#前言:今天我们来聊聊shell脚本中的函数知识,看一下函数的优势,执行过程和相关的使用案例,我们也来看一下shell和python的函数书写方式有什么不同
#简介
1、函数也具有别名类似的功能 2、函数是把程序里多次调用相同的代码部分定义成一份,然后给这份代码定义个名字,如果出现重复的就调用就行了
#函数的优势
1、把相同的程序段定义成函数,可以减少整个程序的代码量 2、可以让程序代码结构更清晰 3、增加程序的可读、易读性、以及管理性 4、可以实现程序功能模块化,不同的程序使用函数模块化
#语法格式
函数名(){ 指令 return n } 规范写法 function 函数名(){ 指令 return n } #提示:shell的返回值是exit输出返回值,函数里用return输出返回值
#函数的执行
调用函数
#1、直接执行函数名即可(不带括号)
#注意
执行函数时,函数后的小括号不要带了
函数定义及函数整体必须在要执行的函数名的前面定义
#2、带参数的函数执行方法
函数名 参数1 参数2
#提示:函数的传参和脚本的传参类似
#shell的位置参数($1 $2 $3 $4 $5 $# $* $? $@)都可以时函数的参数
#$0比较特殊,仍然是父脚本的名称
#在shell函数里面,return命令功能与shell里的exit类似,作用时跳出函数
#在shell函数里面使用exit会退出整个shell脚本,而不是退出shell函数
#return语句会返回一个退出值(返回值)给调用函数的程序
#我们来看一下python的函数书写方式
#提示:def是define的意思,定义
最基本的语法: def 函数名(): 函数体 函数名() #调用函数 带有参数的语法 def 函数名(形参列表): 函数体(代码块,return) 函数名(实参列表) :调用
#看一下执行过程
# def wan(): #定义函数 # print("今天一起去玩") # print("去哪里玩呢") # print("我不知道") # wan() #调用函数 '''讲解执行的过程 1.定义函数wan() 2.调用函数wan() 3.准备开始执行函数 4.打印,今天一起去玩 5.打印,去哪里完 6.打印,我不知道 7.函数执行完毕,本次调用完毕,wan()函数调用完毕 '''
#使用
#例1:没有去调用函数
[root@shell scripts]# pwd /scripts [root@shell scripts]# cat hs01.sh #!/bin/bash guoke(){ echo "I am guoke" } [root@shell scripts]# sh hs01.sh [root@shell scripts]# #如果没有去调用函数的话,那么就没有输出
#例2:调用函数
[root@shell scripts]# cat hs01.sh #!/bin/bash guoke(){ echo "I am guoke" } guoke #调用函数 [root@shell scripts]# sh hs01.sh I am guoke
#例3:多次调用
[root@shell scripts]# cat hs01.sh #!/bin/bash guoke(){ echo "I am guoke" } guoke guoke guoke [root@shell scripts]# sh hs01.sh I am guoke I am guoke I am guoke
#例4:将函数写到/etc/init.d/functions里面,然后通过其他脚本进行调用
#/etc/init.d/functions boy(){ echo "I am guoke-boy" } return 0 #提示:不要放在return 0后面,要不然就是退出了,没有调用 [root@shell scripts]# cat hs01.sh #通过脚本去调用boy函数 #!/bin/bash . /etc/init.d/functions #引入系统函数库 guoke(){ echo "I am guoke" } guoke boy #调用/etc/init.d/functions中的函数
[root@shell scripts]# sh hs01.sh #执行之后打印 I am guoke I am guoke-boy
#例5:将函数写到/etc/init.d/functions里面,通过其他脚本进行调用然后传参
#/etc/init.d/functions boy(){ echo "I am $1" } #提示:$1:脚本的传入的第一个参数 [root@shell scripts]# cat hs01.sh #通过脚本去调用boy函数 #!/bin/bash . /etc/init.d/functions #引入系统函数库 guoke(){ echo "I am guoke" } guoke boy guoke-boy #调用/etc/init.d/functions中的函数,后面接着传参 [root@shell scripts]# sh hs01.sh #执行之后打印 I am guoke I am guoke-boy
#例6:设置提示函数,如果传的参数的值不符合就打印帮助函数
[root@shell scripts]# cat hs02.sh #!/bin/bash usage(){ echo "Usage: $0 key beginservernum endservernum example: $0 ff 1 2" } [[ $# != 3 ]] && usage && exit 1 #如果传入的参数不等于3的话,就调用后面的函数,并退出脚本 [[ -z $1 || -z $2 || -z $3 ]] && usage && exit 1 #如果传入的$1,$2,$3三个参数的值为空,那么就调用后面的函数,并退出脚本
[root@shell scripts]# sh hs02.sh 22 33 #当传入的参数不等于3个的时候就执行usage函数,并退出脚本 Usage: hs02.sh key beginservernum endservernum example: hs02.sh ff 1 2
#例7:将函数的传参转换成脚本文件命令行传参,判断任意指定的URL是否存在异常
[root@shell scripts]# cat hs03.sh #!/bin/bash . /etc/init.d/functions function usage(){ echo $"usage:$0 url" exit 1 } function check_url(){ wget --spider -q -o /dev/null --tries=1 -T 5 $1 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then action "$1 is success." /bin/true else action "$1 is failure." /bin/false fi } function main(){ if [ $# -ne 1 ];then usage fi check_url $1 } main $*
#参数解释
. /etc/init.d/functions #引入系统函数库 function usage(){ #帮助函数 function check_url(){ #检测URL函数 wget --spider -q -o /dev/null --tries=1 -T 5 $1 #--spider:判断网址是否有效,-q:不显示执行过程,-o:将软件输出信息保存到软件,-T:指定超时时间 action "$1 is success." /bin/true #action:调用系统函数库的用法 function main(){ #主函数 if [ $# -ne 1 ];then #判断:如果传参的参数不等1个,那么久打印帮助函数,提示用户 check_url $1 #接收函数的传输
main $* #$*:把命令行接收的所有参数作为函数参数传给函数内部
#测试
[root@shell scripts]# sh hs03.sh #如果没有加参数,就调用提示函数 usage:hs03.sh url [root@shell scripts]# sh hs03.sh www.guokeboy.com #输入错误地址 www.guokeboy.com is failure. [FAILED](失败) [root@shell scripts]# sh hs03.sh www.baidu.com #输入正确地址 www.baidu.com is success. [ OK ]
#例8:给任意字符串加指定颜色
[root@shell scripts]# cat hs04.sh #!/bin/bash RED_COLOR='E[1;31m' GREEN_COLOR='E[1;32m' YELLOW_COLOR='E[1;33m' BLUE_COLOR='E[1;34m' PINK='E[1;35m' RES='E[0m' usage(){ if [ $# -ne 2 ];then echo "USAGE:$0 {red|green|yellow|blue|pink}" contents exit 1 fi } color(){ case "$1" in red) echo -e "${RED_COLOR} $2 ${RES}" ;; green) echo -e "${GREEN_COLOR} $2 ${RES}" ;; yellow) echo -e "${YELLOW_COLOR} $2 ${RES}" ;; blue) echo -e "${BLUE_COLOR} $2 ${RES}" ;; *) usage esac } main(){ if [ $# -ne 2 ];then usage fi color $1 $2 } main $*
#参数解释
#1.定义颜色变量 数字对应的颜色:30(黑色)、31(红色)、32(绿色)、33(黄色)、34(蓝色、35(粉红)、36(青色)、37(白色) #2.定义帮助函数 #3.定义颜色函数,使用case来获取输入的值 #4.主函数,判断输入的参数是否为2个,如果不是就调用帮助函数
#测试
#如果执行脚本,不加参数的话就打印帮助函数
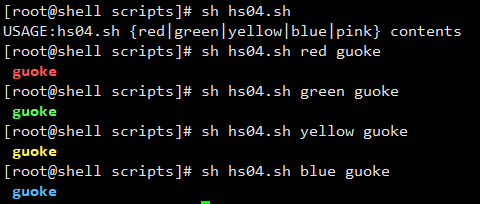
#例9:使用shell函数开发rsync服务启动脚本
#使用start、stop、restart函数将代码 模块化,使用系统函数action优化显示
[root@shell init.d]# cat rsyncd #!/bin/bash #chkconfig: 2345 20 80 #description: Rsyncd start scripts by guoke. . /etc/init.d/functions function usage(){ echo $"usage:$0 {start|stop|restart}" exit 1 } function start(){ rsync --daemon sleep 1 if [ `netstat -unplt | grep rsync | wc -l` -ge 1 ];then action "rsyncd is started." /bin/true else action "rsyncd is started." /bin/false fi } function stop(){ killall rsync &>/dev/null sleep 2 if [ `netstat -unptl | grep rsync |wc -l` -eq 0 ];then action "rsyncd is stopped." /bin/true else action "rsyncd is stopped." /bin/false fi } function restart(){ stop sleep 2 start } function main(){ if [ $# -ne 1 ];then usage fi case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; restart) stop sleep 1 start ;; *) usage esac } main $*
#参数解释:引入系统函数库,定义帮助函数,然后定义start函数,stop函数,restart函数,定义主函数,主函数里面首先使用if判断传入的参数是不是为一个,如果不是就调用帮助函数,然后使用case语句获取传入的参数,再调用相关的函数,$*:把命令行接收的所有参数作为函数参数传给函数内部
#测试
[root@shell init.d]# sh rsyncd stop rsyncd is stopped. [ OK ] [root@shell init.d]# sh rsyncd start rsyncd is started. [ OK ] [root@shell init.d]# sh rsyncd restart rsyncd is stopped. [ OK ] rsyncd is started. [ OK ]
#总结:将脚本中功能进行模块化之后,就会使脚本比较易读和清晰,提升管理效率。好了,这次就分享到这了,写的不好地方还望指出,多多交流提高,下次再会。。。