定义:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象
原型模式其实就是通过一个对象来创建一个新的可定制(可以是源对象的一个副本也可以有所改变)的对象,而且我们并不需要知道具体创建的细节。在java中使用原型模式是非常简单的,因为Object类中提供了一个本地方法clone,就是用来拷贝一个对象,当一个类实现了Cloneable接口就能使用该方法,下面我们来看下原型模式一个简单的实例
public class Prototype implements Cloneable { protected int numberA; protected int numberB; public Prototype() { this.numberA = 2; this.numberB = 3; } public void changeNumber() { this.numberA = 4; this.numberB = 5; } @Override public Prototype clone() { try { return (Prototype) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Override public String toString() { return "numberA=" + numberA + ", numberB=" + numberB; } }
测试代码和输出结果
Prototype prototype = new Prototype(); prototype.changeNumber(); System.out.println(prototype); Prototype copyPrototype = prototype.clone(); System.out.println(copyPrototype);

从上面代码可以看出我们只是调用了clone方法就成功的创建了一个新的对象,若我们通过new对象的方法想要获取这样一个副本,就还得再执行一遍changeNumber方法。而且通过clone创建对象我们不需要知道其中创建的细节,即并有没有执行构造方法,以上代码不太好看出来,可以通过在构造方法中加入一条输出语句来验证这一点,同时这种方法创建对象的速度要比new对象快
接下来我们来思考一个问题,若原型类中的某个属性是引用类型,那拷贝出来的新对象中的该属性是否与源对象中的是指向同一个对象,即地址是否一样,通过以下的例子就能回答这个问题
public class ShallowPrototype extends Prototype { private Shallow shallow; public Shallow getShallow() { return shallow; } public void setShallow(Shallow shallow) { this.shallow = shallow; } public ShallowPrototype() { super(); Shallow shallow = new Shallow(); shallow.setNumberC(4); this.shallow = shallow; } @Override public void changeNumber() { super.changeNumber(); shallow.setNumberC(6); } @Override public String toString() { return super.toString() + ", shallow=" + shallow; } } class Shallow { private int numberC; public int getNumberC() { return numberC; } public void setNumberC(int numberC) { this.numberC = numberC; } }
其中Prototype即为上面贴出来的类,当我们需要编写多个类似ShallowPrototype类的时候,通过以上这种继承的方式,可以让我们省去重写clone方法的代码
测试代码和输出结果
ShallowPrototype prototype = new ShallowPrototype(); prototype.changeNumber(); System.out.println(prototype); ShallowPrototype copyPrototype = (ShallowPrototype) prototype.clone(); System.out.println(copyPrototype);
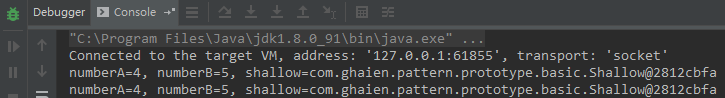
从上面的输出结果可以看出,两个对象中的shallow属性是指向同一个地址,所以若改变其中的一个的nubmerC值,另一个也会发生改变。这种复制为浅表复制,这往往不是我们希望的结果,不过我们可以通过以下的方法来实现深度复制
public class DeepPrototype extends Prototype { private Deep deep; public DeepPrototype() { super(); Deep deep = new Deep(); deep.setNumberC(4); this.deep = deep; } @Override public void changeNumber() { super.changeNumber(); deep.setNumberC(6); } @Override public DeepPrototype clone() { DeepPrototype deepPrototype = (DeepPrototype) super.clone(); deepPrototype.deep = (Deep) deep.clone(); return deepPrototype; } @Override public String toString() { return super.toString() + ", deep=" + deep; } } class Deep implements Cloneable { private int NumberC; public int getNumberC() { return NumberC; } public void setNumberC(int numberC) { NumberC = numberC; } @Override protected Object clone() { try { return super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
可以看出这与上面浅表复制的区别在与,原型类中的引用类型的属性也是一个实现了Cloneable的类并重写了clone方法,而且原型类的clone方法中需要对该属性进行拷贝
测试代码的调用和输出结果
DeepPrototype prototype = new DeepPrototype(); prototype.changeNumber(); System.out.println(prototype); DeepPrototype copyPrototype = prototype.clone(); System.out.println(copyPrototype);
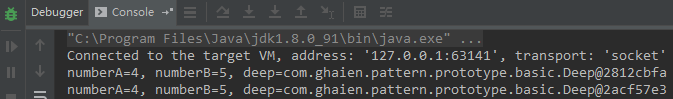
从上面的输出就能看出深度复制与浅表复制的区别,深度复制出来的新对象,将不会因为源对象的改变而改变。接下来通过深度复制来实现一个复制简历的功能,加深一下对原型模式的理解
工作经验的类(省略了get、set、toString和构造方法)
public class WorkExperience implements Cloneable { private LocalDate startWorkDate; private LocalDate endWorkDate; private String companyName; @Override protected Object clone() { try { return super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
简历类(省略了get、set、toString和构造方法)
public class Resume implements Cloneable { private String name; private String sex; private Integer age; private WorkExperience workExperience; @Override protected Object clone() { try { Resume resume = (Resume) super.clone(); resume.setWorkExperience((WorkExperience) workExperience.clone()); return resume; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
测试代码和输出结果
WorkExperience workExperience = new WorkExperience( LocalDate.parse("2018-01-01"), LocalDate.parse("2019-01-01"), "某某公司"); Resume resume = new Resume("张三", "男", 22, workExperience); System.out.println(resume); Resume copyResume = (Resume) resume.clone(); System.out.println(copyResume); resume.getWorkExperience().setEndWorkDate(LocalDate.parse("2020-01-01")); System.out.println(resume); System.out.println(copyResume);

以上就是整个功能的实现代码,可以通过点击以下链接获取完整代码