前言
本篇要说的是ThreadLocal,这个玩意平时在项目中很少用到,但是却有极大的用处;平时在面试中也会经常问到这个问题。
正文
本篇使用jdk1.8版本。
ThreadLocal介绍
先来看看源码中的介绍吧,文档太多,就不全贴出来了
/**
* This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from
* their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its
* {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized
* copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private
* static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g.,
* a user ID or Transaction ID).
*
* <p>For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each
* thread.
* A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()}
* and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.
使用方式
在注释中也写明了使用方法:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ThreadId {
// Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned
private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);
// Thread local variable containing each thread's ID
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId =
new ThreadLocal<Integer>() {
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return nextId.getAndIncrement();
}
};
// Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary
public static int get() {
return threadId.get();
}
}
概括下大概吧:
- ThreadLocal提供一个线程局部变量
- 每个线程只能通过该类的set与get方法获取一个变量
- 独立初始化变量
- 生命周期跟线程的生命周期相同
源码
ThreadLocal中的源码:
首先来看set方法:
public void set(T value) {
// 获取当前线程对象(所以多线程的情况下都是操作的当前线程)
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 从当前线程对象中获取ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 如果ThreadLocalMap不为null,直接存入
if (map != null)
// key为当前Threadlocal实例
map.set(this, value);
else
//如果ThreadLocalMap为null,则为当前线程创建ThreadLocalMap对象
createMap(t, value);
}
接下来在看看get方法:
public T get() {
// 获取当前线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前线程对象的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
// 以当前ThreadLocal实例为key获取map中的Entry对象
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
再来看看上面两个方法中使用到的方法:
- 第一个,getMap方法:
// 多个方法都会调用这个方法
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
// 返回传入线程的ThreadLocalMap
return t.threadLocals;
}
- createMap方法:
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
// 为线程threadLocals赋值(新建)
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
- setInitialValue方法
private T setInitialValue() {
// 调用initialValue方法,获取初始化值
T value = initialValue();
// 获取当前线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
- initialValue方法:
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
小结1: 如果在初始化的时候没用重写这个方法,将会返回null,所以这个方法一般会在初始化ThreadLocal的代码中重写这个方法。
在看看Thread中的代码:
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
小结2:
从上面的代码中可以发现,set方法通过Thread.currentThread()来获取当前线程对象,从而操作当前线程对象中的threadLocals,也就是说通过Threadlocal操作的数据是Thread负责维护的;而threadLocals又是ThreadLocal类中的一个静态内部类ThreadLocalMap,其中key为this(这里就是当前的Threadlocal实例对象);
小结3:
- 从源码上看出,不能从解决多线程程序的并发问题和解决多线程访问资源时的共享问题这两个方面去看待Threadlocal的问题。
- 我对
Threadlocal的大致理解就是:通过Threadlocal的实例对象a去操作当前Thread中ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap对象中key为a所对应的数据;
使用场景
1. 数据库连接池
最典型的应该就是数据库连接池了吧,如何处理线程与数据库连接之间的关系,应该就是用到的Threadlocal,具体的就得去谷歌或去看源码了。
2. 信息或参数传递
这里说一下我所用到过的场景:
- 信息传递
有些接口中不会将某些信息作为参数进行传递,但是在这样的情况下却需要某些信息,而这些信息只在最开始的时候能获取到,这时候就可以使用ThreadLocal来操作了。
内存泄漏
关于内存泄漏,其实我在使用过程中也遇到过一次;下面说一下场景吧:
下面是流程图:
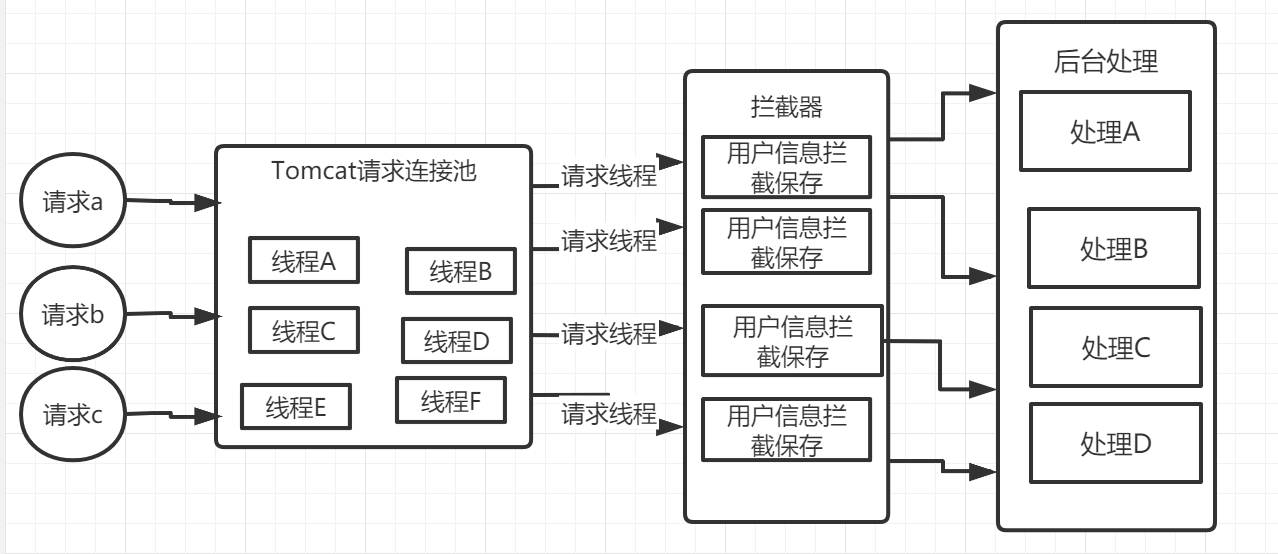
我们使用ThreadLocal来对用户信息进行记录,对请求进行拦截,将用户信息存入,但是在有时候会出现游客模式下回显示已登录,还不是自己的账户;
为什么会出现这种情况呢?
- 请求a(带用户信息a)在请求连接池获取线程A
- 拦截器对线程A进行拦截,并对用户信息a保存Threadlocal
- 然后在后台处理中处理A对线程A进行处理,从Threadlocal中获取用户信息a
- 处理完成后,线程A带着用户信息a又回到了请求连接池,Threadlocal的用户信息a也并未清除,且线程A并未被回收
- 请求b(未带用户信息)又在请求连接池获取了线程A,这时未获取用户信息,也未对Threadlocal进行操作
- 回到步骤2
解决办法:
- 拦截器处每次都对Threadlocal进行信息清除(调用Threadlocal的remove方法)
- 即便用户信息为null,也进行保存;
最后
参考文章:
ThreadLocal就是这么简单
Java ThreadLocal
Java进阶(七)正确理解Thread Local的原理与适用场景