为标准正态累积分布函数:
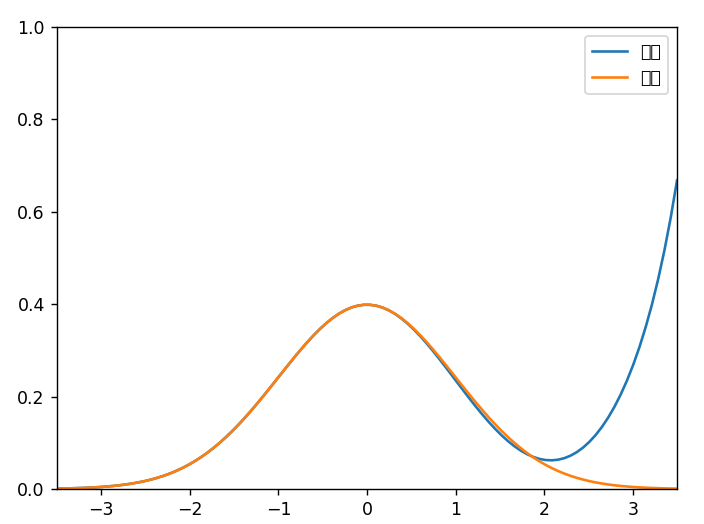
最大绝对误差0.0017。
高斯分布的解析式是 形式,它不可积、没有原函数。但是有时候有需要知道高斯分布任意一段区间的面积,这时就需要用到高斯分布的可积分拟合函数。高斯分布的可积分拟合函数有很多,其中一种形式如下式所示。
我们只需要找到满足上式f(x),那么我们就得到了高斯分布的可积分拟合函数。因为高斯分布具有对称性,所以只考虑x负半轴上的正态分布。
不妨设 是多项式函数,求解的参数包括:多项式中每一项的系数。
求解非线性方程组,瞬间可得很多个可积分的高斯分布。
以下程序尝试了最小二乘法和tensorflow调参两种方法求解非线性方程组。
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 from scipy import optimize 5 6 """ 7 正态分布的拟合是一个很难调节的神经网络 8 9 并非每次运行都能找到合适的解 10 """ 11 12 13 def gauss(xs, mu=0, sigma=1): 14 return 1 / (sigma * (2 * np.pi) ** 0.5) * np.exp(-(xs - mu) ** 2 / (2 * sigma ** 2)) 15 16 17 def my_fun(v): 18 x = np.linspace(-3.5, 0.1, 1000) 19 vv = np.empty(len(v) - 1) 20 for i in range(len(vv)): 21 vv[i] = v[i + 1] * (i + 1) 22 y = ( 23 (x.reshape(-1, 1) ** np.arange(len(vv))) 24 @ vv 25 * np.exp((x.reshape(-1, 1) ** np.arange(len(v))) @ v) 26 ) 27 yy = gauss(x) 28 l = y - yy 29 print(np.linalg.norm(l)) 30 return l 31 32 33 def draw(v): 34 x = np.linspace(-3.5, 3.5, 100) 35 vv = np.empty(len(v) - 1) 36 for i in range(len(vv)): 37 vv[i] = v[i + 1] * (i + 1) 38 y = ( 39 (x.reshape(-1, 1) ** np.arange(len(vv))) 40 @ vv 41 * np.exp((x.reshape(-1, 1) ** np.arange(len(v))) @ v) 42 ) 43 yy = gauss(x) 44 plt.plot(x, y, label="mine") 45 plt.plot(x, yy, label="real") 46 plt.legend() 47 plt.ylim(0, 1) 48 plt.xlim(x.min(), x.max()) 49 plt.show() 50 51 52 def print_latex(v): 53 def pow(y): 54 if y == 0: 55 return "" 56 if y == 1: 57 return "x" 58 return f"x^{y}" 59 60 s = r"""\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}x^2}=""" 61 pre = f"{v[1]:.3f}" 62 for i in range(1, len(v) - 1): 63 if v[i + 1] >= 0 and i > 0: 64 pre += "+" 65 pre += f"{v[i+1]:.3f} \\times {i+1}{pow(i)}" 66 post = "" 67 for i in range(len(v)): 68 if v[i] >= 0 and i > 0: 69 post += "+" 70 post += f"{v[i]:.3f}{pow(i)}" 71 ss = f"({pre}) \\times e^{{{post}}}" 72 s = s + ss + r"\\" 73 print(s) 74 75 76 def get_params_by_tf(n): 77 x = np.linspace(-3.5, 0.1, 10000) 78 y = gauss(x) 79 x_place = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(None,)) 80 y_place = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(None,)) 81 v = tf.Variable(tf.random.uniform((n,), minval=0, maxval=0.1)) 82 learn_rate = tf.Variable(0.01, trainable=False) 83 pre = 0 84 for i in range(n - 1): 85 pre += x_place ** i * v[i + 1] * (i + 1) 86 post = 0 87 for i in range(n): 88 post += x_place ** i * v[i] 89 y_output = pre * tf.exp(post) 90 # lo = tf.reduce_max(tf.abs(y_output - y_place)) 91 # lo = tf.reduce_sum((y_output - y_place) ** 2) 92 # lo = tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(y_output - y_place)) 93 lo = tf.linalg.norm(y_output - y_place) 94 train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learn_rate).minimize(lo) 95 with tf.Session() as sess: 96 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) 97 last = None 98 for epoch in range(10000): 99 _, l = sess.run((train_op, lo), feed_dict={x_place: x, y_place: y}) 100 if epoch % 1000 == 0: 101 rate = sess.run(learn_rate) * 0.99 102 rate = max(rate, 0.0001) 103 sess.run(tf.assign(learn_rate, rate)) 104 print(epoch, l) 105 if last is None: 106 last = l 107 else: 108 if abs(last - l) < 0.0001: 109 print("last loss", l) 110 break 111 last = l 112 res = sess.run(v) 113 return res 114 115 116 def get_param_by_fsolve(n): 117 v = optimize.leastsq(my_fun, np.random.random(n) - 0.5) 118 print("loss", v[1]) 119 return v[0] 120 121 122 def wrap_get_param(n): 123 l = 1 124 res = None 125 while l > 0.1: 126 res, l = get_params_by_tf(n) 127 print("last loss", l) 128 return res 129 130 131 v = get_param_by_fsolve(5) 132 print(v) 133 print_latex(v) 134 draw(v)
效果如下: