time模块
时间分为三种形式
1,时间戳(秒的形式,从1970年1月1日(unix元年)算起)
time.time
2,格式化的字符串
time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M%S %p')
time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X %p')
3,struct_time对象
time.localtime() # 本地时区的struct_time
time.gmtime() #UTC时区的struct_time
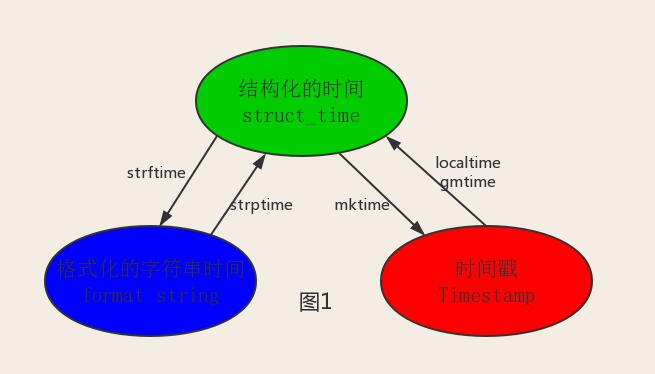
1 #--------------------------按图1转换时间 2 # localtime([secs]) 3 # 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。 4 time.localtime() 5 time.localtime(1473525444.037215) 6 7 # gmtime([secs]) 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。 8 9 # mktime(t) : 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。 10 print(time.mktime(time.localtime()))#1473525749.0 11 12 13 # strftime(format[, t]) : 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和 14 # time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如果元组中任何一个 15 # 元素越界,ValueError的错误将会被抛出。 16 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))#2016-09-11 00:49:56 17 18 # time.strptime(string[, format]) 19 # 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。 20 print(time.strptime('2011-05-05 16:37:06', '%Y-%m-%d %X')) 21 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2011, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=16, tm_min=37, tm_sec=6, 22 # tm_wday=3, tm_yday=125, tm_isdst=-1) 23 #在这个函数中,format默认为:"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y"。

1 #--------------------------按图2转换时间 2 # asctime([t]) : 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:'Sun Jun 20 23:21:05 1993'。 3 # 如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。 4 print(time.asctime())#Sun Sep 11 00:43:43 2016 5 6 # ctime([secs]) : 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为 7 # None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。 8 print(time.ctime()) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 9 print(time.ctime(time.time())) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016
datatime模块
import datetime datetime.datetime.now() #返回 当前时间 datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) #时间戳直接转成时间格式 2018-04-08 datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3) #当前时间+3天 datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3) #当前时间-3天 datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3) #当前时间+3小时 datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30) #当前时间+30分 c_time =datetime.datetime.now() c_time.replace(minutes=3,hour=2) #时间替换