRecord SET NewValue1='1' WHERE ID='4178839'")
# print('ok')
def getSensor(): # 获取所有的传感器
arr_sensors = []
df = pd.read_excel('test.xlsx', dtype={'编码': np.str_}) # dtype指定列的数据类型
for index, row in df.iterrows():
arr_sensors.append({"code":row["编码"], "avgValue":row["均值"]})
return arr_sensors
# # 测试
# sensors = getSensor()
# print(sensors)
# 主逻辑
startTime = time.perf_counter()
curCode = ''
try:
dbConfig = {
'host' : '',
'user' : '',
'pwd' : '',
'db' : ''
}
with open('dbConfig.json', 'r') as f:
dbConfig = eval(json.load(f))
print(dbConfig)
mssql = MSSQL(dbConfig["host"], dbConfig["user"], dbConfig["pwd"], dbConfig["db"])
sensors = getSensor()
for item in sensors: # 遍历传感器
print(item)
code = item["code"]
avgValue = item["avgValue"]
curCode = code
ids = getIdsByCode(code)
points = createData(len(ids), avgValue)
sql = ""
for index, value in enumerate(ids):
print(index, value, points[index])
sql += "UPDATE tb_SensorRecord SET NewValue1='{0}' WHERE ID='{1}'".format(points[index], value)
mssql.ExecNonQuery(sql)
print('处理完成')
except Exception as e:
print('Error:', e)
with open('err.txt', 'w') as f:
json.dump(str(e)+",当前传感器:"+curCode, f)
finally:
endTime = time.perf_counter()
print("The function run time is : %.03f seconds" %(endTime-startTime))
os.system('pause')# 避免执行完后自动关闭控制台
三、效果

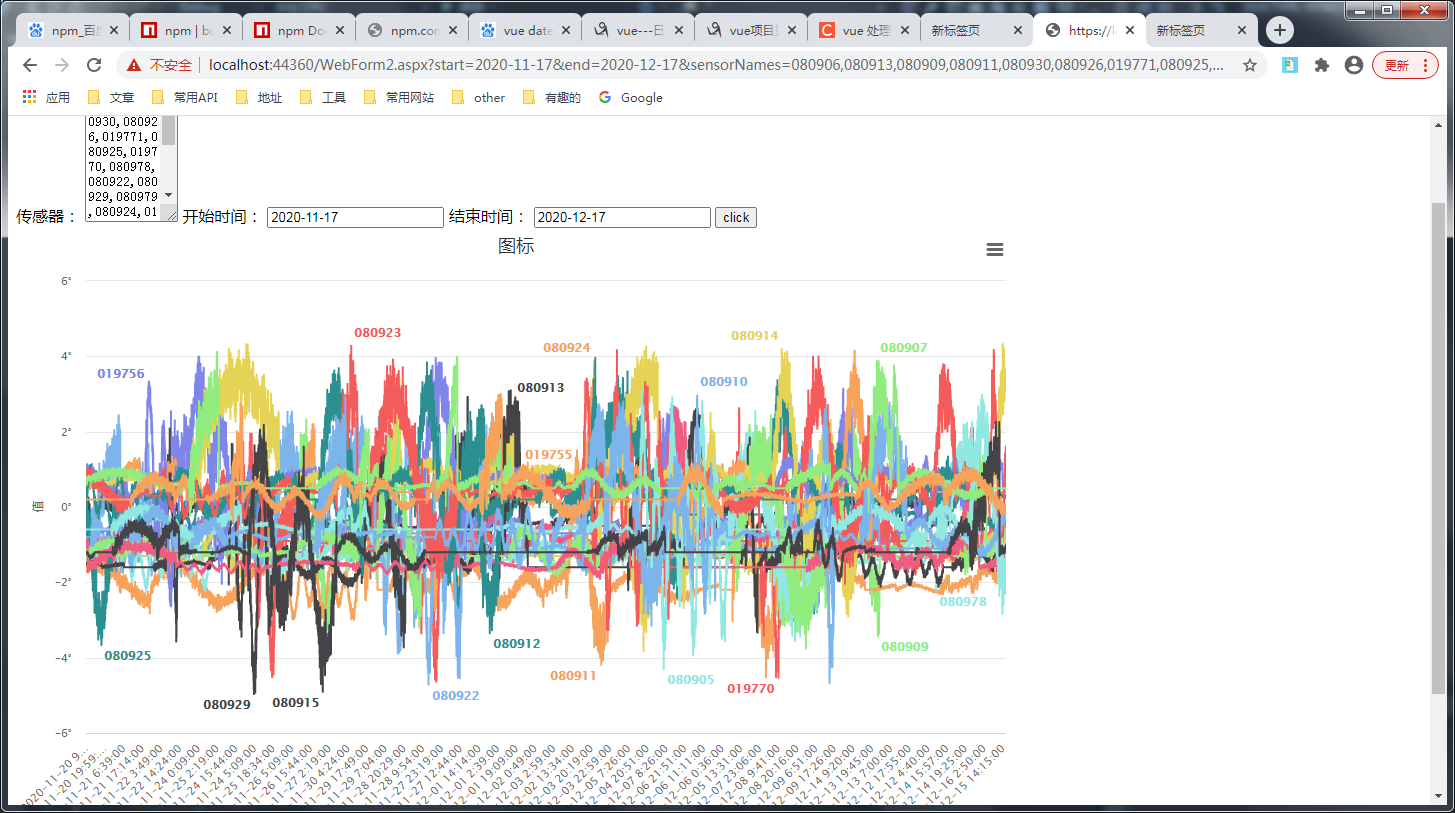
总结
随机是随机了,但是波动的范围还是要再优化一下,万一超过了阈值也哦豁了